Types of Emulsions- A Broader Aspects
In pharmaceutics, emulsions can be explained as a two-phasic system that is immiscible with each other and thereby dispersed as fine globules throughout the other. Emulsions can be further classified on the basis of their constitution, their particle size, and on consideration of their method of administration.
Up till now, you might’ve already been acknowledged by oil in water and water in oil terms. This might even seem confusing to you, right? But no worries, we’re here to help you figure out what actually these double emulsions are! Not only them, but you will also get to know, some other categories in which emulsions can be identified. Are you wondering how come two immiscible or two unlike meet when it’s popularly said, two unlike never meet?
To answer your inquisitive minds, and without further ado, let’s begin so you might hunt for your answers!
1.The Basic Types of Emulsions
Water In Oil Emulsions
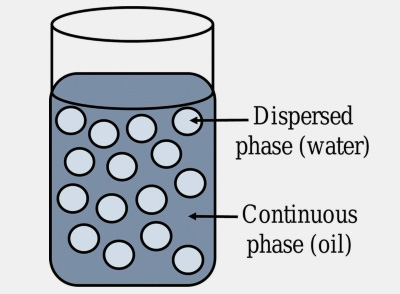
A type of emulsion in which water which is the dispersed phase is distributed throughout oil globules (continuous phase) is termed as Water-in-Oil (W/O) emulsion. It is also known as inverse emulsion. These emulsion intermixed conveniently with oil. Anoleophilic emulsifying agent is used for the formation of W/O emulsion.
Characteristics
- It has an occlusive effect which means they provide protection on the surface of skin preventing loss of moisture.
- They greasy effectwhich is un-washable by water.
- These are mainly formulated as an external preparation.
- Water in oil emulsions have a positive conductivity test as oil is a bad conductor of electricity.
Oil In Water Emulsions
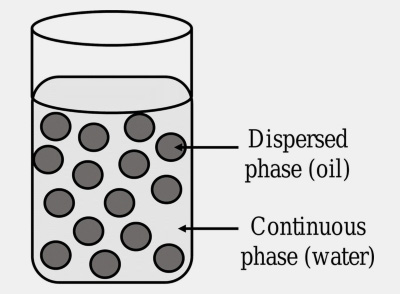
A type of emulsion in which oil (dispersed phase) is distributed throughout aqueous phase (continuous phase) is termed as Oil-in-Water (O/W) emulsion. A hydrophilic emulsifying agent is used for the formation of O/W emulsion.
Characteristics
- Fat containing medications are formulated as oil in water emulsion.
- It has a non-greasy effect and can thus be wiped easily from the skin.
- Mainly formulated as external preparation for providing cooling sensation and also as internal preparation for masking the bitter taste of oil.
- Drugs that are soluble in water are quickly released from O/W emulsion.
- Oil in water emulsion hasa positive conductivity test as water is a good conductor of electricity.
Double Emulsions
They are also known as multiple emulsions or triple emulsions. Multiple emulsions encompass globules of several dispersed phases.
There are two types of double emulsions:
Water in Oil in Water (W/O/W): Water in oil in water emulsion consists of water molecules being distributed throughout oil that is actually distributed in oil in water emulsion.
Oil in Water in Oil (O/W/O): Oil in water in oil emulsion has oil globules dispersed throughout aqueous phase that is dispersed in water in oil emulsion.
Characteristics
- They have pharmaceutical importance as they are employed for sustained release drug delivery systems.
- These emulsions have cosmetic significance since they are utilized in making sunscreens and body lotions.
- They have some limitations as well because they are thermodynamically unstable and possess complex nature.
2 . Difference between Water in Oil and Oil in Water Emulsions
Some differences between oil and water are discussed below:
| Water in Oil Emulsions | Oil in Water Emulsions |
 |
 |
| In these emulsions, water is distributed in oil phase. | Oil act as dispersed phase in oil in water emulsions. Water is the continuous media in these emulsions. |
| These are used in formulation of oil based items for instance creams and tropical products. | They are utilized for manufacturing water based goods such as sunscreens and makeup lotions. |
| They need only one emulsifying agent for ensuring their stability | Water in oil emulsion might require more than one emulsifier |
| Oil in water emulsions are non oily and are easily removed from skin tissues. | These emulsions are not washed out with water. |
| They are used for cooling effect. | They are employed superficially to prevent evaporation of water from external surface of skin. |
| These emulsions are used for delivering water soluble drugs. | These emulsions are used for delivering oil soluble drugs. |
3 . How is it possible that two unlikely meet like water and oil?
Oil and water never go hand in with each other. Usually, when these liquids are mixed, they form distinct layers. Oil molecules when dissolve in water are repelled by the aqueous phase. But with the aid of an emulsifier or surfactant you can mix oil and water together.
The addition of an emulsifying agent prevents molecules of water and oil from creating two separate barriers. Solution of water, oil, and emulsifier creates a cloudy yellowish mixture.
These two phases will separate from each other after some time but two layers that are eventually formed are less distinct and cloudier than original mixture of oil and water.
4 . Where are water in oil and oil in water types of emulsions used?
Oil in water emulsions are used in skin hydrating and some pharmaceutical products and edibles like milk, mayonnaise, and vinaigrette. They contain less oil concentration.
Water in oil emulsions is used in oil based cosmetics products like cold creams. They are also used as food stuff such as in butter, margarine, cod liver oil. They contain more oil in concentration.
5.Emulsions According to Their Particle Size
Emulsions can also be classified according to the size of globules or particles.
Macro emulsions: Its particle size is generally greater than 10 mm.
Macro emulsions are distributed phase through a fluid-fluid unstable system whose particle size ranges from 1-100 μm and are usually spherical in shape.
Micro emulsions: Its particle size is usually around 1-100 nm.
Micro emulsions are thermodynamically stable dispersed phase systems whose particle diameter ranges usually around 10-50 nm and are usually spherical in shape.
Nano emulsions: They have the smallest particle size range, commonly known is the oil in water. However micro emulsions also contain nano particles but they are thermodynamically stable.
6.Emulsions On The Basis Of Their Mode Of Administration
According to their purpose and route of administration, emulsions can also be classified in such ways:
Oral Use Emulsions
They are usually oil in water emulsions masked with palatability, containing one or more active pharmaceutical ingredients. For e.g.: Cod liver oil, liquid paraffin oil etc.
Externally Applied Emulsions
Both oil in water and water in oil types of emulsions are used as external preparation. Emulsions that are applied externally include lotions, liniments, creams and emollients. However O/W emulsions are non greasy and easy to wash away from the skin and have more hydrating effect (emollient), whereas W/O emulsions can be conveniently rubbed onto the skin surface.
Parenteral Use Emulsions
Some emulsions can also be administered in the body via intravenous or intramuscular route known as parenteral route. These are commonly found being used in Total Parenteral Nutrition (TPN), intramuscular injection of some vaccines and drugs.
Rectal Use Emulsions
Rectally administered drugs are also known as suppositories or enemas; they are in the form of emulsions. Rectal use emulsions are intended for analgesic, anti-inflammatory or laxative effects.
7.Pharmaceutical Uses of Different Types of Emulsions
Pharmaceutically applied uses of various emulsions can be found as oral emulsions, rectal emulsions, and parenteral emulsions.
For formulating oil and water-miscible medicines.
For masking the taste of orally taken oils and making them palatable.
Total Parenteral Nutrition which is an example of emulsions is given usually to bedridden, comatose, and unconscious patients.
Intramuscular injection in the application of depot therapy.
8.How Are Variable Types of Emulsions Actually Prepared?
In general, an emulsion is prepared by constituting dispersed globules that are enveloped or surrounded by an emulsifying agent and then these are finally suspended in the continuous phase.
The following methods are utilized to prepare emulsions:
- Continental method or Dry gum method
- Wet gum method
- Bottle method
- In situ soap method
- Membrane emulsification method
9.Tests For Identifying Different Emulsion Types
Many tests are used for recognizing the emulsion’s type. Even though such tests may be performed quickly; the conclusion must be explained with caution. It may be possible that such tests do not indicate whether a multiple emulsion has been produced or a simple one. Such confusion may be cleared by microscopic examination.
| Dilution / Miscibility Test | Miscibility test includes the addition of continuous phase that is water in case of O/W emulsion. The emulsion remains in balance upon limitless addition of water but will become unsteady upon unlimited addition of oil, which means the oil will form a separate layer. The opposite of this happens is the case with W/O emulsion. |
| Electrical Conductivity Test | Water is a great conductor of electricity therefore an emulsion with an aqueous continuous phase will conveniently conduct electricity while that with an oily continuous phase will not. |
| Staining Test / Dye Solubility Test | In this test a little quantity of water soluble dye such as methylene blue is incorporated into the emulsion, if water is in the continuous phase (O/W emulsion), the dye is completely dissolved in the system. If oil forms a continuous phase (W/O emulsion) then particles of dye will remain undissolved on the upper layer of the system. |
|
Cobalt Chloride Test |
If the filter paper is dipped in cobalt chloride solution and then added to an emulsion afterward, dried, it changes its color from blue to pink displaying that the emulsion is o/w type. |
| Fluorescence Test | If the emulsion comes in contact with ultra-violet radiations and persistent fluorescence is seen under a microscope, then it is Water in Oil (w/o) type and if it shows only spots in fluorescence, then it is Oil in Water (o/w) type emulsion. |
10.Applications Of Different Emulsions Used for Various Purposes:
Emulsions are used in wide-ranging industries, some of useful applications of emulsion in various industries are:
Pharmaceutical Application
Burn cream, ointments, enemas, and various rectal drugs are all emulsions. Oleophilic drugs are formulated as emulsions to ease their absorption inside the body. Vaccines and antibodies are kind of micro-emulsion.
Nutraceutical Application
Emulsions are used as vehicle of delivering vitamins, minerals, supplements, enzymes, hormones, and other nutraceuticals. These are used in formulations of omega 3 fatty acids, coenzyme Q10 and other biological compounds.
Cosmetic Application
Sunscreens, lotions, skin care creams, and makeup removers are applications of water-in-oil and oil-in-water emulsions in cosmetic industry.
Personal Care Application
Conditioners, shampoos, bath lotions, are emulsions. Cleansing action of soaps and shampoos is because of creation of oil-in-water emulsions.
Food Stuff Application
Ice creams, frozen desserts, and milk are example of oil based emulsion. Every day food emulsions are used such as mayonnaise, butter, margarine, salad dressing. Confectionaries and bakery products are also made with oil-in-water emulsions.
Chemical Application
Metallurgy chemicals and other lubricants are oil-in-water emulsions. Similarly, road building process involves Asphalt emulsified in water. Disinfectants like Dettol and Lysol produces an oil-in-water emulsion when added to water. Paints and inks are examples of pigments dispersed in emulsions.
Conclusion
In Pharmaceutical practice the significance emulsion ranges from low viscosity to high viscosity products. Emulsion is fundamental element of the pharmaceutical preparations include drug, lotions, creams, lotions etc., Do you any query? Let’s talk! Aipak Pharmaceutical is one stop solution offering unlimited innovative range of emulsifying equipment suitable for your production growth. Please contact for Free Consultation about Equipment and Buying Guidelines.
Don't forget to share this post!
Vacuum Emulsifying Mixer Related Posts
Vacuum Emulsifying Mixer Related Products
Vacuum Emulsifying Mixer Related Videos
CONTACT US
Tell us your raw material and project budget to get quotations within 24 hours.
WhatsApp Us: +86 181 6426 8586
Want the best price & newest pharmaceutical machinery buying guide,tips and trends sent straightly to your box?Sign up for Aipak’s monthly newsletter,we’re free for your consultation and Offer you the most suitable solutions!
The Buyer's Guide
- Capsule Filling Buyer's Guide
- Blister Packaging Buyer's Guide
- Tablet Counting Buyer's Guide
- Tube Filling Buyer's Guide
- Cartoning Buyer's Guide
- Gummy Making Buyer's Guide
- CO2 Extraction Buyer's Guide
- Empty Capsules Buyer's Guide
- Suppository Filling Buyer's Guide
- Tablet Coating Buyer's Guide
- Tablet Press Buyer's Guide
- Softgel Encapsulation Buyer's Guide
Most Popular
- 7 Importance Of Pharmaceutical Packaging In Different Applications You Must Know
- 6 Advantages You Must Know About Tablet Counting Machine
- 8 Advantages of Blister Packaging You Must Know
- 6 Critical Applications of Automatic Capsule Filling Machine
- 6 Stations You must Know to Improve the Filling Quality of Automatic Capsule Filling Machine