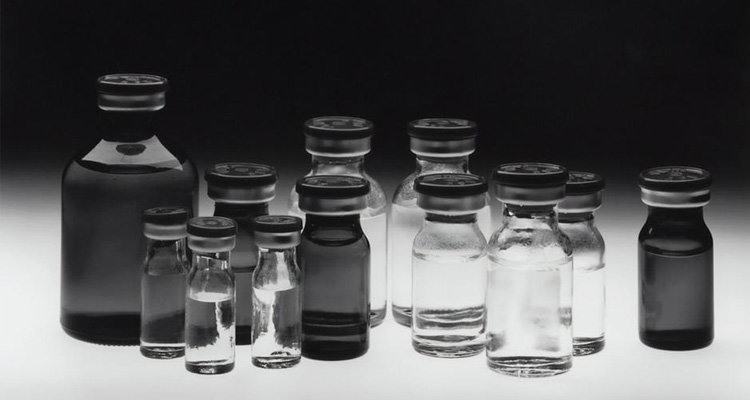
Vial Liquid-Small But Sustainable
A vial is small but a great solution with broad range of industrial applications. They are marketed in the form of glass or plastic that practically stores powders and liquid solutions. In the pharmaceutical production sector, vials are the preferred choice due to various reasons such as child-resistant closures, product safety, and stability. To know more about evolutions and current state, and future development; just stay with us!
1.Vial Liquid: What they are?
The small container or bottles typically used for filling liquid formulations like biologics, antibodies, proteins, gene therapies, and vaccines are referred to as vials. Vial liquids are also known as prescription vials.
These are a small tube with flat or slightly concave bottoms and bottle-shaped neck as compared to test tubes which usually have round bottom.
These vials are typically made of glass or plastic. They are primarily employed as a means for storing liquid medication because of their inertness and low metal traces. These are highly suitable for storing small volumes below 1 ml.
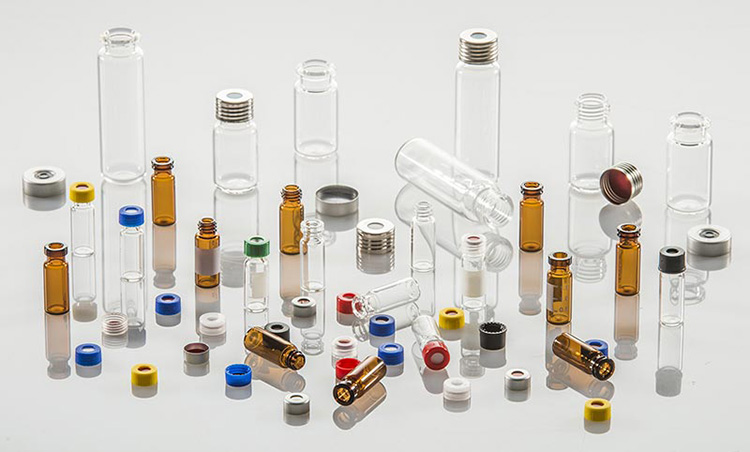
2.Different Types of Vials Used in Pharmaceuticals
The vials used for pharmaceutical procedures are categorized in various categories on the different basis such as:
Based on Design
Types of vials on the basis of design style are given below:
Tubular Vial
These are tube shaped vials having walls of uniform thickness. Tubular vials are best for lyophilisation procedures because of their even bottom that result in even heat transfer.
Moulded Vial
These vials have tube like shape but with concave bottom and thick walls. Usually marks and symbols are seen on the bottom of moulded vials. They have more weight than tubular one and vertical seam is visible around edges of these vials.
High Recovery Vials
These vials have conical bottom interior or v-shaped centre. Drug formulations settle down at the bottom resulting in utmost retrieval of products using syringe.
Dual Chamber Vials
They have two compartment used for holding and mixing two-part medication. These are two part glass vials separated with middle rubber closures. Dual Chamber Vials have active lyophilized drug in lower chamber and reconstitution solution in upper one.
Based on Application
Some vial categories on applications basis are as follows:
Cryogenic Vials
These are comprised of extremely cold resistant materials. These vials are apt in preserving biological samples at very low temperatures of about -196°C.
Autosampler Vials
These vials are used to storing samples that is immediately loaded in analyzer with the aid of needle. The syringe pierce vial cap and extract inside contents.
Sample Vials
They are containers that are generally employed for collecting, safekeeping, and transporting biological or chemicals sample specimens.
Injection Vials
These are tubular vials excellent for storing different liquid formulation such as cytotoxic, antibodies, and various clinical purposes. The liquid can be easily drawn by inserting syringe in vial.
Based on Dosage
There are two kinds of vials based on medication
Single-use Vial
This is used for administrating parenteral injection to single patient or in single procedure. It is discarded after use.
Multi-use Vial
These are also called multi-dose vials and contain more than one dose of parenteral infusion. These vials have antimicrobial agent to prevent growth of microorganisms and are used multiple times for various patient.
Based on Neck Type
Vials are classified in different categories based on neck shaped.
Crimp Necked Vials
Crimp neck vials are best for hygienic filling of drugs. These vials are closed with crimp caps requiring special crimping tools for cap insertion. These provide maximum protection against contamination.
Screw Necked Vials
The neck of these vials has screwed threads. These kinds of vials are tightly sealed using screw caps.
Snap on Vials
These are small necked vials and are generally secured via snap caps that are pushed on bottles by force.
3.Need for Vial Liquid in Pharma
Vial liquid are need of every pharmaceutical industry that is dealing with potent and highly sensitive drugs. Some applications of these sterile containers are discussed below:
Antibodies
Vials are employed for storing antibodies or antigens. These molecules are used for conducting serology studies and various clinical diagnostic procedures. Treatment of various diseases like cancer involved the usage of injectable antibodies.
Cytotoxic
An important application of liquid vial is packaging of cytotoxic drugs. These drugs are extremely potent medications employed for curing cancer, arthritis, etc. These medications require special vials for their storage.
Vaccines
The vials have been use for the packaging of vaccine since 19th century. These vials were first utilized for holding of injectable small pox vaccine.
Narcotics
This is type of analgesic drugs administrated for pain reliving especially after surgery. Sterile vial requiring aseptic filling are utilize for packing these medications.
Antibiotics
Penicillin and Cephalosporin are filled in glass vials for treatment bacterial infections.
Biologics
Biologics for instance fusion proteins and insulin increasingly employed in biotherapeutics, are filled in sterile vial that decreases their chance of contamination.
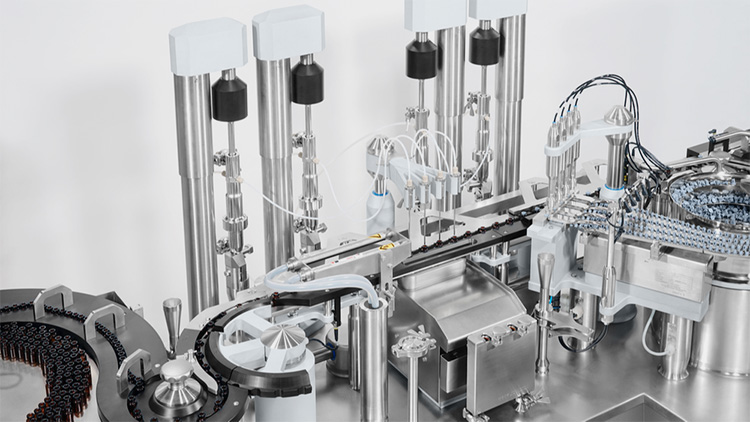
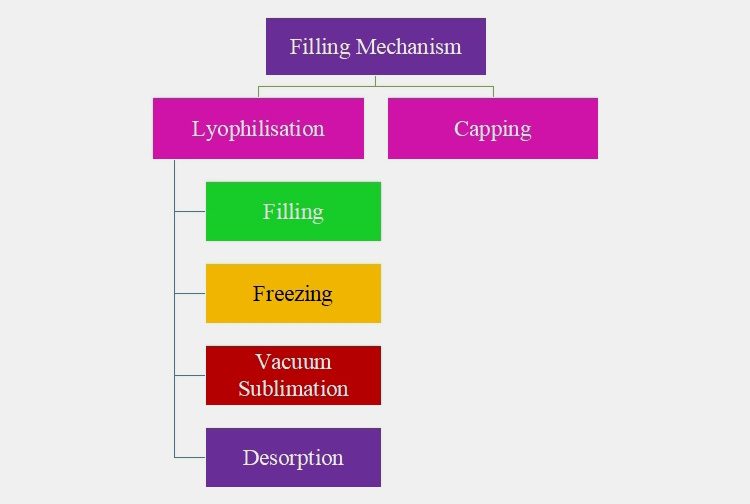
4.The Filling Mechanism
Aseptic filling is regularly used for manufacturing various parenteral medications like biologics, vaccines, eye drops, etc.
This approach was first introduced as the means of sterile manufacturing practice for injectable and plasma products in 1920 during World War II. Lyophilisation is an integral step during aseptic filling.
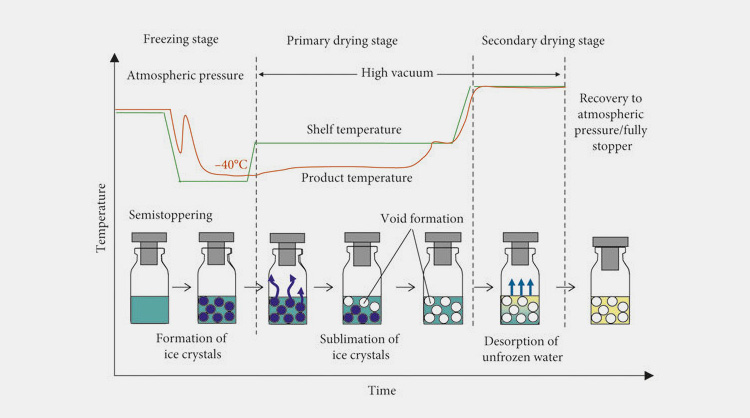
LYOPHILISATION
This is also known as freeze dry; widely employed in pharmaceutical manufacturing for providing stability to temperature sensitive drug medication such as biologics. This procedure involves the removal of water content from drugs for prolonging their shelf-life.
This procedure is usually carried out under barrier isolation. These isolators are safety cabinets or laminar flow hoods which use glove box technology for decreasing human involvement during aseptic processing. These isolators are sanitized via hydrogen peroxide before use.
Steps during lyophilisation include:
Filling
The liquid formulation is loaded into vials and the vials are transferred to Lyophilizer.
Freezing
In this step, the temperature is decreased to -50°C and the liquid drug turned into solid. This is done by placing formulation vials in freeze-dryer or chillers.
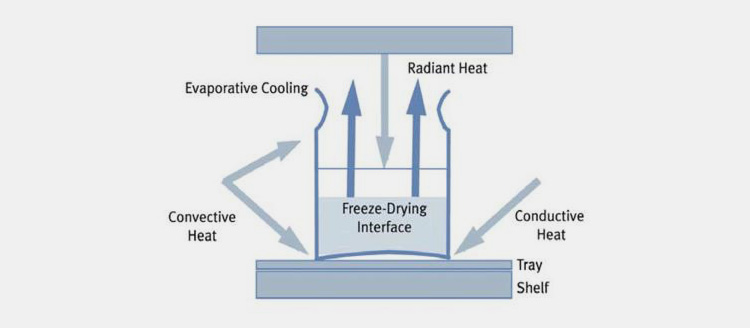
Vacuum Sublimation
It is a slow process conducted under vacuum conditions for evaporation of water from freezed product. The heat is applied to shelf of dryer, which changes the formulation from solid to gas without going through liquid phase. This is a primary drying step- drying materials from top-to-bottom. The water content is about 5% to 10% in this partially dried product.
Desorption
This step is carried out for completely drying the formulation. The final lyophilized products have 0.5% to 3% water content. This usually starts in primary drying stage but require high temperature of 30ºC to 50ºC.
CAPPING
The vials are completely stoppered using hydraulic or screw rod stopper. These vials are then transferred to capping and crimping unit. Force or torque is applied fixing crimp and screw caps respectively on vials.
5.Vial Liquid- Significance
Vials have replaced ampoules as a choice of packaging potent drugs. There are several advantages of using liquid vials in pharmaceutical industry such as:
Lower Contamination Risk
Vials are always filled under control sterile condition with filters. This decreases the chance of dust or airborne particle penetration side the vials thus minimizing contamination risk.
Easier Handling
Products are removed from the vial without any difficulty. Syringes are inserted in vials and products are drawn with these devices. But with ampoules, first top is broken which increase the damage to product.
Lightweight
These containers are tremendously light and are carried easily. So this saves shipment or transport expenses.
Small Volumes
Vials are manufactured for filling small volumes of products. These can be used to hold volume less than 1 ml.
Accuracy
It is employed for filling accurate volume of the drugs with minimal chances of overfills. The shape of vials helps in loading precise amount of liquid formulation in these containers.
Heat Resistant
Materials like glass and plastics have extremely high melting point so the vials made of these materials are best for storing temperature-sensitive drugs.
Inertness
Vials are suitable for storing potent drugs because material of vials do not chemically react with active ingredient and alter their chemical profile. This increases lifetime of drugs.
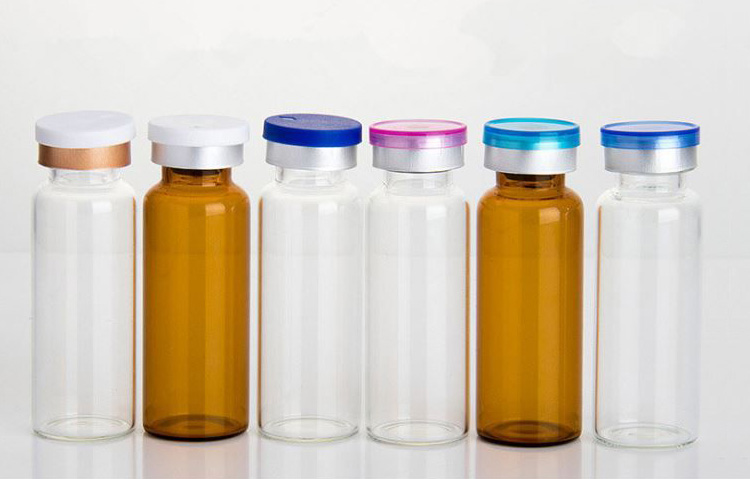
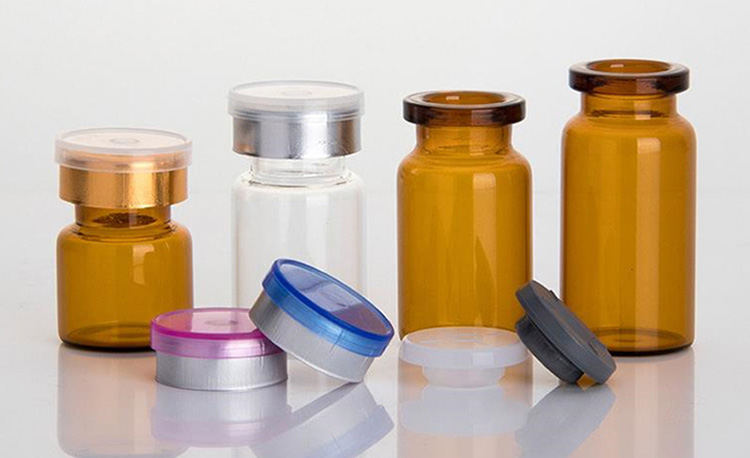
6.Vial Liquid- Plastic OR Glass
Traditionally, vials were formulated with glass but with the invention of plastic, like many other packaging materials, vials are also made from plastic materials. Both glass and plastic vials with their benefits that are discussed below:
Glass Vial
Ancient civilization like Egyptian civilization use glass vials for storing fragrances and essential oils. Vials have been in use for several hundred years for storing drugs. The first tubular glass vial was developed in 1912 by E. Danner of Libby glass company.
Materials
Glass vials are comprised of borosilicate and soda-lime-silica. Borosilicate glass vials are commonly used in pharmaceutical industry for research and development. Soda-lime-silica glass is device for keeping parenteral and non- parenteral drugs.
Significance
- Clear and transparent surface of glass aids in degradation inspection of drugs present in glass vials.
- Borosilicate glass is an inert substance that is chemically nonreactive upon exposures to potent drug compounds.
- Drugs in glass vials do not evaporate due to its non-porous characteristics.
- Iron tinted amber glass vials protect active ingredients from harmful UV rays, making it a suitable candidate for storing light-sensitive drugs.
Plastic Vials
Plastic was introduced as the packaging material since the invention of polyethene (PE) in 1935. These vials are popular due to their forensic and cryogenic applications.
Materials
Plastic vials are generally manufactured with polypropylene or polyethylene. High-density polyethylene (HDPE) is the widespread manufacturing material for plastic vials.
Significance
- Plastic vials are chemically resistant but can react with some oxidizing agents. These do not react with acidic or alkaline drugs and are not prone to leaching.
- These are long-lasting, durable and does not break upon impact
- Plastics are very light in weight so these vials are easy carried and transported.
- These materials have high melting point therefore are frequently used in autoclaves and cod storage.
- Plastic is fairly inexpensive hence manufacturing cost of plastic vial is significantly less than glass vials.
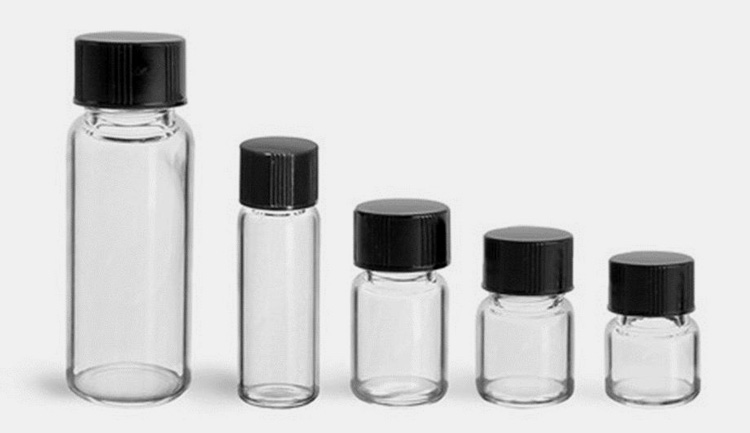
7.Sizes and Options of Vial Liquid
Vial liquids are available in variety of sizes. Small unit vials are of 20 mm to 28 mm and can hold volume of 1 ml-2 ml.
Some tubes have small volume capacity and can store about 0.1 ml of drug. Sizes of some vials are detailed below:
Unit dose vials are used for packing extremely small volume below 1ml.
| Height (mm) | Volume (ml) | Diameter (mm) |
| 19.5 | 1 | 6.6 |
| 28 | 2 | 6.6 |
Larger sized vials have 35 mm to 120 mm and are store about 1 ml to 300 ml of liquid drug.
| Height (mm) | Volume (ml) | Diameter (mm) |
| 35 | 5 | 18 |
| 90 | 70 | 40 |
| 95 | 100 | 40 |
| 125 | 110 | 47 |
CONCLUSION
Despite being the most traditional form of packaging, vial liquid are still facing some challenges. There is a continous ongoing upgradation in modern biosciences exploring new techniques and innovation to overcome difficulties and create better solutions . If you’re interested to learn more about vial liquid; then we welcome you to send us a short message. Our experts will contact you shortly!
Don't forget to share this post!
Vial Filling Machine Related Posts
Vial Filling Machine Related Products
Vial Filling Machine Related Videos
CONTACT US
Tell us your raw material and project budget to get quotations within 24 hours.
WhatsApp Us: +86 181 6426 8586
Want the best price & newest pharmaceutical machinery buying guide,tips and trends sent straightly to your box?Sign up for Aipak’s monthly newsletter,we’re free for your consultation and Offer you the most suitable solutions!
The Buyer's Guide
- Capsule Filling Buyer's Guide
- Blister Packaging Buyer's Guide
- Tablet Counting Buyer's Guide
- Tube Filling Buyer's Guide
- Cartoning Buyer's Guide
- Gummy Making Buyer's Guide
- CO2 Extraction Buyer's Guide
- Empty Capsules Buyer's Guide
- Suppository Filling Buyer's Guide
- Tablet Coating Buyer's Guide
- Tablet Press Buyer's Guide
- Softgel Encapsulation Buyer's Guide
Most Popular
- 7 Importance Of Pharmaceutical Packaging In Different Applications You Must Know
- 6 Advantages You Must Know About Tablet Counting Machine
- 8 Advantages of Blister Packaging You Must Know
- 6 Critical Applications of Automatic Capsule Filling Machine
- 6 Stations You must Know to Improve the Filling Quality of Automatic Capsule Filling Machine