Types Of Wet Granulation
Granulation techniques hold prime importance in the preparation of different dosage forms in pharmaceuticals. the process mainly involves conversion of small fine particles into large agglomerates or granules for making tablets and capsules. There are two distinct types of granulations are dry granulation and wet granulation.
Wet granulation is distinguished from dry granulation based on the fact that it requires a liquid called granulating fluid for the processing or making of granules. Instead of compaction the binding or making of granules occurs due to binder in the granulating fluid.

Benefits
- Better flow properties of the granules
- The attributes of formulation constituents are enhanced for the tableting process
- Low pressure required due to improved compression ability of drug powder
- Conventional excipients are used
- Dissolution rate is improved
- Less variability
- Lessens dust produced during dry granulation for tablet manufacturing.
- Post processing like tablet coating is possible.
Limitations
- Longer process
- High labor and energy requirement
- Wet granulation is not meant for heat sensitive and moisture sensitive drugs
- Low Dissolution rate of the resulting tablets upon ageing as compared to dry granulation
We will discuss several aspects important to wet granulation in this blog, and it will be helpful to understand the process along with different types of wet granulation and their importance.
Ⅰ.What Are Different Types of Wet Granulation?
In pharmaceutical industry wet granulation is broadly used technique due to its attributes specifically improving the flow properties, also produce homogenous mixture of powder mix with enhanced ability of compression.
The main purpose of wet granulation is to agglomerate particles by using a liquid solvent/binder that is preferred in many cases to avoid high compaction and slugging techniques.
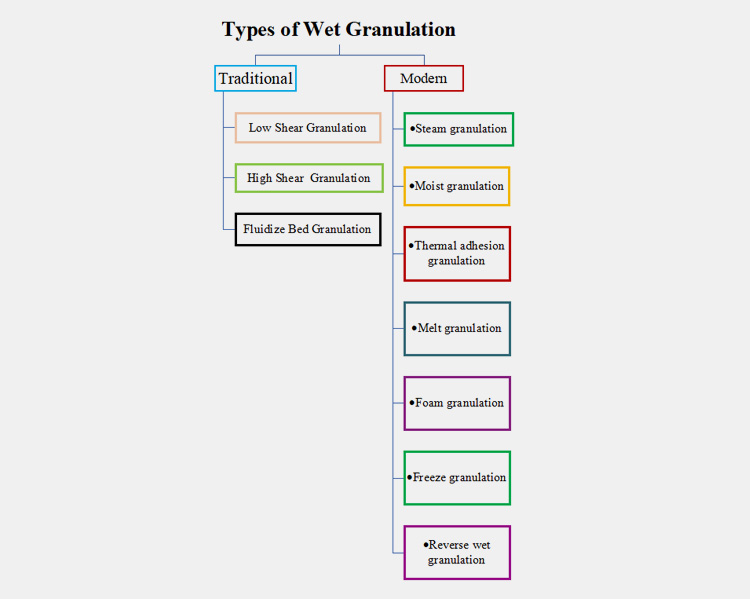
Wet granulation has subsequent classification which we simplified into the following: the conventional types and then the recent techniques. The following figure explains the hierarchy of different types of wet granulation techniques.
Ⅱ.Explain Traditional or Classical Methods Of Wet Granulation?
There are three main types of wet granulation
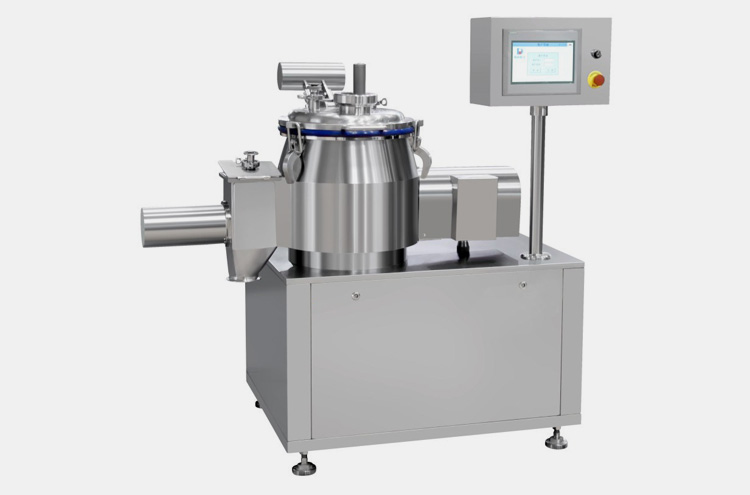
1.Low shear granulation
This is the classical method of wet granulation where the drug powder excipients are mixed in presence of binder solution, the resulting granules from the wetting technique are dried in a drier usually in a tray dryer. The dried granules are further processed to get desired size. Furthermore, lubrication and compression are done to get the end product.
Figure: Low Shear Mixer Granulator
Benefits
- Low quantity of binder solution needed
- Method is time efficient and less costly
- More compressibility of granules that are produced in comparison to high shear granulation.
Limitation
- The main disadvantage of the process is manual transfer and longer drying requirements.
- Over wetting can cause lumps
Application
This technique has applications in various fields and used for formation of granules from powdered material in industries like food industry, pharmaceuticals, minerals and fertilizers.
2.High Shear Granulation
High shear granulation involves the equipment i.e. high shear granulators containing double blade for mixing, a rotator and a high-speed chopper that continually break down the wet mass during the granulation process. This type of wet granulation can be used for any formulation type. But due to high speed over granulation can occur.
Figure: High shear mixer granulator
Benefits
- Less quantity of binder solution is required
- Generate uniform particles and granules
- The process makes less drug dust
- Endpoint can be anticipated
- Can be used for any type of formulation
Limitations
- Generates less compressible granules
- Over wetting can be a problem leading to larger oversized granules
- High temperature can affect temperature sensitive drugs.
Application
High shear granulators are utilized in several industries including pharmaceutical, detergent and agrochemical industries.
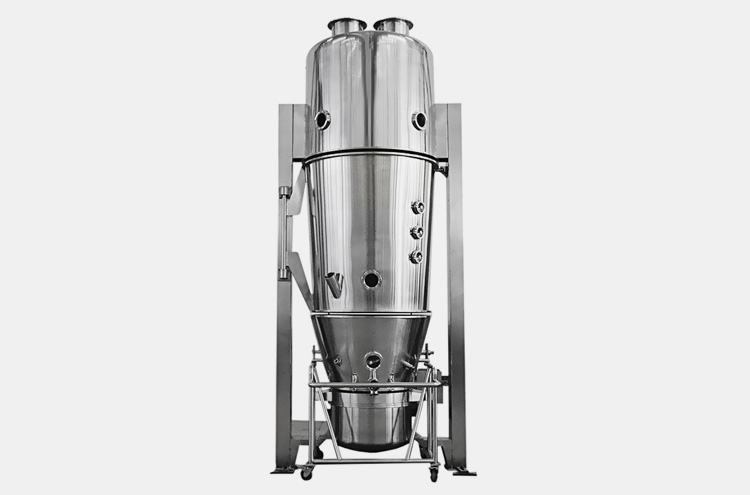
3.Fluidized bed granulation
In this type of bed granulation as the name suggests a fluidized bed granulator is used where the granulation fluid is added in the form of spray. Firstly, blending of drug and excipients is done with the help of low fluidizing air. In the second step binder solution is sprayed to make granules. The final step is drying of the granules. During drying process, the spraying is stopped while the temperature is increased to accelerate the process. The main advantage of fluidized wet granulation process is its controlled and contained nature.
Figure: Fluidized bed granulator
Benefits
- Less labor cost and time efficient
- Efficient drying as much more heat transfer as compared to tray dryer
- Process can be automated
Limitations
- Long resident time of the machinery
- Produces granules with lesser density
- More granulating fluid is needed compared to other types
- More expensive
Application
Many industries like pharmaceutical, agrochemical, chemical and others use fluidized bed granulator where it can be used as multipurpose machine making granules and also drying powdered material or granules etc.
III.What are advanced types of wet granulation?
Wet granulation is gaining importance due to the recent progress that has made it easy for pharmacists to adopt those techniques with minimum limitations. Several advance techniques have been provided to the pharmaceutical industry including
1.Steam Granulation
The main difference in steam granulation in comparison to conventional wet granulation method is the usage of steam as a binder instead of water as granulating fluid. Usually a steam generator and a mixer (high shear) is sufficient for the steam granulation method.
Rotary Drum for Steam Granulation
Benefits
- The advantage of steam is that it can diffuse better readily into the powder due to its purity and gaseous state which also helps in better drying.
- Produces spherical granules with more surface area less processing time
Limitations
- This method cannot be used for thermolabile drugs due to high temperature of steam which can affect the properties of the drug.
- High energy required for making steam
- This technique generates granules with high dissolution rate compared to conventional wet granulation techniques.
Application
This method is being employed greatly in the pharmaceutical industry as it is ecofriendly due to no involvement of organic solvents.
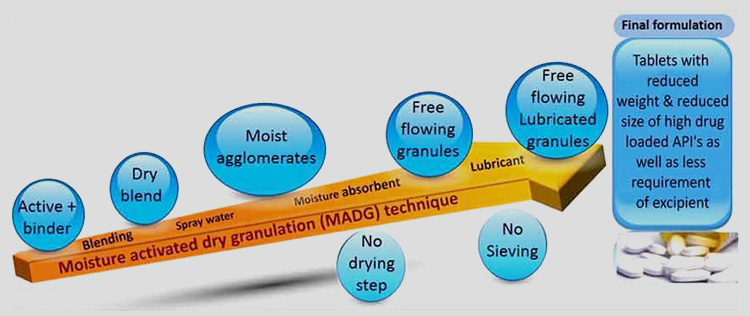
2.Moisture Activated Dry Granulation
MADG or Moisture activated dry granulation is modification of the classical wet granulation technique. It is done in two main steps first by wet agglomeration which is done by addition of small quantity of water to the mixture of drug and binder. The second step after agglomeration is drying which is done by addition of silicon dioxide or microcrystalline cellulose absorbing the extra moistness.
The name moisture activated dry granulation usually creates confusion as someone can get dry granulation to be involving compactors and slugging techniques but actually the drying process in MADG is quite different and does not involve any of the two.
Pharmaceutical Granulation Plant
Benefits
Main advantages of this technique are
- Less chances of lump formation due to less water required for the process
- less energy requirement,
- Efficient
- widely applicable.
Limitations
Accounting to the stability and processing issues this technique cannot work best for
- moisture sensitive drugs
- hygroscopic drugs
Application
This technique is getting popular in the pharmaceutical industry and is being widely used due to its efficiency and less water requirement.
3.Thermal Adhesion Granulation or TAG
This advanced technique of wet granulation involves both water and solvent for granulation and as the name suggests it also utilizes heat to expedite the granulation process. The drug along with the excipient is heated at a high temperature and less amount of liquid is used which eliminates the requirement of the drying process.
Binders are a very important element in wet granulation without them it's impossible to achieve specific properties of the granules. A good binder is responsible for required adhesive and cohesive forces between surfaces of different particles and ensures the binding ability.
The significance of binder in wet granulation makes the selection process much critical as much of the properties of resulting granules are dependent upon it.
Benefits
- This technique is useful for generating particles with high tensile strength and better flow properties.
- No need for an additional drying process
- Simple and convenient
Limitations
- It cannot be used for all types of binders and drugs that are heat-sensitive.
- Special equipment for heat generation is required
- High energy inputs are needed.
Application
This technique is a good alternative to conventional wet granulation techniques and is adopted by the pharmaceutical industries as it is simple and fewer steps are involved.
4.Melt granulation
Also known as thermoplastic granulation involves the usage of binders that have low melting temperatures i.e. 50-90 °C). the binders are added during the granulation process in two ways, as solid particles or as a molten liquid and then the drug, binder, and excipients mixture is heated to a suitable temperature according to the binder’s melting temperature.
Benefits
- This technique can be used as an alternative to other wet granulation techniques that are not suitable for moisture-sensitive drugs.
- It eliminates the usage of water which ultimately eradicates the requirement of drying after agglomeration.
Limitation
- Similar to most heat involving wet granulation techniques, this technique is not best for heat-sensitive drugs.
Application
Pharmaceutical industries have shown interest in this method owing to the advantages over wet granulation techniques for the preparation of drug formulations. Also, as it eliminates the environmental concerns due to the elimination of organic solvents it is becoming popular.
5.Foam granulation
Foam granulation is similar to spray agglomeration, but the binder is poured in form of foam onto the powder instead of spraying. This technique is a patent of Dow Chemical Company, Midland, MI. A foam generator is used in the binder tank to convert the binder into foam form which is then introduced onto the powder. This technique provides uniform distribution of the binder to the powder.
Benefits
- The processing time is less as it requires less binding liquid thus the drying process is shorter making it faster.
- This wet granulation technique is useful for water-sensitive formulations.
- In a shorter time, more binder mass is absorbed via foam granulation as compared to the addition of liquid or spray thus making 40% larger nuclei.
- Uniformity of granules is achieved
- Controlled and immediate release of drug
Limitations
- Foam generation requires high energy and resource as compared to other techniques.
Application
This technology is gaining importance in the pharmaceutical industry and being employed by many companies due to its various advantages the most beneficial being even distribution of drugs.
6.Freeze Granulation
Freeze granulation is based on two primary steps. The powder suspension is sprayed on liquid nitrogen which results in instant freezing of the droplets into granules which are dried in the subsequent step via sublimation. Both water-based and solvent-based granules can be synthesized by this method.
Freeze Granulation of Particles
Benefits
- Homogenous particles are formed by this technique.
- Freeze drying or low temperature minimizes damage and enhances the stability of the drug.
- Controlled granule density
- Less material gets wasted
Limitations
Mostly water is preferred over organic solvents in this process which is the limitation of the technique because of less solubility of drugs and excipients.
Application
Freeze granulation is a widely used technique in the pharmaceutical as well as ceramic and food industries.
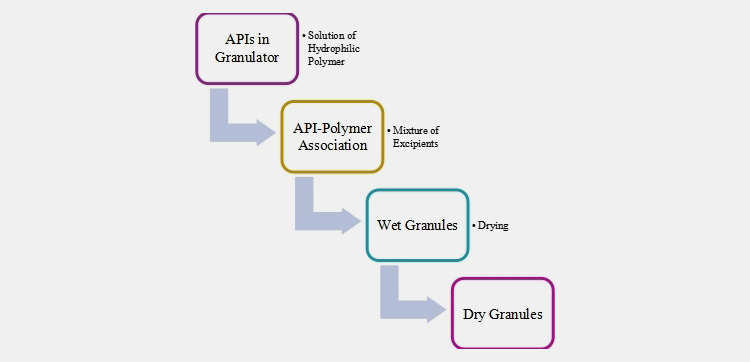
7.Reverse wet granulation
It is the recent development in wet granulation technique where the dry powder is immersed into the solvent or binder which is then broken down into granules under controlled conditions. First, the binder solvent is prepared, and the dry excipients are mixed with it in a granulator. Granule formation occurs when other dry excipients are added to the drug-binder mixture. The wet granules undergo milling after drying in the subsequent steps.
Reverse Granulation
Benefits
- This method produces granules having good flow and handling properties.
- The best characteristic is uniform dissolution in comparison with other wet granulation techniques.
- Controlled breakage of the granules occurs in this process resulting in tablets having an even dissolution rate
Limitation
- The granules generated by this process are often with less intragranular porosity and of greater mass mean diameter.
Application
- This technique can be used for fewer water-soluble drugs due to the close contact of between the drug and polymer.
Conclusion
We hope you have got the knowledge about different wet granulation techniques and their importance. Wet granulation is a widely used technique in several industries including pharmaceutical, food, chemical fertilizer, and other such industries.
The recent advances have improved the formulation of dosage forms specifically benefitting the pharmaceutical industry In addition to the other industries. Further research and modifications in these techniques can enhance the uniformity and stability of tablets and other dosage forms. For More Expert Guidance and Equipment Information- Please Contact Us by Click HERE. We are here to welcome you 24/7.
Don't forget to share this post!
Granulator Machine Related Posts
Granulator Machine Related Products
Granulator Machine Related Videos
CONTACT US
Tell us your raw material and project budget to get quotations within 24 hours.
WhatsApp Us: +86 181 6426 8586

Want the best price & newest pharmaceutical machinery buying guide,tips and trends sent straightly to your box?Sign up for AIPAK’s monthly newsletter,we’re free for your consultation and Offer you the most suitable solutions!
The Buyer's Guide
- Capsule Filling Buyer's Guide
- Blister Packaging Buyer's Guide
- Tablet Counting Buyer's Guide
- Tube Filling Buyer's Guide
- Cartoning Buyer's Guide
- Gummy Making Buyer's Guide
- CO2 Extraction Buyer's Guide
- Empty Capsules Buyer's Guide
- Suppository Filling Buyer's Guide
- Tablet Coating Buyer's Guide
- Tablet Press Buyer's Guide
- Softgel Encapsulation Buyer's Guide
Most Popular
- 7 Importance Of Pharmaceutical Packaging In Different Applications You Must Know
- 6 Advantages You Must Know About Tablet Counting Machine
- 8 Advantages of Blister Packaging You Must Know
- 6 Critical Applications of Automatic Capsule Filling Machine
- 6 Stations You must Know to Improve the Filling Quality of Automatic Capsule Filling Machine