Pharmaceutical Granultion Understanding A Big Picture
Granulation is a commonly used term in the pharmaceutical industry that refers to the formation of grains or granules ranging in size from 0.2-0.4mm.
The granulation process plays a vital role in the production of solid dosage form both capsules and tablets. It is the procedure in which particles are enlarged and granules are produced. Granulation modifies the powder into dust-free granules.
Compression of tablets is achieved by granulation. It also enhances the packing of dry granules and creates a coating for drugs for their sustained release. There are two main types of granulation: wet and dry granulation.
To know more about the major differences between wet and dry granulation. Keep reading this informative review.
Table of Contents
I.Granulation
Most companies implement the granulation technique to strengthen their productivity. When blending or mixing properties of powder do not support tableting then manufacturer opt for granulation process to obtain a desirable flowability with reduced dust formation. This is necessary to achieve lower weight variation in solid dosage forms, greater tablet filling weight, more compressibility and tablet compactness.
A method of particle enlargement by agglomeration is a key operation of pharmaceutical formulations. Usually, it is commenced after drying mixing of APIs and with necessary ingredients. This is because, it offers a uniform distribution throughout the mixture.
A granule size for solid dosage forms varies from 0.2 to 4.0 mm. They are basically formed as an intermediate with a particle size varies from 0.2 to 0.5mm which is either compact or mixed with other excipients before compression. The granulation narrows down the spectrum of particle size distribution from bulk’s powder and minimizes the chances of segregation. So, the overall quality of material is improved and ensuring perfect active distribution in the blend.
II.Aim of Achieving the Granulation
While with any type of product formulation, the main objective is to get desired outcome with fewest process steps and lowest cost. The primary aim behind obtaining granules is as followed:
For tablet dosage form, the major concern is to keep formulation in intact form. Powder particle generally tends to segregate those results in poor product quality. Granule formation is the solution to minimize the chances of particles separation during direct compression.
Particles with high porosity has low flowability. In contrast, particles with greater density, low porosity has high flowability. Furthermore, non-uniform powder particles may induce friction and more dust formation during process. You need granulation process to make granules in spherical shape to improve flowability and less friction.
In pharmaceutical, compaction of powder particles is certainly important to improve tablet, capsule, and powders handling. During granulation, powder particles adhere closely to each other resulting in a large, multi-particle moiety.
During formulation process, you may encounter with various substances that are toxic upon inhalation or more exposure. Granulation is perfect solution as it reduced toxic dust that may form during handling.
Granules are ideally occupying lesser space (volume/unit weight), so you may get higher storage space for powder during transportation from place to place.
III.Categories of Granulation Method in Pharmaceuticals
Based on process methodology, granulation is mainly categorized as follows:
- Conventional Method
- Direct Compression
Conventional Method
- Dry Granulation
In this method, the compression of powdered particles takes place without heat and solvent. The particles are agglomerated under strong compression. Dry granulation is basically divided into two processes:
2.Slugging
This is produced by heavy tablet compression.
3.Roller Compaction
Powder is pressed between a set of counter rotating rollers that forms a sheet of material (flake). The following procedure do not require heat or liquid. The flake is further treated with suitable milling device to form granular substance that is separated via sieving process to get desirable size of the granule.
4.Wet Granulation
The process is involved a wet massing of particles blend with granulating liquid. For instance, a solvent that is possibly a volatile in nature allows an easy evaporation after procedure; water, ethanol, isopropanol are commonly used solvents for wet granulation.
Direct Compression
This is a popular technique to create granules because it takes a shorter time with effective procedures. You just need to blend APIs with other excipients followed by direct compression, and that’s it!
This is ideal procedure for those substances that are heat and moisture sensitive. Because wet granulation is contraindicated for such substances, so we recommend you go for direct compression. However, for this procedure, you need to assess your raw ingredients, its compressibility ratio and flowability for successful process.
IV.Summary of Recent Granulation Technique used in Pharma
With increase demand in pharmaceutical granules, many recent technologies are developed offering more preferred methods. Discussed below is a short overview of each development progressed in the granulation technique. For your ease, we have categorized them as dry and wet granulation.
Recent Advancements in Dry Granulation
Upon comparing with wet granulation, there has not been considerable advancement taken place in the dry granulation technique except:
Pneumatic Dry Granulation (PDG)
This is an innovative technology that encompasses roller compaction and air classification method to form extraordinary granules with excellent flowability and compressibility. Firstly, granules are produced by the application of compaction force. Secondly, the fine or smaller granules are separated from the intended granules in a fraction chamber by the application of a gas stream or pneumatic system. While intended granules are passed through a fraction chamber for tablet compression. The fine granules are transferred to a device where it recycles and recirculates to a roller compactor for re-processing.
Recent Advancements in Wet Granulation
Wet granulation is a popular technique where granules are formed by wet massing and incorporation of APIs liquid granulation with or without desirable binders. The technique has improved with high performance and more advancement to give you high significance in pharmaceutical production. Some of them are:
Reverse Wet Granulation
This technology is also known as reverse-phase wet granulation. This is indeed a new development where dry powder formulation incorporated with liquid binder followed by a controlled breakage in order to form granules.
Here, a binder solution is prepared prior to immersion of dry powder in the granulator. Later wet granules are milled soon after achieving optimum drying. The granules formed by this method are well-defined, well handled, with have a good flowability ratio as compared to the conventional wet granulation method.
Steam Granulation
This is a well-modified version of the conventional wet granulation technique where steam is used as a substitution for the liquid binder. It involves a steam injection over the fluidized bed particles that are meant to be granulated.
A steam offers a higher diffusion rate to powder particle that favors thermal drying requiring only a small amount of energy for evaporation of liquid particles.
Moisture Activated Dry Granulation
This is also known as a ‘single pot’ or ‘one pot process’.
MADG process was explained over 20 years ago although it was not widely accepted. This is because of its unusual simple methodology with equipment uncertainty. This process does not require a drying step because the concentration of the binder is almost negligible. Here moisture is utilized for granule formation. The moist agglomerates blends with common raw material resulting in a uniform and free-flowing particles. In this technique, only 14% of solvent content is incorporated to form agglomerates.
Thermal Adhesion Granulation
Wei- Ming Pharmaceutical was the first who developed this methodology which is analogous to moist granulation. In contrast to MADG, this process utilizes moisture and organic solvents with the help of fine spray. The mixture is subjected to heat ranging from 90 to 105◦C for water while 70 to 90◦C for organic solvents in a closed system. It is followed by a tumble rotation for 3 to 20 minutes to achieve powder agglomerates. The formed granules are sieved through 24 mesh.
Melt Granulation
This is also known as ‘Thermo-Plastic Granulation’ where granules are formed by the incorporation of molten binder or solid binder. The technique is ideal for water-sensitive substances and a perfect alternative to other wet granulation techniques.
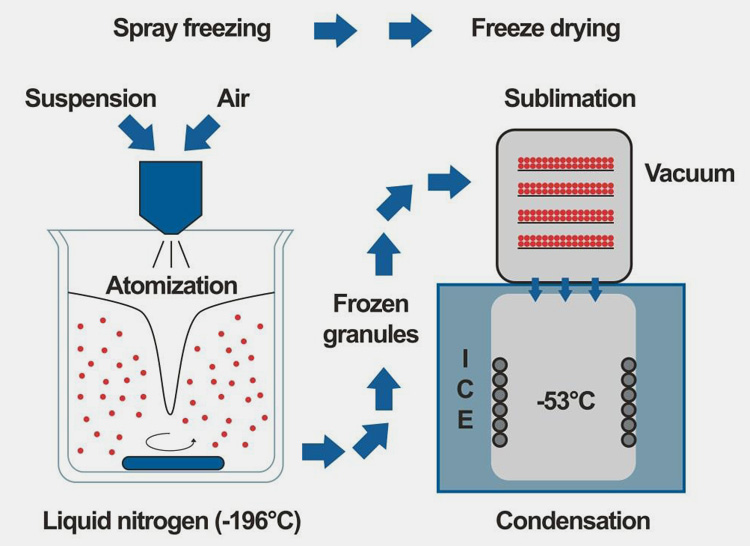
Freeze Granulation
W. Rhodes and S. Prochazka in the mid 70thclaimed about free granulation technology for the first time. So, according to our analysis, freeze-drying (spray freeze drying and spray freezing) was first established in the 1980s by the Swedish Ceramic Institute. The following techniques help to create homogenous, free-flowing granules with binders. In the 1990s, this method was successfully employed for commercial projects. Primarily, this technique involved spray droplets or atomization of powder into liquid nitrogen where they are transformed into frozen granules. The freeze-drying of these droplets forms free-flowing granules with excellent homogeneity.
Foam Granulation
This technique is involved a continuous addition of liquid binder as foam rather than spraying or direct pouring over the powder bed. After achieving homogenous granules, they are dried in a fluidized bed dryer till obtaining the desired moisture content.
V.The Challenges and Solutions of the Granulation Method
When developing any formulation, a formulator often counteracts many challenges to bring a desirable outcome. An uneven powder exerts a negative impact on the equal distribution of active pharmaceutical ingredients (APIs) in capsules or tablets. While you can easily face and solve these challenges by following mentioned solutions:
| Problem | Causes | Solution |
| How to Counteract Lumps or Oversized Particles? | This problem might be due to:
Excessive moisture Herbal or Natural Products Stick Polymers High quantity of local binder. |
You need to:
Reduce the fluid spray rate Increase air pressure and temperature Correct Spray nozzle |
| How to manage Powder Segregation? | This problem is occurred due to:
Large scale powder bed Bigger aggregates Poor quality product
|
To solve segregation problem:
Initially apply mild compression Do premixing with fluid if angle of repose is present. Assess particle size, density, shape Change excipients. |
| How manage sticking of powder particles during process? | The reasons of sticking are:
Granules are too wet Wearing off die punches May be lack of lubrication and cleaning Particles with low melting points |
To rectify this problem:
Use an optimized concentration of fluid Punch must be replaced with new one You need to pay attention on maintenance and cleaning procedure of the machines |
| How to manage sieving problem? | Sieving is preferable method to achieve ideal granules but sometimes it is difficult because:
Manual sieving Large granules size Improper milling machine |
We recommend to:
Avoid manual sieving Use an oscillating granulator Always cover top lid of granulator to prevent material from dust Assess the sieving condition |
| How to manage under wetting? | The reasons of under wetting are:
Inadequate binder or more solvent concentration Less blending Or addition of material was slow |
To deal this problem:
You need to validate the concentration of solvent during mixing process Adjust the mixing time by critical monitoring Improve the quantity of binder |
| How to manage problem of slugging? | During slugging more fines are formed, this is due to:
Low hardness of a slug |
To manage this problem, you need to:
Optimized a slug with defined hardness. Monitor the screening of powder Optimized the drying speed of the dry mill. |
VI.Comparing Granulation Method: The Significance and Weakness of Each Technology
| PDG | Reverse Wet Granulation | Steam Granulation | Moisture Activated Dry Granulation | Thermal Adhesion Granulation | Melt Granulation | Freeze Granulation | Foam Granulation | |
| Significance | Fast and Efficient
Time-friendly
No material wastage
Low dust |
Good flowability
More uniform particles |
High diffusion rate
Less drying energy
Eco friendly- No organic solvents |
Low granulating fluid is required
Good flowability |
High diffusion rate
User friendly
Rapid process |
No solvents are used
Uniform dispersion
Safe for users |
Good for fine powders
Uniform dispersion
Good for suspension
Uniform particle
Low product wastage |
Good distribution for low formulation drugs
More process flexibility
Low binder is required
|
| Weaknesses | Suitability with low concentration material
friability |
Stickiness | Not suitable for binders
Not recommended for thermolabile drugs |
Not suitable for high drug load
Not ideal for hygroscopic drug |
Not good for thermolabile
Not for all binders
PPIs required |
High temperature may degrade ingredient. | Critical monitoring for organic solvents is required | Difficult procedure for production scale up |
Conclusion
The technical and technological advancement for granule formation methodology has improved the processability and quality of pharmaceutical products formulation. Indeed, the techniques are kept on improving leap and bound. Our short overview on ‘Pharmaceutical Granulation’ tried to highlight the substantial method and improvement of granulation technique. Nevertheless, new, and cost-effective techniques are always keen interest of the pharma companies globally. If you want to know more or need our expert consultation about granulating tools and techniques, we always warmly welcome you to contact us just by sending a short message.
Don't forget to share this post!
Granulator Machine Related Posts
Granulator Machine Related Products
Granulator Machine Related Videos
CONTACT US
Tell us your raw material and project budget to get quotations within 24 hours.
WhatsApp Us: +86 181 6426 8586
Want the best price & newest pharmaceutical machinery buying guide,tips and trends sent straightly to your box?Sign up for Aipak’s monthly newsletter,we’re free for your consultation and Offer you the most suitable solutions!
The Buyer's Guide
- Capsule Filling Buyer's Guide
- Blister Packaging Buyer's Guide
- Tablet Counting Buyer's Guide
- Tube Filling Buyer's Guide
- Cartoning Buyer's Guide
- Gummy Making Buyer's Guide
- CO2 Extraction Buyer's Guide
- Empty Capsules Buyer's Guide
- Suppository Filling Buyer's Guide
- Tablet Coating Buyer's Guide
- Tablet Press Buyer's Guide
- Softgel Encapsulation Buyer's Guide
Most Popular
- 7 Importance Of Pharmaceutical Packaging In Different Applications You Must Know
- 6 Advantages You Must Know About Tablet Counting Machine
- 8 Advantages of Blister Packaging You Must Know
- 6 Critical Applications of Automatic Capsule Filling Machine
- 6 Stations You must Know to Improve the Filling Quality of Automatic Capsule Filling Machine
Tell us your material or budget,we'll reply you ASAP within 24 hours