Pharmaceutical Powder Handling: A Guide to Flowability & Precision Filling
Having in-depth knowledge of managing pharmaceutical powder behavior can help you in successful formulation, effective product designing, and high-quality processing. This is very important in the pharma sector as a major portion of active pharmaceutical ingredients (APIs) are composed of powders such as tablets, capsules, suspensions, inhalation, etc. In this informative review on Pharmaceutical Powder, we will explore the basic science, benefits, and techniques of powder characterization. Read On!
| Powder Trait | Production Challenge | AIPAK Recommended Solution |
| Poor Flowability | Bridging and clogging in hoppers | Auger Filler with specialized vibration motor |
| High Dust Content | Cross-contamination & safety risks | Vacuum Conveyor & integrated dust collection |
| Heat Sensitivity | Material melting during high-speed mixing | Jacketed Bin Blender with water-cooling system |
| Fine Micronized API | Inconsistent dosing & weight errors | Servo-driven Powder Filling Machine |
1.What are pharmaceutical powders?
Powders have been in use for medicinal purposes since ancient times. It is the type of solid dosage comprising of fine particles. Pharmaceutical powders are dry substances used for dispensing drugs or chemical substances either internally or externally.
Even if, now a days, pharmaceutical powders are not extensively used in medication form, these form the basis of other oral solid medicine such as tablets or capsules as well as paste or ointments. The particles in powders have a size in the range of 10nm to 1000 µm.
2.Why is powder so important to the pharmaceutical industry?
The powders have a huge importance in the pharmaceutical industry due to their use as raw materials. More than 60% of the medicinal sale is reported because of powdered drug formulations either in tablet, capsule, or inhalation powder.
Powders offer tremendous benefits to the pharmaceutical industry due to their ease of preparation and compounding.
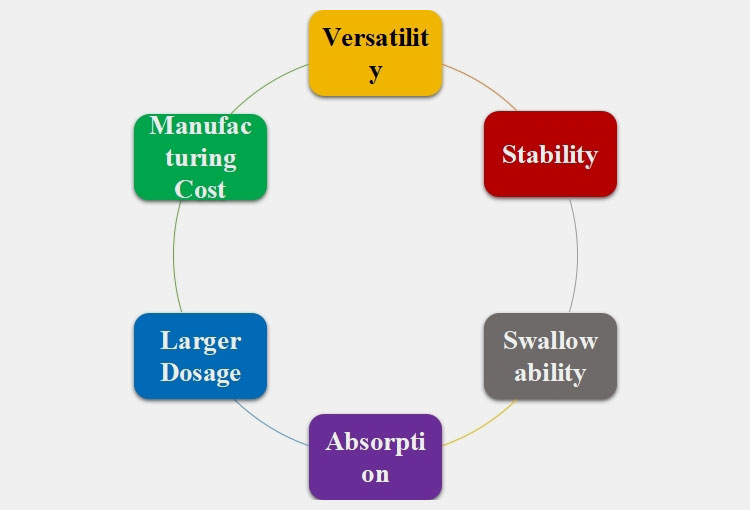
Versatility
Powders can be composed of multiple ingredients and practitioners easily prescribed powder dosages for patients. Moreover, doctors can deviate from recommended dosage as per the needs of patients.
Stability
These dosage forms are stable and do not chemically interact with other ingredients consequently lasting longer than liquids about 2 to 3 years.
Swallowability
Powders have preferred the choice of medication, especially for infants and young children to tablets or capsules. These can be mixed with water, honey or applesauce for better palatability.
Absorption
The disintegration of pharmaceutical powders in the stomach is very rapid thus providing a large surface area for better absorption and preventing irritation of the gastrointestinal tract.
Larger Dosage
It is possible to take the larger dosage of 1 to 5 grams with powders. It is sometimes problematic to formulate tablets of a much larger dose.
Manufacturing Cost
Manufacturing pharmaceutical powders are quite economic due to the simple and undemanding production steps of formulating tablets. This makes powder fairly inexpensive to purchase.
3.Principle Applications of Pharmaceutical Powders
There are two principle applications of pharmaceutical powders:
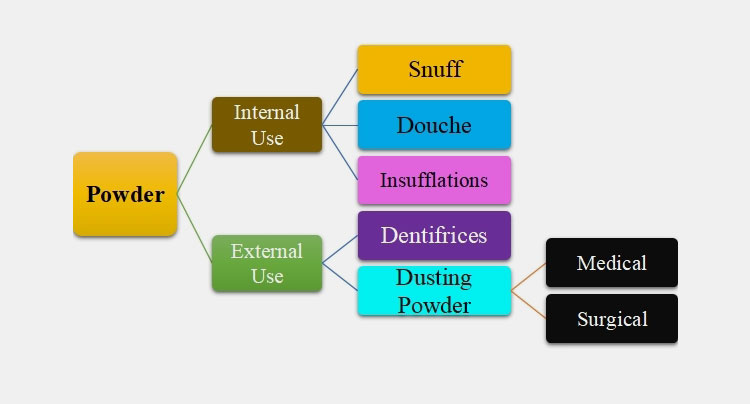
Ⅰ.INTERNAL USE
These medicated powders are dry, loose preparation having diversity in particle fineness. These are either consumed orally such as antacids, and laxatives or are inhaled via air for instance snuff. Some types of powders for internal use are:
Snuff
These are fine particle dosages administered by nostrils for bronchodilator and decongestion effect.
Douche Powder
These types of powders are used for nasal, ophthalmic, and vaginal irrigation cleansing. This antiseptic action reduces the growth of microbes.
Insufflations
These powders are made of fine particles that are applied to body parts such as the nose, gums, throats, and ears by the means of a device called insufflators. This device when pushed dispenses air current containing powders in gaseous form to the required area.
Ⅱ.EXTERNAL USE
These are non-potent powders and are externally used for localized treatment effects. These are not used for systemic administration. These are used as antibacterial agents or are used for decreasing skin irritation.
Dusting powders
These are external lubricating, antiseptic, protective agents that act on localized areas to prevent irritation from humidity, chemicals, as well as friction. These powders also aid in protecting skin from grazing or bruising. There are two kinds of dusting powders
Medical Dusting powders-spread over intact skin for treating infection
Surgical Dusting powders-smeared into deep skin tissues such as open wounds, burns, and umbilical tissues.
Dentifrices
These are the powder smeared on the tooth surface via brush for cleansing action. They are composed of abrasive agents like sodium carbonate, detergents, and sweeteners.
4.Classification of Pharmaceutical Powders
There are various ways to classify the powders such as:
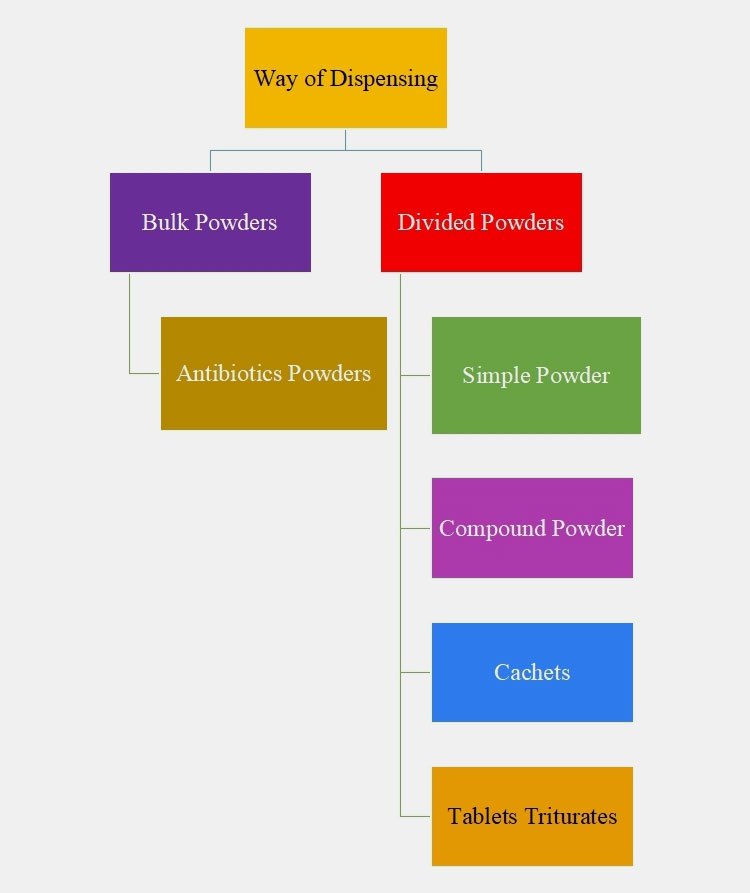
Ⅰ.Based on the Way of Dispensing
There are two main types of powders based on the way of dispensing:
Bulk Powders
These are pharmaceutical powders comprising non-potent substances dispense in bulk quantities. These are packaged in air-tight containers for instance wide-necked plastic or glass bottles. These powders contain several doses of medications.
These are not used for drugs that are administered in small dosages but drugs in bulk powder are well-suited if they have a large dosage.
Antibiotics Powder
These are the pharmaceutical powders containing one or more antibiotics for treating bacterial infections, especially in pediatric patients. These are often mixed with water for consumption.
Divided Powders
They are mixed by geometric dilution and are dispensed usually as single doses. Divided powders are enclosed or wrapped inside the paper, cellophane, and metallic foil packages ensuring great benefits.
Some types of divided powders are:
Simple Powders
Simple powders contain only one active ingredient in finely divided form and are packaged in individual doses.
Compound Powders
They are formed by mixing two or more two active ingredients and other excipients. These powders are divided into smaller doses and then wrapped.
Cachets
They are called wafer capsules and are comprised of powders encapsulated in a shell that is manufactured from rice flour. Cachets are best for delivering large doses of bitter-tasting drugs.
Tablets Triturate
They are formed by mixing the potent drug with sugar like lactose or sucrose or with another diluent that acts as a base.
Ⅱ.Based on Uniqueness
There are two kinds of powder based on uniqueness.
Eutectic Mixtures
They are composed of ingredients having a low melting point. This substance often liquefies upon mixing because of its below-normal melting temperature. This problem is avoided by adding absorbent to the mixture.
Effervescent Powders
Effervescent powders react with water and release effervescent-containing carbon dioxide. They are formed by compounding carbonate salts and organic acids e-g citric acid.
5.Why are powders difficult to characterize?
Powder characterization is of paramount importance in the pharmaceutical industry since particle geometry impacts several processes like blending, dosing, distribution, and bioavailability.
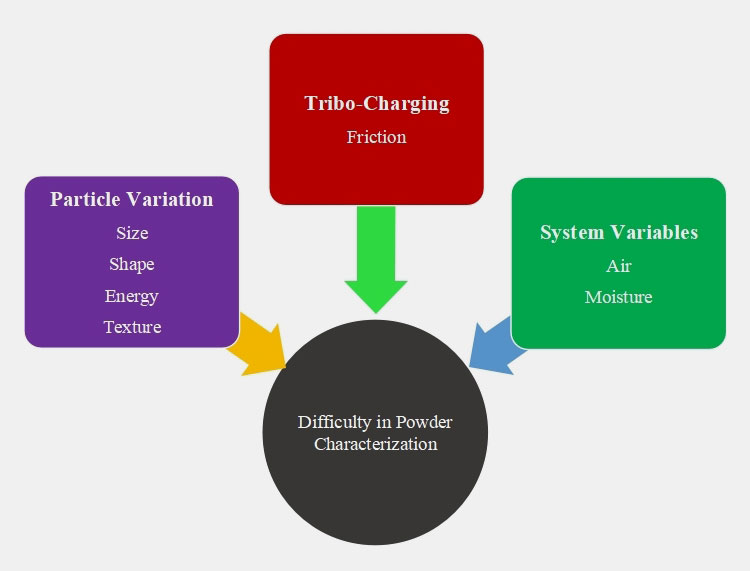
Powders are difficult to characterize owing to a number of factors like:
Ⅰ.Particle Variation
Differences in the size, shape, free energy, as well as particle texture make the characterization process of powders a bit complicated. The distribution of particles in assembly is another factor that causes issues in powder flow.
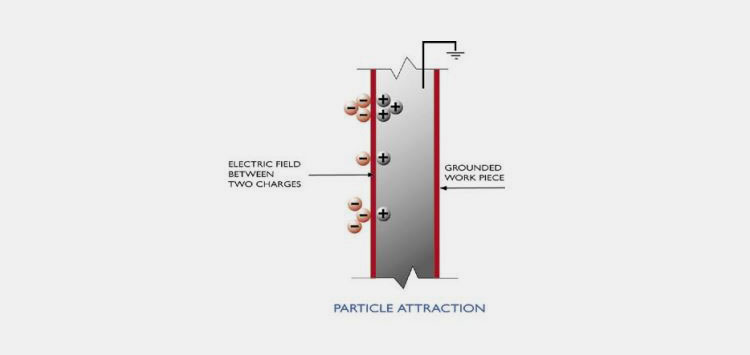
Ⅱ.Tribo-Charging
It is a phenomenon of charge transfer from frictional contact between particles. This can cause particle lumping and adherence to container walls. This results in the poor characterization of powders.
Ⅲ.System Variables
System variables such as air presence between particles and level of moisture (either from surrounding or from upstream processing) present within powder particles and their surface impact the behaviour of powders consequently causing problems in their handling.
AIPAK Expert Insight: Why "Angle of Repose" Matters for Your ROI "In our testing lab, we often see clients struggle with inconsistent bottle weights. The culprit is usually the Angle of Repose. If your powder has poor flow, a gravity-fed system will fail. For these materials, AIPAK recommends an Auger Filling system with a specialized agitator. Understanding the characterization of your API isn't just science—it's the key to selecting a machine that maintains ±1% dosing accuracy."
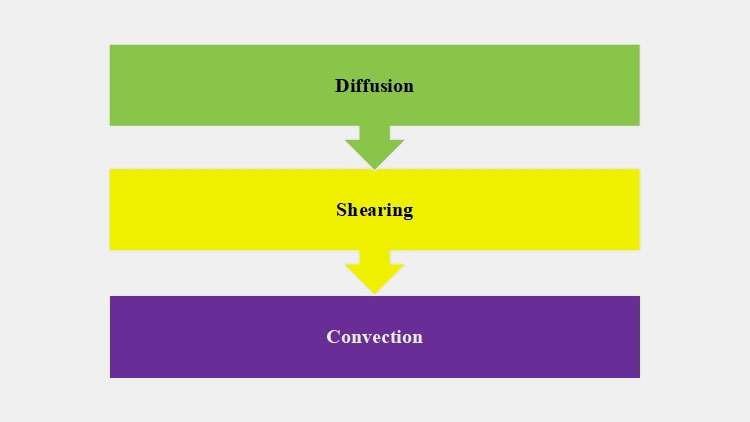
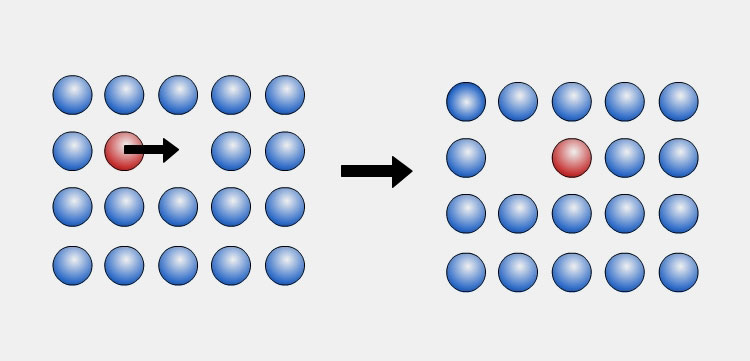
6.Mechanism Involved in Pharmaceutical Powders Mixing
There are kind different mechanisms involved in the mixing of pharmaceutical powders. These mechanisms are related to various particles' motions. Such as
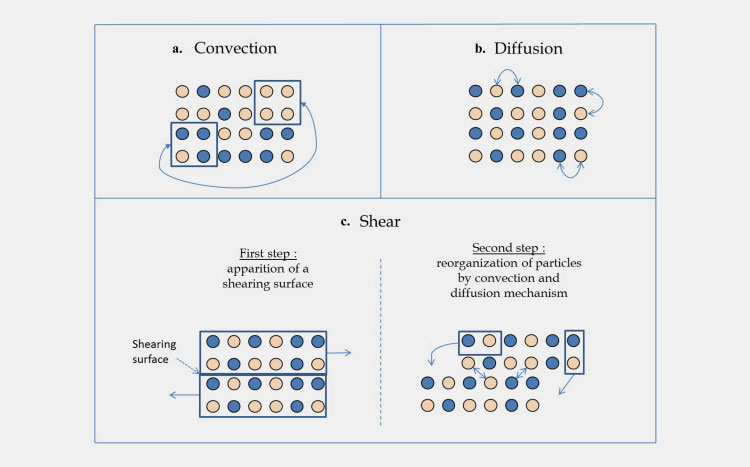
Diffusion
It is the random movement of particles. The volume of powders is increased in mixers due to shearing and convective forces. Consequently, the intra-particles space is escalated which initiates superior mixing of particles with each other.
Diffusion usually aids in microscopic mixing but the rate of mixing is less when compared with shearing and convection.
Shearing
The movement of one particle layer compared to the other layer is called shearing. This mixing is the result of various speeds of layers in the rotary vessel and compaction force.
Shearing is not due to the movement of individual powder particles but owing to the movement of layers in a powder bed.
It is microscopic mixing and the rate of shearing mixing is intermediate.
Convection
This is a macroscopic type of mixing generally performed by the movement of particles as a group. Convective mixing is primarily influenced by a number of factors like system design including paddles and baffles.
The mixing speed is high however more time is required for uniform and thorough mixing as particles present in the group do not mix effectively.
7.Compounding of Pharmaceutical Powders
Compounding of powders is important for dosage flexibility and chemical stability of drugs.
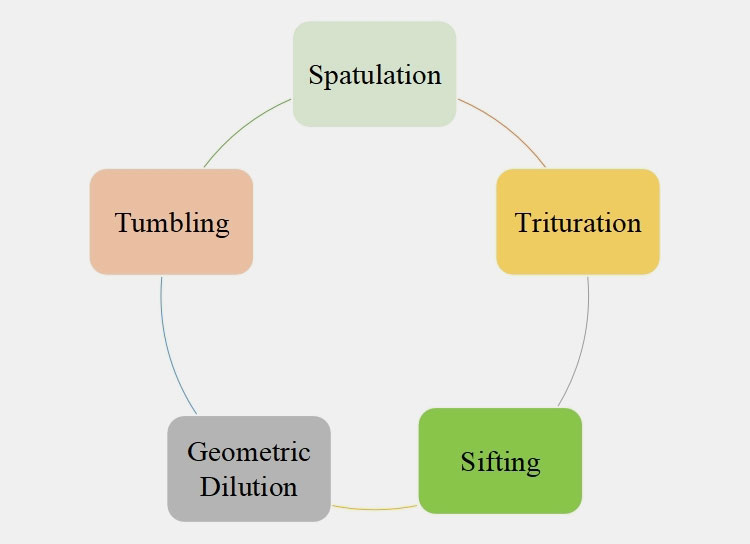
Some techniques for compounding powders are:
Spatulation
This technique involves the use of a spatula for mixing small quantities of powders on the paper sheet or porcelain tile. Spatulation is useful in compounding powders that form a eutectic mixture when placed in close proximity to each other for an extended period.
Trituration
It is the mixing of powder by size reduction in mortar and pestle. This pulverization technique creates fine particles of powders for superior therapeutic effect. Glass and wedgewood mortars are used for crushing powders.
Sifting
Sifting uses sieves or sifters for mixing various pharmaceutical powders. This method is suitable for removing large powder lumps. This is usually used for processing fluffy lightweight pharmaceutical powders.
Geometric Dilution
It is an efficient process of compounding a small amount of potent powder with a large quantity of diluent powder. First, equal quantities of potent drug and diluent are mixed. This resultant mixture is compounded with an equal quantity of diluent. This process is repeated many times till all the diluent is used.
Tumbling
The powders are mixed by agitating motion of a closed vessel in tumbling. The powders varying in densities are mixed by this technique. This technique is suitable for large-scale uniform compounding of powders in a short time.
8.Troubleshooting Common Pharmaceutical Powder Handling Issues
In a high-stakes pharmaceutical environment, even minor powder characterization issues can lead to significant production downtime. At AIPAK, we help our clients overcome these three common engineering hurdles:
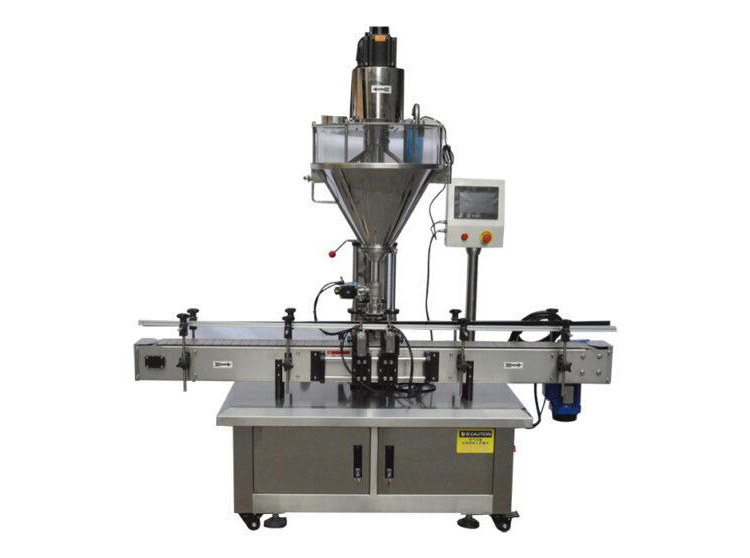
Q1: How to prevent "Arching" or "Bridging" in the hopper?
-
The Problem: Fine or cohesive powders often form a stable "arch" over the discharge outlet, stopping the flow entirely.
-
AIPAK Solution: We recommend an Auger Filling system equipped with a specialized vertical agitator (stirrer). By continuously breaking the cohesive bonds of the powder, the agitator ensures a steady gravitational feed into the screw, maintaining dosing accuracy.
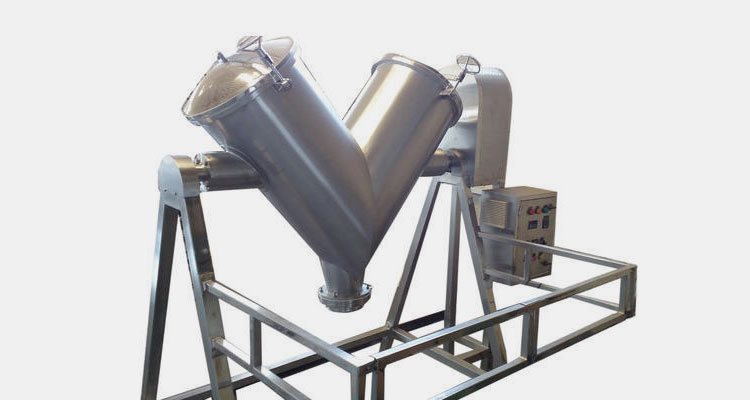
Q2: How to ensure uniform blending of powders with different densities?
-
The Problem: When mixing active pharmaceutical ingredients (APIs) with excipients of varying bulk densities, traditional blenders often face "segregation" issues.
-
AIPAK Solution: For high-potency or sensitive formulas, we recommend the 3D Bin Mixer. Unlike standard 2D rotation, the 3D multi-directional movement ensures that particles of different weights and sizes are interlaced at a molecular level, achieving a CV (Coefficient of Variation) of less than 5%.
Q3: How to handle hazardous or potent powders (OEB 4/5)?
-
The Problem: Handling toxic or highly potent powders requires strict containment to protect operators and prevent cross-contamination.
-
AIPAK Solution: We implement closed-loop Vacuum Conveying systems integrated with HEPA filtration. This ensures that powders are transferred from the source to the filling machine in a completely sealed environment, meeting OEB 4/5 containment standards without compromising production speed.
CONCLUSION
Pharmaceutical powders comprising fine particles are one of the oldest medication forms. These are fairly inexpensive to manufacture and their dose can be varied according to individuals' needs. Hope you have learned about various classification ways of powders, their benefits, and their usage by reading this guide. Feel free to contact us for additional queries related to medicinal powders.
Don't forget to share this post!
Powder Filling Machine Related Posts
Powder Filling Machine Related Products
Powder Filling Machine Related Videos
CONTACT US
Tell us your raw material and project budget to get quotations within 24 hours.
WhatsApp Us: +86 156 0710 8630
Want the best price & newest pharmaceutical machinery buying guide,tips and trends sent straightly to your box?Sign up for Aipak’s monthly newsletter,we’re free for your consultation and Offer you the most suitable solutions!
The Buyer's Guide
- Capsule Filling Buyer's Guide
- Blister Packaging Buyer's Guide
- Tablet Counting Buyer's Guide
- Tube Filling Buyer's Guide
- Cartoning Buyer's Guide
- Gummy Making Buyer's Guide
- CO2 Extraction Buyer's Guide
- Empty Capsules Buyer's Guide
- Suppository Filling Buyer's Guide
- Tablet Coating Buyer's Guide
- Tablet Press Buyer's Guide
- Softgel Encapsulation Buyer's Guide
Most Popular
- 7 Importance Of Pharmaceutical Packaging In Different Applications You Must Know
- 6 Advantages You Must Know About Tablet Counting Machine
- 8 Advantages of Blister Packaging You Must Know
- 6 Critical Applications of Automatic Capsule Filling Machine
- 6 Stations You must Know to Improve the Filling Quality of Automatic Capsule Filling Machine
Tell us your material or budget,we'll reply you ASAP within 24 hours