Pharmaceutical Water And Pharmaceutical Liquid: A Seed For Pharmaceutical Manufcaturing
The pharmaceutical preparations use a sterile water as a prime ingredient. In general, this is a highly specialized area that needs critical control as overall production outcomes depend upon it. Do you think pharmaceutical water and pharmaceutical liquid as the same entity?
In this article we are highlighting diversified aspects to consider before and after pharmaceutical formulation.
Table of Contents
I.IS PHARMACEUTICAL WATER AND PHARMACEUTICAL LIQUID SAME?
If you consider pharmaceutical liquid or water as same, then you might be wrong at some extent because technically, they are not!
Let me tell you how:
Pharmaceutical Water
In pharmaceutics, water is more complicated than you think.
The United State PHARMACOPEIA has designated water as an official monograph with certain specifications. According to this, pharmaceutical water can be an excipient in parenteral and non-parental preparations.
Pharmaceutical water is a fundamental utility commonly used in the pharma industry. For instance, during the synthesis of elements, extraction, purification, spectroscopic analysis, cell culturing, volume make-up, cleaning tools & equipment, rinsing, granulation, etc.
Pharmaceutical Liquid
You all know the term ‘Liquid’ is generally intended for a substance that flows free, like water, oils, etc. The pharmaceutical liquid is a special category used for the formulation of therapeutic medicines. It has own formulation identity that is confined to APIs ultimately supporting clinical response. Simply, this form is composed of one or more pharmaceutically active ingredients. Not only this, but it is also the major commodity commonly utilized in the pharmaceutical industry as an excipient, final reconstitution, or solubilizing the suspended particles.
They are of great demand as it gives maximum therapeutic response to the target population who face difficulties in swallowing solid dosage form or seeking a rapid physiological response. In addition, pharmaceutical liquids are free from unwanted microorganisms and also available commercially with specified classifications. It is mandatory to conform to standardized purity and sterility tests. They have wide applications such as injectables, injected in body cavities, surgical regions (dialysates), etc., That’s why you must consider it as the most critical factor behind any successful formulation.
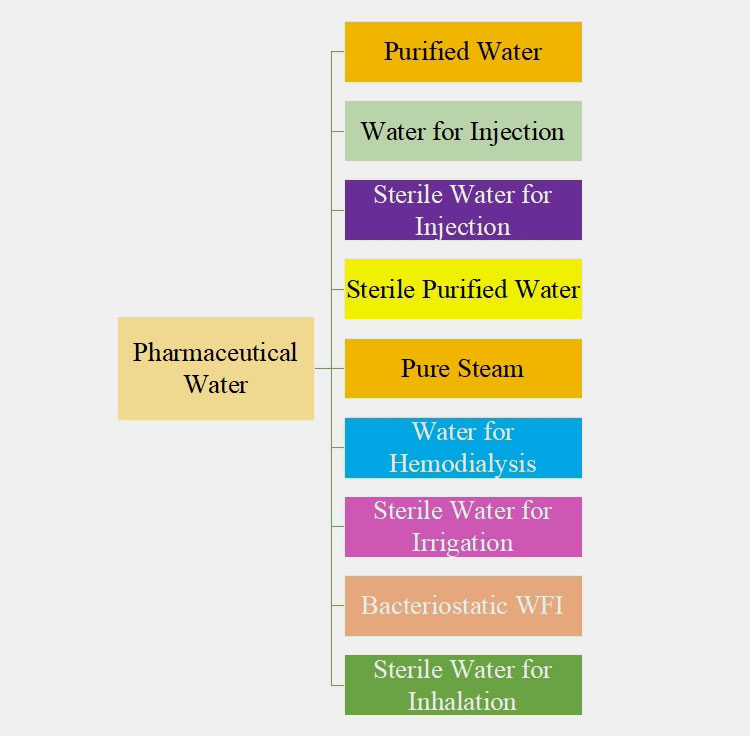
Ⅱ.UNDERSTANDING THE CATEGORIES OF PHARMACEUTICAL WATER
The following classification will help to navigate the major complexities in its types and give you a better understanding.
Purified Water
This is commonly used in the non-sterile section such as cleaning tools, contact equipment, and material used for preparing injections, and infusions. Purified water must be validated to sustain the quality of the production. Somehow, this water is susceptible to microbial growth or producing undesirable effects. That’s why frequent monitoring and sanitization are recommended.
PREPARATION
- It is prepared by the following techniques:
- Deionization
- Reverse Osmosis (RO)
- Filtration
Water for Injection
This category of pharmaceutical water is used as an excipient for highly sterile formulation. It is well-controlled preparation used for pharmaceutical applications including sterile and nonsterile usage.
PREPARATION
- It is prepared by the following methods:
- RO
- Distillation
- Membrane Method
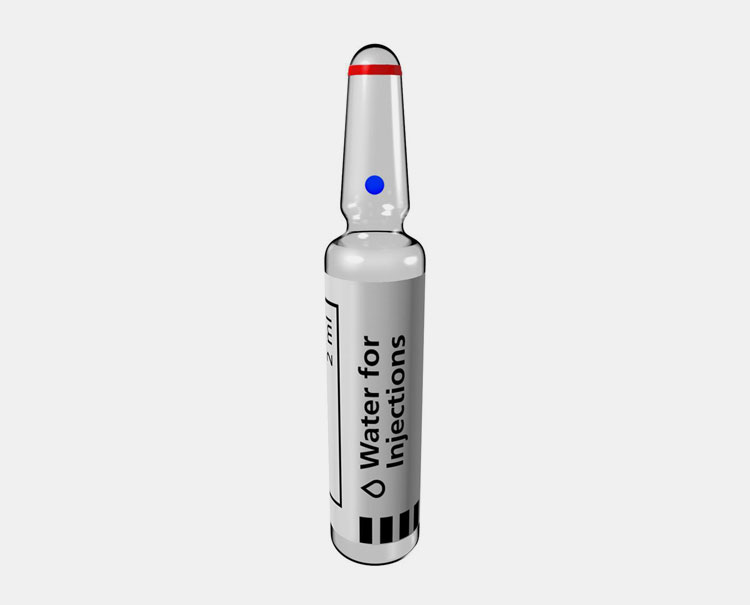
Sterile Water for Injection
This water is specifically intended for intravenous administration. The sterile WFI is packed in single unit vials that typically available in type I glass up to 1000ml.
PREPARATION
It is prepared by distillation of WFI
Sterile Purified Water
This is used for analytical applications in the pharmaceutical industry. This required validation where the chance of microbial growth is well-controlled.
PREPARATION
The water is prepared by reverse osmosis.
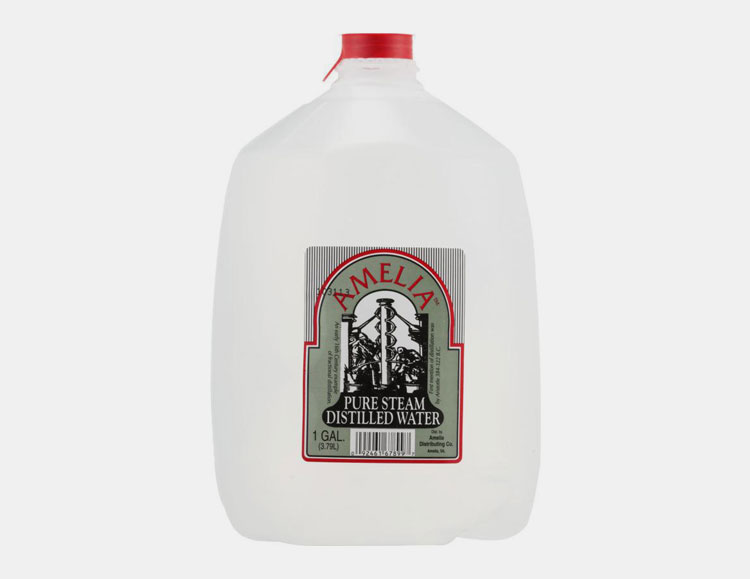
Pure Steam
As its name shows, it is utilized in the pharmaceutical industry for sterilization and cleaning of equipment such as containers, or other contact parts.
PREPARATION
This water is produced by already pre-treated water that is analogous to WFI.
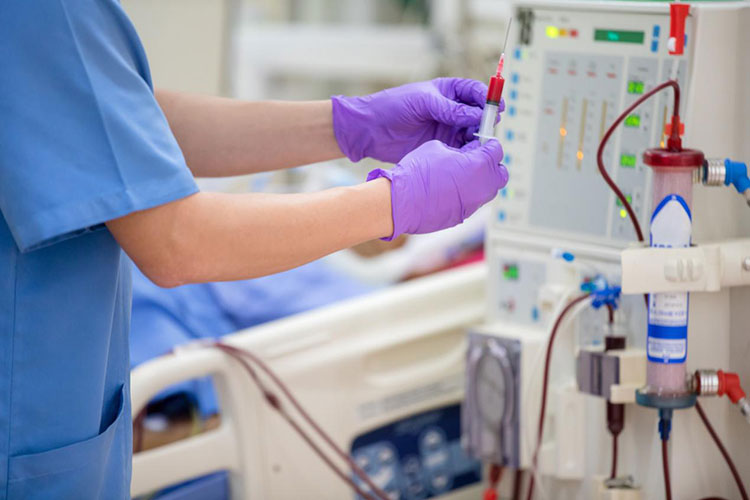
Water for Hemodialysis
This form of pharmaceutical water is specially used for hemodialysis procedures such as dilution of hemodialysis solution. This is packed in a bulk volume with no risk of microbial or foreign particles in it.
PREPARATION
Reverse Osmosis
Sterile Water for Irrigation
This form of water is also considered critically sterile. This is commonly delivered in large packaging types (drips) recommended where a large quantity of water is suggested such as more than 1litre. This is mainly used for surgery procedures and bathing body tissues.
PREPARATION
From WFI
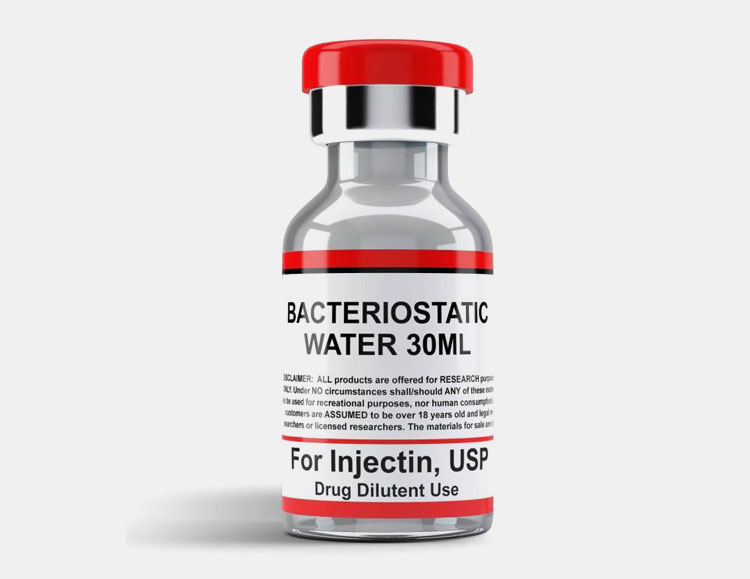
Bacteriostatic WFI
In this form of water, the preservative is mixed to combat microbial growth. This is generally used for the preparation of pharmaceutical liquid dosage forms as a diluent. In a single dose vial, it has volume up to 5ml; for multi-dose vial, a volume limit is up to 30ml.
PREPARATION
Sterile WFI.
Sterile Water for Inhalation
This form of water is used in the reconstitution of inhalators and inhalation solutions. The specification of bacterial control is lesser that’s why it is not used for parenteral administration.
PREPARATION
Sterile WFI
III.UNDERSTANDING THE CATEGORIES OF LIQUID DOSAGE FORMS
Pharmaceutical liquid dosage form is having an extensive category; more research and clinical studies growing this field increasingly. Let’s have a look!
Initially, you can start with its basic types such as:
MONOPHASIC FORM is a type of pharmaceutical liquid dosage form consisting of two or more constituents dissolved in a solution. These are intended for oral and other particular uses.
ORAL USE
| Mixtures are aqueous formulation consisting of more than one medicinal agent dissolved or suspended as insoluble solids in a liquid vehicle. Generally used for cough, diarrhea, and constipation drugs. |
|
| LINCTUS’S are thick liquid formulation prepared with one or more medicinal agent, rich in sucrose or other sugars. They are majorly used as cough relief medications, demulcent and expectorants. |
|
| ELIXIRS are hydro alcoholic, sweetened, clear, aqueous preparations which may or may not be medicated. They are administered orally. |
|
| SYRUPS are aqueous solutions containing about 66.7% w/w sugar content, which might also be either medicated or non-medicated. |
|
| DRAUGHTS are an ancient pharmaceutical dosage form which contained large volumes of drug to be taken in one or two doses. |
|
PARTICULAR USE
| NASAL DROPS are administered via nostrils. It is used to relive nasal congestions, allergies, and respiratory problems. |
|
| EAR DROPS are instilled directly into ear canal with dropper. It is used for cleaning, treating infections and relieving the earaches. |
|
| EYE DROPS are extremely sterile directly used to administered into ocular route to for treating allergies, infections, and protection. |
|
| MOUTHWASHES are monophasic solutions that deodorizes your mouth via exerting antiseptic effects in your oral cavity. |
|
| AEROSOLS are monophasic solvent preparation in the gaseous form. Its spray is used for asthmatic problems and migraine. |
|
| GARGLES are aqueous hydro-alcoholic solutions intended to be used for throat infections. After dilution with warm water, brought in contact with throat’s mucus lining and after few seconds of gargling to be spit out. |
|
EXTERNAL USE
| Lotions: are monophasic liquid preparations intended for external use, supposed to be rubbed onto the skin without applying friction. Lotions are indicated as topical drugs as anti-biotic, anti-microbial, anti-septic, corticosteroids, and protective agents. |
|
| Liniments: are liquid dosage forms intended to be rubbed on the skin with friction, as a pain reliever or to relief stiffness usually for muscle pains, arthritis. |
|
PARENTERAL USE
PARENTERAL LIQUID DOSAGE FORMS are germ-free solutions or suspension of drug in an aqueous or oily vehicle administered directly into the veins, muscles or under the skin. Parenteral dosage form applies to any drug that is not supposed to be given by alimentary canal route. For instance:
|
|
BIPHASIC FORM: are liquid dosage forms which constitutes two phases, which contains one solid dispersed phase and the aqueous continuous phase. They have two types: Emulsion and Suspension. Their intended use is often parenteral, oral and also external.
| EMULSIONS are a type of biphasic liquid dosage forms containing two liquids which are not miscible, one of which is distributed as globules within the other. It further can be classified into two types, Oil in Water emulsions and Water in Oil emulsions. |
|
| SUSPENSIONS: are also a type of biphasic liquid dosage forms which can be defined as fine distribution of solid particles throughout the aqueous medium. They are administered orally, parenterally, intra-nasal, applied as topical preparation, etc. |
|
IV.PHARMACEUTICAL WATER VS PHARMACEUTICAL LIQUID
| Pharmaceutical Water | Pharmaceutical Liquid |
| It is commonly used as a vehicle for the preparation of pharmaceutical dosage form. | This is a mixture of Active Pharmaceutical Ingredient (APIs) and excipients dissolved in the solvent. |
| Pharmaceutical water is obtained by various methods such as distillation, reverse osmosis, deionization, filtration, etc., | It is prepared by mixing medicament in an aqueous vehicle. |
| Pharmaceutical water is inert in nature | The pharmaceutical liquid is reactive in nature. |
| You can’t call it a medicine | You can call it a medicine due to its therapeutic response. |
Conclusion
With the above discussion about pharmaceutical water and pharmaceutical liquid, it is crucial to understand how each factor can impact your product. We consider ‘Water’ as a ‘HERO’ behind the strong hierarchy of Liquid Dosage Form.What do you think?Still, have a Question? We are Here to Assist!Just Quote a message, Our Guidance Team will contact you shortly.
Don't forget to share this post!
Vial Filling Machine Related Posts
Vial Filling Machine Related Products
Vial Filling Machine Related Videos
CONTACT US
Tell us your raw material and project budget to get quotations within 24 hours.
WhatsApp Us: +86 181 6426 8586
Want the best price & newest pharmaceutical machinery buying guide,tips and trends sent straightly to your box?Sign up for Aipak’s monthly newsletter,we’re free for your consultation and Offer you the most suitable solutions!
The Buyer's Guide
- Capsule Filling Buyer's Guide
- Blister Packaging Buyer's Guide
- Tablet Counting Buyer's Guide
- Tube Filling Buyer's Guide
- Cartoning Buyer's Guide
- Gummy Making Buyer's Guide
- CO2 Extraction Buyer's Guide
- Empty Capsules Buyer's Guide
- Suppository Filling Buyer's Guide
- Tablet Coating Buyer's Guide
- Tablet Press Buyer's Guide
- Softgel Encapsulation Buyer's Guide
Most Popular
- 7 Importance Of Pharmaceutical Packaging In Different Applications You Must Know
- 6 Advantages You Must Know About Tablet Counting Machine
- 8 Advantages of Blister Packaging You Must Know
- 6 Critical Applications of Automatic Capsule Filling Machine
- 6 Stations You must Know to Improve the Filling Quality of Automatic Capsule Filling Machine