What Is Enteric Coating
You must have seen enteric coating substances in your routine life. Have you wondered what the purpose of the coating was? The enteric coating has existed for several years. Pharmaceutical enteric coating products are consumed by millions of people across the globe every day. But are they safe as a standard drug?
If such questions pop into your mind, then we promise you’ll love this informative review.
Table of Contents
Ⅰ.What Is the Enteric Coating?
Enteric coating medications are solid-dosage forms specially designed to bypass the stomach environment and release its active ingredients into the small intestine.
Enteric signifies the small intestine. The enteric coating are a colon-targeted drug delivery system. That’s why they simply protect the drug and release its active ingredient into the small intestine.
But did you ever think about how enteric coating is only released in the intestine?
The ‘pH’ is a game-changer in this case. The stomach’s environment has high acidic pH (1.0-3.5) whereas the intestine has alkaline pH (7.9- 8.0). So, enteric coating medication resists stomach pH as it is specifically designed for alkaline pH and rapidly releases the drug once it reaches the intestine.
Ⅱ.Why Enteric Coating Made to Medication?
An enteric coating is a preferred choice due to the following reasons:
1.Protection Against Acid Labile Drug
Enteric coating is applied to avoid the interaction of acid-labile drugs with the acidic pH of the stomach. For instance, erythromycin, omeprazole or Risek, etc.,
2.Stomach Protection
Several therapeutical medications can cause gastric distress or ulceration as it interrupts the stomach lining. For instance, aspirin or certain NSAIDs drugs. To get therapeutic activity under consumer’s safety they are now available in the enteric coating as well.
3.Drug Delivery at Specific Site of Action
To release the drug which is optimally absorbed in the small intestine in its most concentrated form.
4.Delayed-Release Components/Night-Time Dosing
You require an enteric coating to get a sustained or delayed-release drug. This is an ideal opportunity to create a night-time dosing strategy where you require effective and sustained drug effects just prior to waking.
5.Capsule Enteric Coated
The enteric-coated capsules are specially designed for oral delivery of therapeutic agents such as insulin. This form of medication is prone to dissolve rapidly and degrade by enzymes, therefore capsules are enteric-coated to prevent the rapid releasing of the drug in the acidic environment.
Ⅲ.What Does Enteric Coating Do?
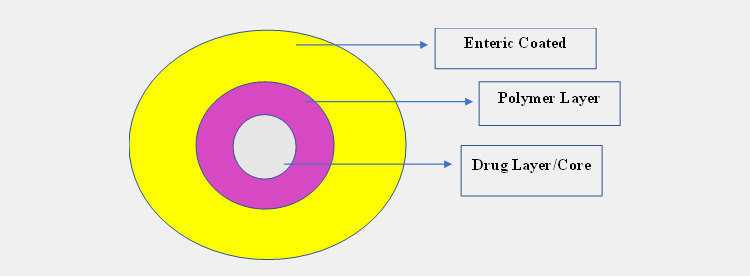
An Illustration demonstrating Layers of Enteric Coated Drug
An enteric coating drug is composed of a base core for e.g tablet core or capsule, a swellable hydrophobic polymer, and an enteric coating layer.
Just after gastric emptying or tablet leaves your stomach, the intestinal fluid slowly and gradually erodes the enteric coating layer.
A rapid release of active ingredients occurs when a core reaches the erosion process, and you get a therapeutic response.
Thanks to the pharmaceutical manufacturing companies who can assure you drug release and its accurate site of action. Through the combination of ingredients today medical professionals can easily tell when a drug can spring into action.
Ⅳ. What Is an Enteric Coating Made Of?
The making of enteric coating is described in two sections:
- Composition
- Manufacturing
Composition of Enteric Coating
Commercially manufactured enteric coating material includes the following ingredients:
POLYMER
Synthetic as well as natural polymers are utilized in the preparation of enteric coating drugs. They are used to enhance the flexibility of the coating and protect the drug from undesirable breakage and cracking.
| Common polymer utilized in enteric coating | DISSOLUtion pH |
| Cellulose Acetate Phthalate | Above 6 |
| Cellulose Acetate Trimellitate | 5 |
| Hydroxyl Propyl Methyl Cellulose Phthalate | Above 6 |
| Hydroxyl Propyl Methyl Cellulose Acetate Succinate | 4.5-5.5 |
| Polyvinyl Acetate Phthalate | 5 |
| Methacrylic Acid Copolymers | 5.5-7.0 |
| Shellac | 7 |
The common polymers used in the Enteric Coating substances are:
Cellulose Acetate Phthalate (CAP)
- Cellulose acetate phthalate or CAP is also considered cellacefate.
- This is one of the traditional and broadly used synthetic enteric coating polymers. It was patented as an enteric entity in 1940 by Eastman Kodak Company.
- CAP is insoluble in water, alcoholic solution, hydrocarbons, and chlorinated hydrocarbons.
- CAP dissolved rapidly in alkaline pH > 6 and is comparatively permeable to moisture and gastric juices.
- CAP is susceptible to hydrolysis under a high temperature and moisture.
Cellulose Acetate Trimellitate (CAT)
Chemically, CAT is strongly resembling CAP.
It is the most soluble cellulose derivative that can dissolve under pH ranges from 4.7 to 5.0. Thus, this is an ideal property of CAT which makes it most suitable for drug delivery at the proximal site of the small intestine.
Hydroxyl Propyl Methyl Cellulose Phthalate (HPMCP)
HPMCP was introduced in 1971 as a cellulose derivative used for enteric coating.
- It is soluble in an aqueous medium at pH ranging from 5.0 to 5.5.
- It is insoluble in the stomach although rapidly swells and is solubilized in the small intestine.
Hydroxy Propyl Methyl Cellulose Acetate Succinate (HPMCAS)
HPMCAS is also termed Hypromellose Acetate Succinate.
- Commercially available in the various grade pH-dependent releasing profiles. For instance, low pH 5.0, Medium pH 5.5, and high pH 6.5.
- Since it is a relatively as rigid polymer, hence plasticization is used to enhance the film’s flexibility and overcome the chances of cracking.
Polyvinyl Acetate Phthalate (PVAP)
PVAP is a free-flowing powder that is more stable than CAP. This is because of moisture permeability.
It begins to dissolve when reaches pH 5.0, this property makes it a targeted substance to release at the proximal site of the small intestine.
Methacrylic Acid Copolymers
This group is extensively used for enteric coating applications firstly introduced in the mid-1960s.
- It can easily dissolve at a pH above 5.5.
- It is suitable for certain drugs that have some specific target delivery sites.
SHELLAC
It is one of the main components used for enteric coating applications. Shellac is a secretion of an insect habitat in the tropic and subtropical regions. It is a natural bio adhesive polymer associated with several benefits.
- Shellac is reliable, cost economical and acid-proof substance that ensures a uniform coating.
- Shellac can dissolve at pH above the range of 7.0.
NATURAL WAXES
The implementation of waxes in pharmaceutical coating is well-recognized step as it helps in achieve polished and glossy tablets. Waxes like stearic acids, palmitic acids, etc are considered as a potential functional coating agent possessing enteric properties. An ideal percentage oof wax for enteric coating must be 25-43% to meet compendial criteria for modified release content.
SODIUM ALGINATE
It is a water-soluble polysaccharide extensively utilized in the pharmaceutical industries for enteric coating applications. Alginate is refined from brown seaweed. For a novel coating it is recommended to use Alginate with wax with ratio of 2:4 to 9:7.
Manufacturing of Enteric Coating
The manufacturing of enteric coating medication includes of the following steps:
STEP#1. Manufacturing of Tablet Core
A tablet core is prepared by direct compression method where entire weighed ingredients are milled and passed through mesh no 60 are used. Before compression materials are blended using the mixer for half an hour and then compressed on a punching machine.
In the case of the capsule, an encapsulation machine is used to obtain gelatin capsules.
STEP#2. Pre-Coating/Sub-Coating/Undercoat
The formulation is now sub-coated with sealing coating using HPMC. It is prepared by using HPMC in a solvent mixture of isopropyl alcohol and dichloromethane (2:1).
STEP#3. Enteric Coating
The polymer is softened in volatile solvents to make a coating solution. The coating solution is sprayed over the tablet core by using s coating pan accompanied by continuous air. The medicines are allowed to be dried after being coated.
STEP#4. Color Coating
Approximately around 3% of coated tablets are applied with the same coating solution as described above. But in this step, a coating solution could be colored. This step gives more flexibility and prevents coated medicines to stick under high temperatures.
STEP#5. Polishing
In this step, a coated tablet is polished by sprinkling 0.01% polishing wax over the surface of the rotating enteric-coated tablet bed.
Conclusion
Enteric coating is an extensive field of biopharmaceutical formulation associated from solid dosage form to implants and stent. In recent years, this solid dosage form has been subjected to a remarkable development and quality improvement.
We hope ‘what is enteric coating’ have made you competent enough to execute the knowledge for future tasks. Need our consultation? Our high-tech staff always welcome your queries 24/7/365. Just give us little details and get connect us right now.
Don't forget to share this post!
Tablet Coating Machine Related Posts
Tablet Coating Machine Related Products
Tablet Coating Machine Related Videos
CONTACT US
Tell us your raw material and project budget to get quotations within 24 hours.
WhatsApp Us: +86 181 6426 8586
Want the best price & newest pharmaceutical machinery buying guide,tips and trends sent straightly to your box?Sign up for Aipak’s monthly newsletter,we’re free for your consultation and Offer you the most suitable solutions!
The Buyer's Guide
- Capsule Filling Buyer's Guide
- Blister Packaging Buyer's Guide
- Tablet Counting Buyer's Guide
- Tube Filling Buyer's Guide
- Cartoning Buyer's Guide
- Gummy Making Buyer's Guide
- CO2 Extraction Buyer's Guide
- Empty Capsules Buyer's Guide
- Suppository Filling Buyer's Guide
- Tablet Coating Buyer's Guide
- Tablet Press Buyer's Guide
- Softgel Encapsulation Buyer's Guide
Most Popular
- 7 Importance Of Pharmaceutical Packaging In Different Applications You Must Know
- 6 Advantages You Must Know About Tablet Counting Machine
- 8 Advantages of Blister Packaging You Must Know
- 6 Critical Applications of Automatic Capsule Filling Machine
- 6 Stations You must Know to Improve the Filling Quality of Automatic Capsule Filling Machine