Stages Involved In Manufacturing Of Pharmaceutical Tablets
Tablets are small yet powerful- Pharmaceutical industry has come a long way over decades in the manufacturing of tablets. Many of you may consume tablets regularly but seldom understands how they form. Possibly one question may trigger your mind how a pharmaceutical tablet be so tiny? Indeed, manufacturing pharmaceutical tablets require a lot of planning and research. The primary purpose behind it is to make patients compliant and have ease of swallowing.
Here you can find the stages involved in manufacturing pharmaceutical tablets and expand your knowledge of how they can be so effective.
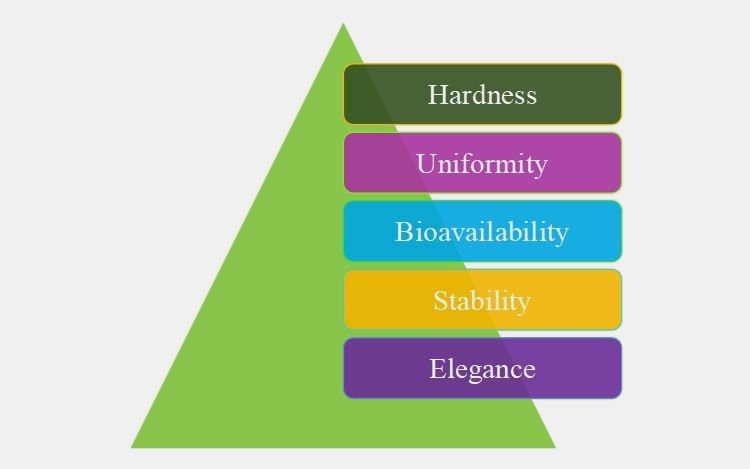
1.Major Goals of Manufacturing Pharmaceutical Tablets
Tablets are the most popular solid dosage types. These are the best means for formulating drugs. Some major goals of manufacturing pharmaceutical tablets are discussed below for your understanding.
Hardness
The major goal of tablet manufacturing is to prepare tablets with hardness and strong tensile strength so that they can withstand and tolerate rough treatment and mechanical forces during packaging, transport, and delivery.
Uniformity
It is a fundamental objective of tablet production since there can be variance in dosage and weight of tablet because of blending and processing of powders before tabletting. An ideal tablet should have API dosage constituency for providing patient maximum relief.
Bioavailability
This is termed as the amount of active drug that reaches systematic circulation to provide desired response. During tabletting, it is necessary for ensure that tablets are readily disintegrated and bind to plasma protein for boosting bioavailability.
Stability
This is a key objective of tablet formulation. Tablets can be degraded in humid and warm conditions. Good chemical coating aids in chemical and physical stability of drug throughout its shelf life. These covering protect tablets from humidity, high temperature, oxidative and hydrolytic conditions.
Elegance
Appearance and elegance is a striking feature that enhances patient compliance. The aim of tabletting is to create a product that has unique identity, easily recognizable and free of defects such as chipping or cracking.
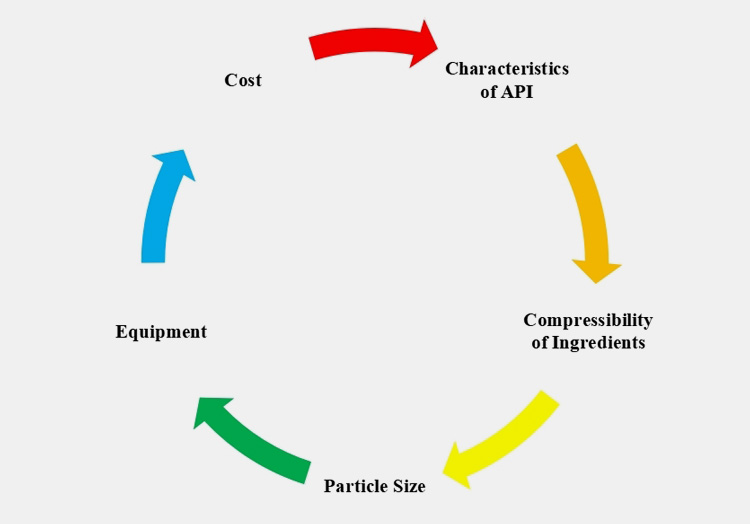
2.Basic Parameters Influencing Pharmaceutical Tablets Process
There are many parameters that play a significant role in selecting pharmaceutical tablet manufacturing process for instance:
Characteristics of APIs
If your drug ingredients are more liable to heat and moisture degradation then you should consider opting for dry granulation. In comparison, wet granulation is employed for enhancing cohesively and fluidly of APIs. Tablets produced by direct compression are fragile and too prone to breakage.
Compressibility of Ingredients
If ingredients have good compressibility profile then direct compression is employed. Consider using dry granulation if your ingredients have flowability problem that make them unsuitable for direct compression.
Particle Size
Ingredients with varying particle sizes are subjected to unblending or separation of particles if they are compressed using direct compression. Wet granulation is best if you are dealing with powders having variation in particle sizes or density.
Equipment
Wet and dry granulation generally requires the use of heavy duty equipments. Direct compression entails limited number of steps and fewer types of equipment.
Cost
Since direct compression employs less equipments hence it is fairly inexpensive but the excipients used in this methods cost more than those used in dry and wet granulation. Wet granulation employs multiple expensive instruments thus wet granulation requires initial high capital.
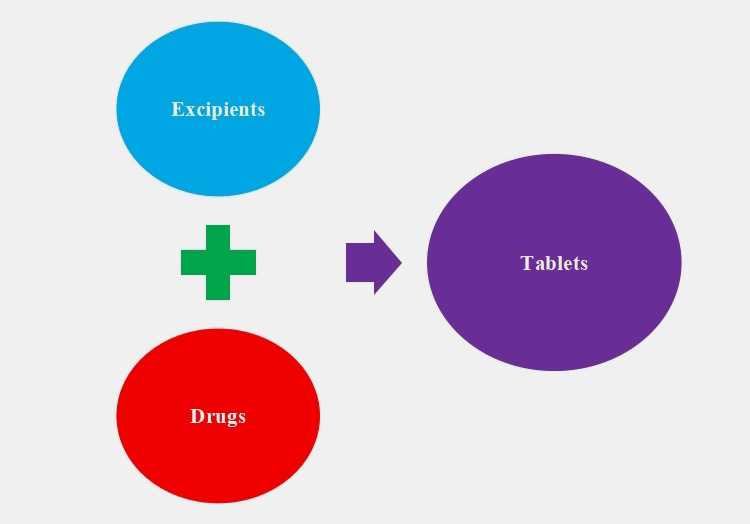
3.Major Raw Material and List of Excipients Used in the Manufacture of Pharmaceutical Tablets
Did you assume that tablets are made up of only drugs? Well in this case are wrong. Tablets also have excipients in them.
Excipients and raw materials are utilized in manufacturing of pharmaceutical tablets for making certain that tablets are of good quality.
These are used to increase bulkiness of drugs and impart desired physical attributes to APIs. List of some excipients and their function include:
| Binders | These excipients improve the plasticity, cohesiveness and strength of tablets. Binders are also employed for controlling the release of inner drug. |  |
| Lubricants | Lubrication materials avoid the sticking of tablets. By the addition of these ingredients in tablet mixture, friction between walls of die and tablets get reduced. Hence, tablets are easily removed from die without breaking. |  |
| Disintegrants | They are incorporated in tablet formulation for providing cohesive strength to ingredients. Moreover, these agents aid in fast disintegration of tablets by improving porosity of tablets. |  |
| Glidants | These are anticaking agents that enhance fluidity of powder ingredients and reduce the friction between particles. |  |
| Fillers | Fillers are also called bulking agents or diluents and are used for increasing the diameter of tablets if APIs are in small quantity. These are added for making tablets of desired weight. |  |
| Sweetening Agents | These are added for increasing palatability of tablets and also patient compliance. They give characteristic sweetness to bitter APIs. |  |
| Coloring Agents | Colorants improve the aesthetic characteristics of tablets by imparting various colors to them. They also give tablets their unique recognition profile. |  |
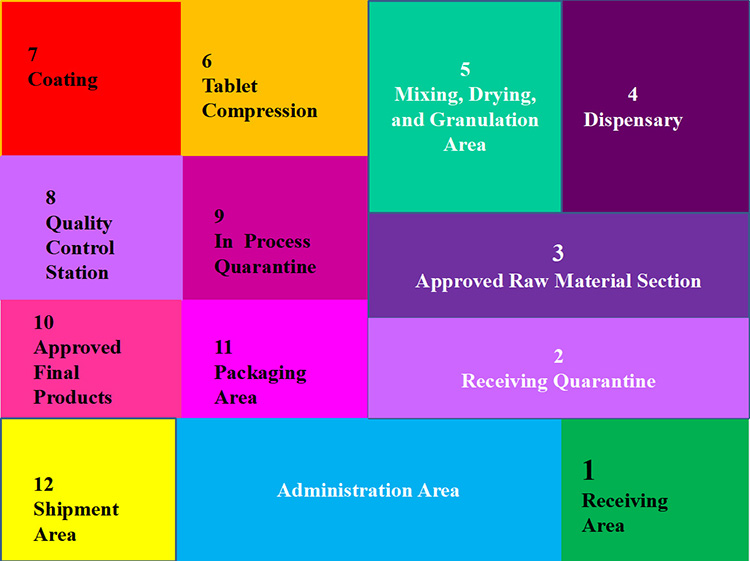
4.Area Layout Needed for Manufacturing Pharmaceutical Tablets
General area layout needed for formulating pharmaceutical tablets include:
Receiving Station for Raw Materials
In this section, raw material for instance pharmaceutical compounds and excipients are received. This is further divided into two sections:
Quarantine Section
This is a storage area where materials are kept until they are cleared for further processing.
Raw Material Approving Section
At this location, raw materials are examined and then given clearance for dispensing into production.
Dispensary
In dispensary section, raw materials are unwrapped from their original packages and are placed in intermediate bulk containers for moving in main processing area.
Processing Station
At processing station, raw materials are mixed together to form granules and then these are compacted into tablets. This is further subdivided into three areas:
- Blending, granulating, and drying station
- Tablet Press Station
- Coating Station
Quality Control Station
Quality testing and inspection processes such as testing hardness, uniformity in drug content, weight checking, and examination of tensile strength are done at quality control station.
Packaging Area
End products are packaged in various containers such as blister, strips, bottles, etc in the packaging area.
Shipment Station
The packaged tablets are finally moved to shipment area from where they are delivered to worldwide markets.
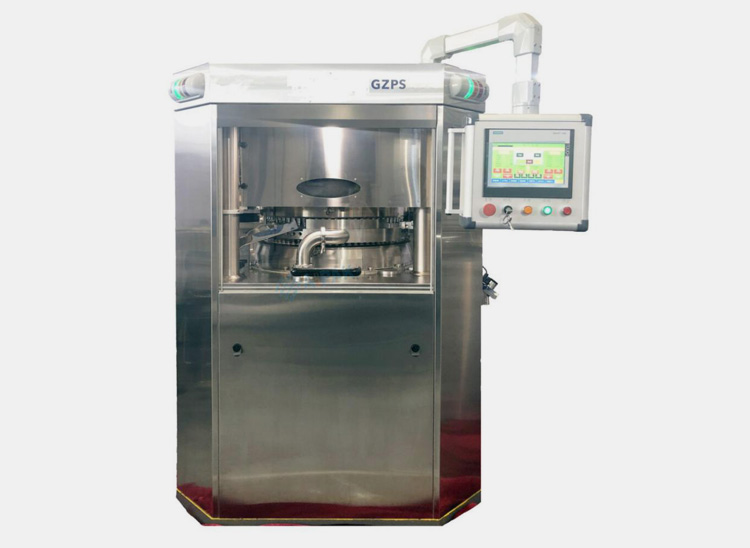
5.Need of Equipment Used in Pharmaceutical Tablets
There are various type of equipments used for formulating tablets some of which are discussed below for your information.
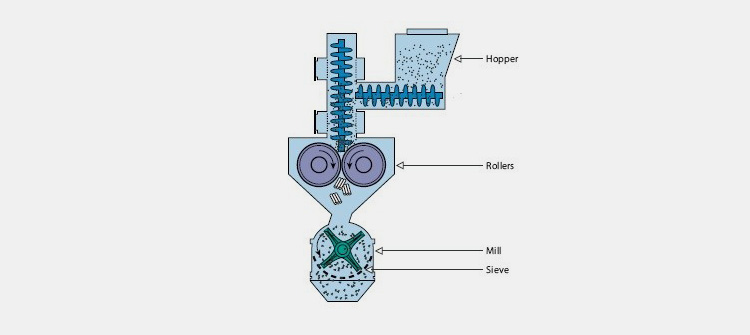
Mills
Various kinds of mills such as conical mills or ball mills are employed for reducing the size of ingredients particles.
Blenders/Mixers
Equipments like tumbling mixers or ribbon blenders are utilized for uniform mixing and blending of APIs and excipients.
Granulators
These machines are used at wet and dry granulation stage of tablet formulation for particle enlargement, massing, and agglomeration.
Dryers
Fluid bed dryer or spray dryers are exploited at drying step for evaporating excess moisture from the granules.
Tablet Press
These machines are used for purpose of compression of granules into tablets.
Coaters
Standard coating pan or perforated coating pan are utilized for improving aesthetic appearance of tablet by film coating them.
Tablet Counters
These are used while packing tablet for precise and accurate counting of tablets.
Packaging Machines
Blister packer or strip packers are employed for tablets packaging in between layer of paper, aluminum or plastic.
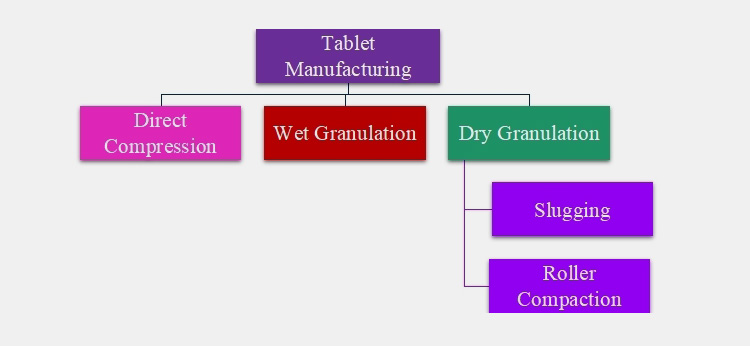
6.Different Techniques Used for Manufacturing Pharmaceutical Tablets
There are three main techniques that are involved manufacturing of tablets. These are
Now let’s discuss each technique one by one:
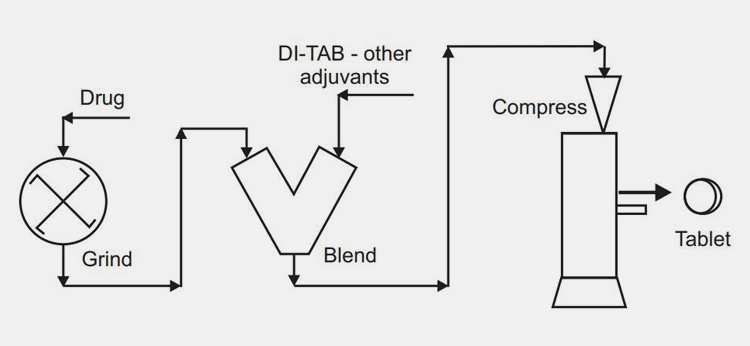
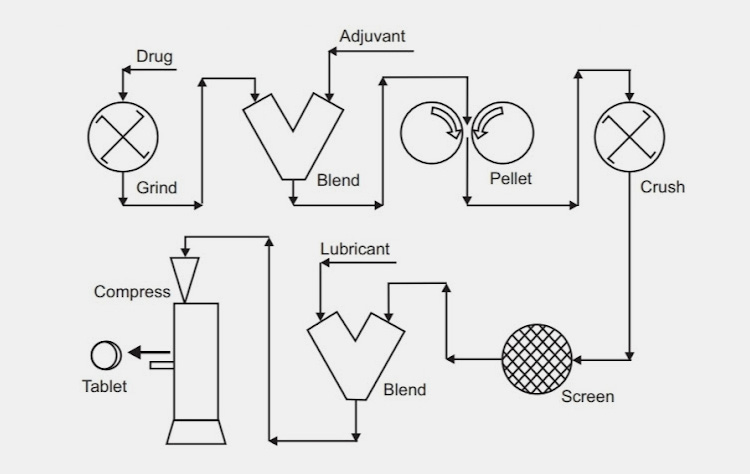
Direct Compression
This technique as the name indicates encompasses direct compaction of powdered active drug substances as well as excipients into tablet dosage. Does this involve change of physical state? The answer is no. It does not alter the physical state of powdered substance as there is no heating or drying involved.
Direct compression has principal importance as it is the least expensive approach for tablet formulation particularly when generic mediations are produced. Moreover, the problems associated with dry and wet granulation are not issue in this method.
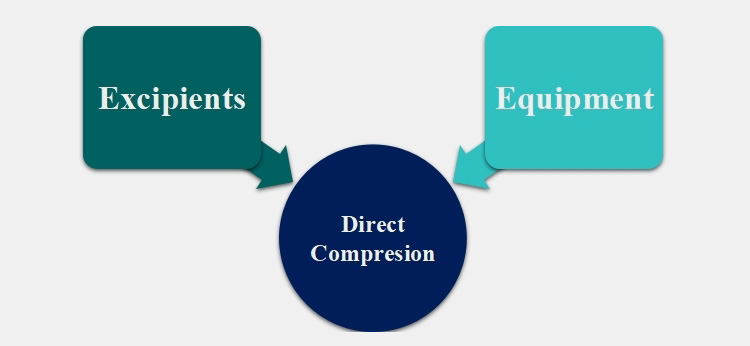
Two factors influence productivity of direct compression, which are:
7.Steps Involved in Direct Compression
Various steps entailed in direct compression are
- Size reduction of active substance and excipients materials
- Blending of milled powdered mixed, fillers, and disintegrants
- Pressing of blended slurry into tablets
Wet Granulation
If you assumed that wet granulation involve some kind of wetting technique well you are absolutely right. This is the method in which powdered raw materials are mixed together with binders or adhesives. This approach includes material size enlargement.
In wet granulation, powder particles are agglomerated together to create larger granules. Wet granulation has several advantages such as
8.Steps Involved in Wet Granulation
Some steps involved in wet granulation are:
- Weighing, size reduction, and mixing of drug ingredients with other excipients except binders
- Preparation of granulating fluid or binder
- Formation of wet mass by mixing binder with milled powders
- By using sieve of 6- to 12-mesh, the wet powder blend is screened to obtain wet granules.
- Afterwards, these pellets dried in oven at temperature of 55 °C.
- Granules are then passed through 14- to 20- mesh for getting granules of smaller size.
- These pellets are then mixed with lubricants and disintegrants
- Finally the pellets are compressed into tablets by tablet press machine.
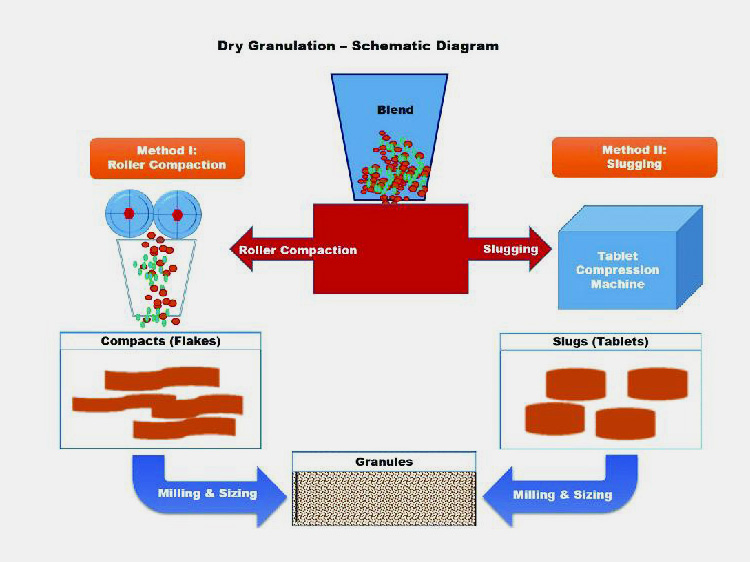
Dry Granulation
It is as the name indicates this is size enlargement without the use of granulating fluid. It is also called pre-compression or double compression usually employed for increasing the fluidity of powders that would otherwise be difficult to compress.
This process simply entails the massing of particles into larger compacts which are then broken down into granules for compression into tablets.
Some advantages of dry granulation are:
9.Steps Involved in Dry Granulation
Some basic stages involved in dry granulation are:
- Measuring and milling of powders (drugs and excipients)
- Blending of milled ingredients
- Compaction of blended ingredients in slugs or compacts
- Size reduction and screening of slugs
- Blending sieved compacts with lubricants and other excipients
- Compression of these granules into tablets
Classification of Dry Granulation
There are two categories of dry granulation which are:
Slugging
In slugging, powders are pressed via tablet press machine into large tablet having 1 inch diameter. Afterwards, these large pills are broken down into smaller granules either by hands or by using mills.
Lubricants are added next and finally mixed granules are again compressed into tablets.
Roller Compaction
You have guessed correctly, the roller compaction technique involve the use of rollers. First the drug ingredients and excipients are mixed and then compact using compression rollers which apply pressure of about 1-6 tons on powders.
These compacts are crushed using mills to create uniform sized granules. Lubricants are incorporated in these milled granules and eventually granules are condensed in tablets.
10.Primary Tablet Manufacturing Defects in Pharmaceutical Industry
Tablet manufacturing is not free from error. But do not worry these can be easily resolve by following some guidelines. Some defects in the pharmaceutical tablet manufacture and their solution are detailed below for your learning.
| Defects | Causes | Solutions |
| Lamination
The breakdown of tablets into two or more fragments |
Granules have oily components
Presence of air molecules in granules Fast decompression |
Incorporate absorbent when blending powders.
Switch die with tapered die. Lower turret speed and final pressure of compression. |
| Chipping
Small piece of tablets missing from edges. |
Inadequate tablet polishing
Decreased moisture content in granules The groove of tablet is damaged at the compression pressure area The corner of die is pushed inward. |
Polish or replace the punches.
Properly wet the granule mixture so their plasticity is increased. Replace the die cavity |
| Mottling
Uneven distribution of color (presence of light and dark area) in tablets |
Presence of color drug
Dye moves to either smaller or larger sized granules. |
Lower the drying temperature
Crush granules into small uniform sized granules. Add suitable coloring dye. |
| Capping
Full or partial disjointing of top and bottom parts of tablets |
Air is trapped inside granules particles
Small particles in the granules. Granules have insufficient quantity of binders. Increased turret velocity Concavity of punches |
Remove tiny particles with 100 or 200 size mesh
Increase the amount of binder in granule mixture. Lower the speed of turret Replace concave punches with flat ones. |
| Cracking
Small facture lines present on upper and lower surface of tablets |
Temperature during granulation is too low.
Granules are very dry The size of granules is extremely large |
Punch the tablets at room temperature
Decrease the size of granules by screening. Wet the granules by adding suitable binder. |
| Binding
The adhering, seizing or tearing of tablets in die cavity |
Inadequate amount of lubricant
Temperature of granules is too high. Granules material is very coarse and enter in the die |
Use effective lubricant or increase the quantity of lubricant
Lower the temperature Reduce the size of granules to decrease their abrasiveness |
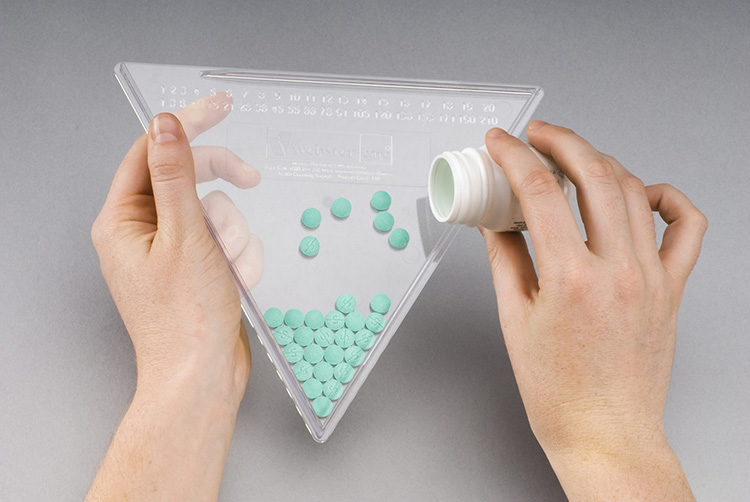
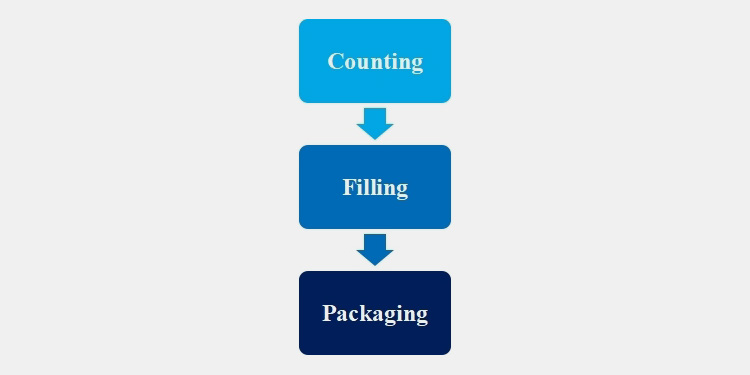
11.Final Step: Counting, Filling, & Packaging of Pharmaceutical Tablets
In final step of pharmaceutical tablet manufacturing tablets are counted, filled, and packaged.
Counting
The counting step is performed for accurate and precise measuring of tablets quantity. Intelligent and high-grade sensors are used for counting tablets. The number of tablets translates into desired dose of drugs which ultimately determines the accuracy of therapeutic effect.
This is the way of cutting down error in the packaging process and also tells about the production rate of pharmaceutical line.
Filling
After counting, tablets are filled in bottles by filling nozzles. These nozzles are controlled through PLC unit and drop tablets one at the time in the bottles.
Packaging
There are various ways to package tablets and two most popular are blister and strip packs.
Blister Packs
The aluminum or plastic film polymers are heated and shaped into pockets or cavity. These pockets are then filled with tablets and covered with aluminum or paper layer.
Strip Packs
In strip packaging, polymers sheets are heated and then tablets are dropped inside these heated films. Tablets are hermetically sealed and enclosed between two layers of film.
Conclusion
The latest processing and manufacturing technologies have improved the rate of tablet production. Intense research oriented planning is involved at each and every stage for instance mixing, granulation, compression, counting and packaging of tablet manufacture. Our short review “Stages Involved in Manufacturing of Pharmaceutical Tablets” detailed various state-of-the-art processes involved in tablet formulation. If you are keen to learn about cost-effective and high-grade pharmaceutical tablet production then you can contact our knowledgeable technologists who are ready to guide you anytime and anywhere.
Don't forget to share this post!
Drier Machine Related Products
Drier Machine Related Videos
CONTACT US
Tell us your raw material and project budget to get quotations within 24 hours.
WhatsApp Us: +86 181 6426 8586
Want the best price & newest pharmaceutical machinery buying guide,tips and trends sent straightly to your box?Sign up for Aipak’s monthly newsletter,we’re free for your consultation and Offer you the most suitable solutions!
The Buyer's Guide
- Capsule Filling Buyer's Guide
- Blister Packaging Buyer's Guide
- Tablet Counting Buyer's Guide
- Tube Filling Buyer's Guide
- Cartoning Buyer's Guide
- Gummy Making Buyer's Guide
- CO2 Extraction Buyer's Guide
- Empty Capsules Buyer's Guide
- Suppository Filling Buyer's Guide
- Tablet Coating Buyer's Guide
- Tablet Press Buyer's Guide
- Softgel Encapsulation Buyer's Guide
Most Popular
- 7 Importance Of Pharmaceutical Packaging In Different Applications You Must Know
- 6 Advantages You Must Know About Tablet Counting Machine
- 8 Advantages of Blister Packaging You Must Know
- 6 Critical Applications of Automatic Capsule Filling Machine
- 6 Stations You must Know to Improve the Filling Quality of Automatic Capsule Filling Machine