Types Of Dry Granulation
Blending is the first step in the tablet manufacturing process. This step involved active pharmaceutical ingredients and excipients until to form a homogenous mixture. Granulation supports this and is done either by free-fall blender or high shear mixer that accompanied with strong shear forces.
Powders always cause dust during treatment, to make free-flowing and dust-free particles, transform them into a fine granule using the granulation technique. This is the most significant process in the production of the solid dosage form.
Do you need expert guidance in understanding the types of dry granulation?
This assessment review is exactly what you’re looking for! We have highlighted the types of dry granulations, advantages, disadvantages, mechanical approach, influencing parameters, and much more.
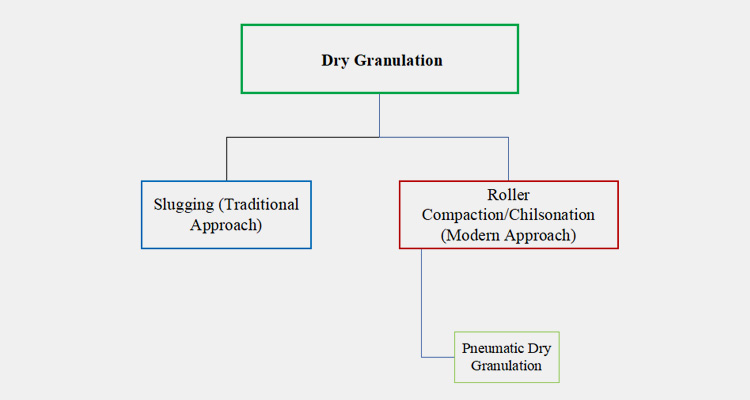
Ⅰ.Types Of Dry Granulation
Slugging and compaction are the basic two types of dry granulation. These are frequently employed in the pharmaceutical industry for the manufacturing of products.
Previously, during the 1950s to 1970s slugging was often used method of dry granulation. However, with advancement slugging was replaced by roll compaction.
Indeed, roll compaction was the most preferred over slugging. Because it offers you greater production capacity and a continuous process.
Types of Dry Granulation
Slugging
1.Definition
If you use a tablet press for the compaction process, the term slugging is used. Slugging is the cheapest approach to granulation. It is highly appropriate for moisture and heat-labile products. This technique is also referred to as “double compression” or “precompression method”. Slugging is a seldom-used method for granulation.
Since a particle with a smaller particle size does not flow well into a die of the tablet press. Therefore, it causes weight variation from tablet to tablet. This results in a large variation in the forces employed onto the individual slug as well as its mechanical strength. So, the obtained result is not satisfactory and uncontrolled. That’s why slugging is a hardly used method in industries.
2.Working Principle of Slugging
The principle of slugging is based on the following steps:
Step #1
Compression of the mixture of powders without using solvent and heat is taken place on a conventional tablet machine or heavy-duty rotary press specially designed for this purpose.
The powders blend is poured into a wide volume dies followed by compaction by big size punches, then the compact mass is reduced into granules by milling using conventional milling equipment or hammer milling.
Slugs:
Compact mass or large, flat-shaped disks like tablets which are obtained at the first step of slugging under high pressure arecalled slugs.
Step #2
The next step is milling of these large size slugs by passing through the appropriate sieves (No.20 and No.10) installed in an oscillating granulator which reduces the size of these slugs into appropriate granules.
The obtained granules are then homogenized with some other excipients including lubricants, additives, or other excipients (if needed) followed by compression into finished tablet form using the standard protocol.
3.Equipment used in Slugging
Hammer Mill:The ideal equipment used for slugging is the hammer mill. A Hammer mill is preferred for breaking down the slug in order to create fine granules.
A Hammer mill is old and conventional equipment widely used for grinding and crushing the aggregates into fine smaller particles due to the repetition of a striking set of hammers.
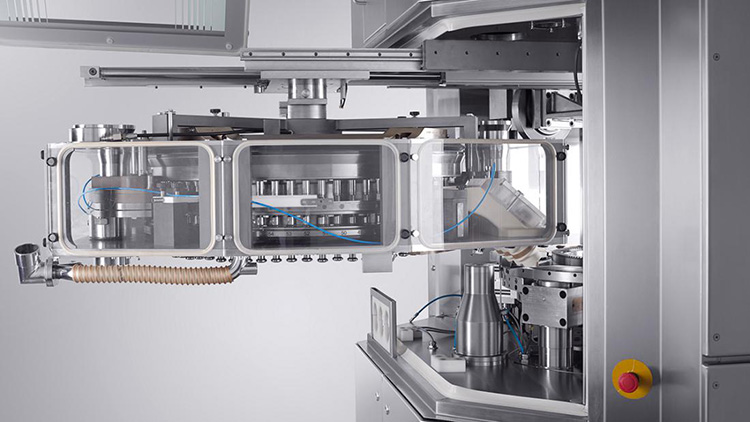
Rotary Press: Some manufacturing companies may also prefer using heavy-duty conventional tablet machines or rotary presses for compacting the powder particles.
A rotary tablet press is a mechanical tool that unlike a single punch press comprised of multiple tooling stations press the granules or powder upon rotation.
4.Advantages of Slugging
- Slugging is the traditional method preferred for dry granulation of hydrolyzable entities i.e., aspirin, which is not significant for wet granulation.
- Powder with poor flowability is suitable for the slugging process.
- Difficult compressing material can be pressed using slugging.
5.Disadvantages of slugging
- Dust production is a major concern that may cause cross-contamination among different products and increase the risk of health problems in working staff.
- Small-scale processing or only short batch production (30–50 kg/hour throughput)is possible.
- Poor operation control.
- Periodic maintenance requirement.
- Weight variation
Considering all these problems, the slugging technique has been replaced with a more advanced roller compaction technique.
6.Applications
As discussed, earlier slugging is a traditional method. This method of dry granulation was previously used for the following applications.
In the pharmaceutical industry, slugging- is a pre-compression method used for the formation of larger size tablets. To break down large, and difficult particles some pharmaceutical companies still use this method for breaking down particles.
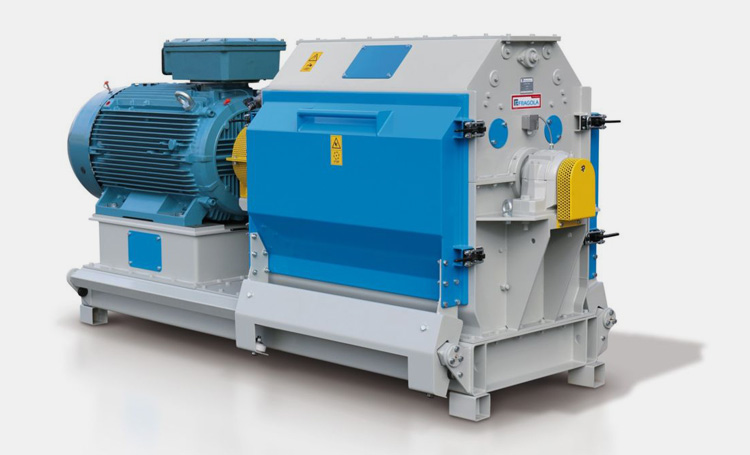
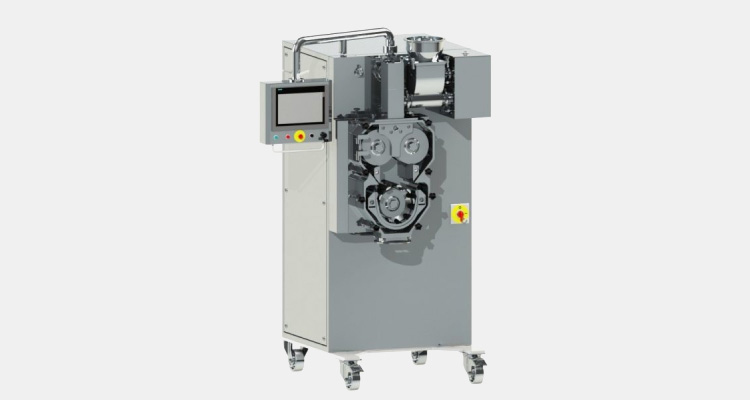
Roller Compaction
1.Definition
Roller compaction (also known as “dry granulator”) is a type of dry granulation that transforms powders (possess active ingredients) into granules by applying an appropriate force which is then compressed to a finished tablet form.
2.Principle of Roller Compaction
Three main units are the basic steps of roller compaction.
- The powder mixture is carried to the compaction area between the rotating rolls by the feeding system/unit.
- Subsequently, the powder blend is compacted to a ribbon between the counter rolls under specific force with the help of the compaction unit.
- The obtained ribbon-like compact is then reduced to the required granule size by the size reduction unit.
3.Equipment Used in Roller Compaction
A Roller compactor is the most common equipment used in pharmaceutical industries for manufacturing tablets and capsules.
The roller compactor consists of a pair of counters-rotating rolls in which a fine powder blend is forced to pass to make it a solid compact mass (strips, sheets, flakes).
4.Advantages of Roller Compaction
Some features of the roller compactor make it highly advantageous for pharmaceutical industries.
- Most importantly, it is an economical process in a way that it offers dry granulation and skipssome steps of granulation such as wetting, then drying, and mixing, hence increasing the company’s profit.
- The ideal approach for moisture-sensitive drugs.
- It allows the production of granules of varying sizes hence, raising productivity.
- The entire procedure is without a drying step, therefore suitable for formulating heat-sensitive compounds or those having a low melting point.
- Porous tablets which offer a high disintegration rate,therefore, high bioavailability, are produced from granules obtained by roller compaction.
- Cleaning of roller compactor is relatively easy because of having a roll exchange system, resulting in theproduction of quality products.
- In most cases, the initial investment for a roller compactor is low. Additionally, it offers a wide variety of designs for specific applications.
- It is an environmentallyfriendly procedure; low dust production hence protects the environment from drug contamination.
- The roller compaction technique may also minimize the capping problem of tablets.
- In some cases, a roller compactor can be used for powder densification before encapsulating it into capsules.
5.Disadvantages of Roller Compaction
Roller compaction also possesses few disadvantages like any other technique however, they are conveniently manageable.
- Tablets/capsules made by this technique possess low tensile strength that makes them relatively weak for effective packaging in comparison to the tablet/capsules formulated by direct compaction or wet granulation. This phenomenon is referred to as ‘loss of reworkability’.
- Due to the absence of liquid binder in the entire procedure, a considerable number of fine particles were left uncompacted, resulting in lessproduct yield compared to wet granulation.
- The Roller compactor utilizes a high amount of energy for the operation which increases the electricity bill cost, however, it is quite bearable because the productivity of the roller compactor is also high.
- Another drawback is the high probability of the generation of static charges during operation. It is due to the absence of any liquid throughout the process, therefore no lubrication. In some cases, it can be dangerous because it may cause a spark and burnthe Therefore, routine maintenance of equipment is necessary.
6.Application of Roller Compaction
- High compatibility and flowability are the desirable features of excipients used for direct compression. Agglomeration by roller compactor generally is the most appropriate approach to form directly compressible excipients.
- Problems associated with some drugs such as inconsistent and low bulk, varying and ultra-fine particles size, poor compatibility, and flow properties can be overcome by the roller compaction method.
- Herbal dry extracts are generally difficult to transform into tablets because of the presence of hydrophilic ingredients (like organic acids or sugars), they are highly hygroscopic.
In addition, generally exhibit poor compression and flow properties therefore agglomeration step by roller compaction becomes an essential step before tablet formulation.
- This technique is also used to formulate immediate release tablets/capsules for attaining optimal dissolution.
- Some drugs such as aspirin, vitamins are highly moisture sensitive, in this case, roller compaction is an ideal choice.
- Further, it is effective in the formulation of controlled-release tablets/capsules.
II.What is Pneumatic Dry Granulation?
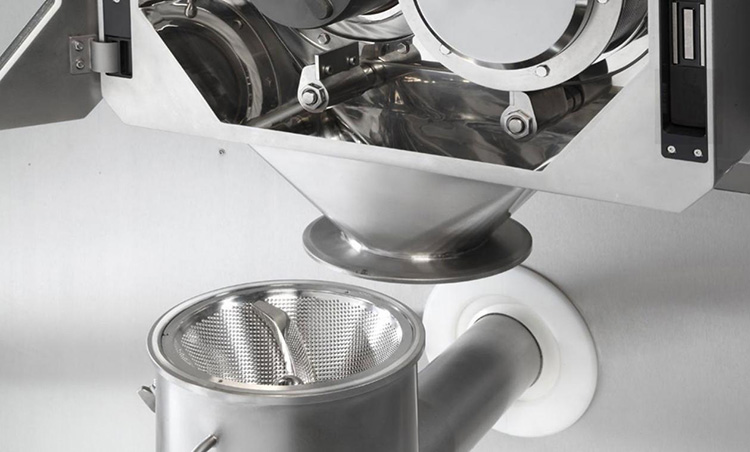
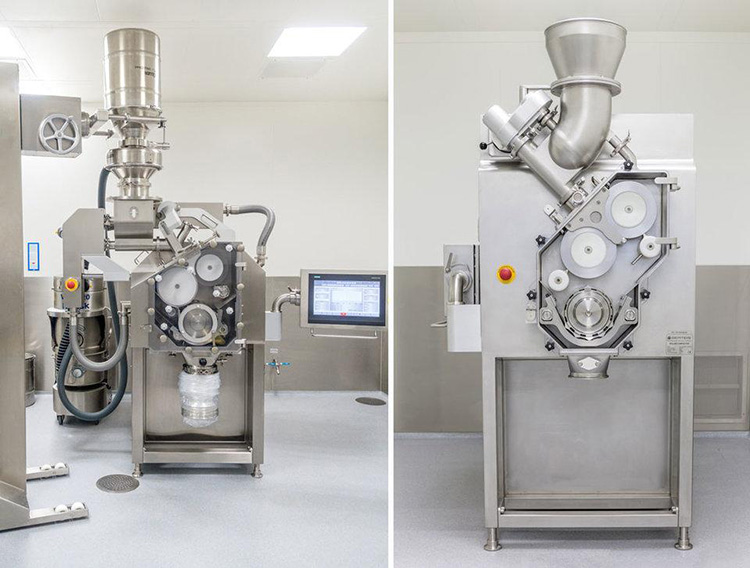
Pneumatic dry granulation (PDG) is an advanced dry granulation method for granules formation.
The operation is both automatic and semi-automatic.
Tablet hardness, disintegration time, and drug load can be easily modified in this technology.
PDG technology provides high stability of the product, taste masking, and increased drug loading of almost all API and excipients combinations.
High compatibility with other procedures such as coating, fast release, and sustained-release formulations.
Highly appropriate for moisture and heat-sensitive drugs.
Porous granules produced from the PDG approach offer greater compressibility and flow properties.
Another salient feature of the PDG method is that almost all solid active pharmaceutical ingredients (API) can be granulated efficiently.
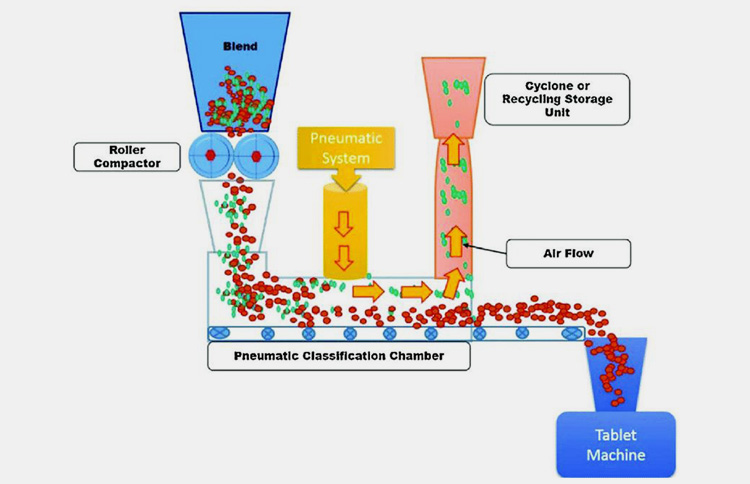
III.What is PDG Mechanism?
In the PDG approach, powder particles are transformed into compacted mass (which is a blend of both granules and fine particles) in a roller compactor initially under light compaction force.
The granules of the desired size in a fractionating chamber are then compressed into finished tablet form.
Undesirable smaller granules/fine particles are then segregated from desirable granules by entering in a pneumatic system/ gas stream, subsequently then transferred to a cyclone device. Then either immediately recycled/reprocessed by re-entering to the roller compactor or carried in a chamber for recycling in the future.
IV.PDG: an effective alternate of wet granulation?
Pharmaceutical industries prefer wet granulation in most cases compared to dry granulation.
However, there are a lot of drawbacks linked with wet granulation. Such as, it is not appropriate for heat and moisture labile drugs, being more costly, labour-intensive, requiring longer process time.
The complicated process involves many steps, therefore, need quality assurance in each step and require prolonged drying.
Pneumatic dry granulation offers a solution to these problems and is considered an appropriate replacement for wet granulation.
Granules produced from PDG technology possess excellent properties over direct compression, dry granulation, and wet granulation technique.
Ⅴ.What are the advantages of Pneumatic Dry Granulation Technology?
PDG technology offers high drug loading (up to 100%) of almost all active ingredients.
Processing speed is even faster for those compounds previously proved to have difficult properties and are tough to handle.
Appropriate for both moisture and heat-labile drugs.
Safe, and closed system, highly suitable for processing toxic materials.
Additionally, appropriate for handling sterile products.
Final products produced from PDG technology possess improved shelf life, offer optimal stability, and disintegration.
There is almost no loss of raw material, thus offering high productivity at a low cost.
Convenient scale-up
The release time of drug dosage is adjustable based on protocol need.
ⅤI.What are the disadvantages of Pneumatic Dry Granulation Technology?
PDG principle is based on double compression of API and excipients which may cause raw material degradation during the process.
Undesirable small granules/fine particles are recycled in PDGoperation, however, the impact of this reprocessing on the quality of produced granules and whether this technique is appropriate for low dose formulations remain a problem.
Conclusion
Tablets are designed to liberate medicaments at an improved rate. Using conventional technologies always compromise pharmaceutical activities and cause production cost.
To fulfill a therapeutic requirement, novel granulation techniques are developed with recent advancements in dry granulation; such as the Pneumatic Dry Granulation method is introduced to improve the formulation approach.
AIPAK Pharmaceutical Equipment offers an extensive range of high shear granulation. Click Here to get guidance support about the type of raw materials, and project budget.
Don't forget to share this post!
Granulator Machine Related Posts
Granulator Machine Related Products
Granulator Machine Related Videos
CONTACT US
Tell us your raw material and project budget to get quotations within 24 hours.
WhatsApp Us: +86 181 6426 8586
Want the best price & newest pharmaceutical machinery buying guide,tips and trends sent straightly to your box?Sign up for AIPAK’s monthly newsletter,we’re free for your consultation and Offer you the most suitable solutions!
The Buyer's Guide
- Capsule Filling Buyer's Guide
- Blister Packaging Buyer's Guide
- Tablet Counting Buyer's Guide
- Tube Filling Buyer's Guide
- Cartoning Buyer's Guide
- Gummy Making Buyer's Guide
- CO2 Extraction Buyer's Guide
- Empty Capsules Buyer's Guide
- Suppository Filling Buyer's Guide
- Tablet Coating Buyer's Guide
- Tablet Press Buyer's Guide
- Softgel Encapsulation Buyer's Guide
Most Popular
- 7 Importance Of Pharmaceutical Packaging In Different Applications You Must Know
- 6 Advantages You Must Know About Tablet Counting Machine
- 8 Advantages of Blister Packaging You Must Know
- 6 Critical Applications of Automatic Capsule Filling Machine
- 6 Stations You must Know to Improve the Filling Quality of Automatic Capsule Filling Machine