Pharmaceutical Emulsion- Deepen Your Knowledge!
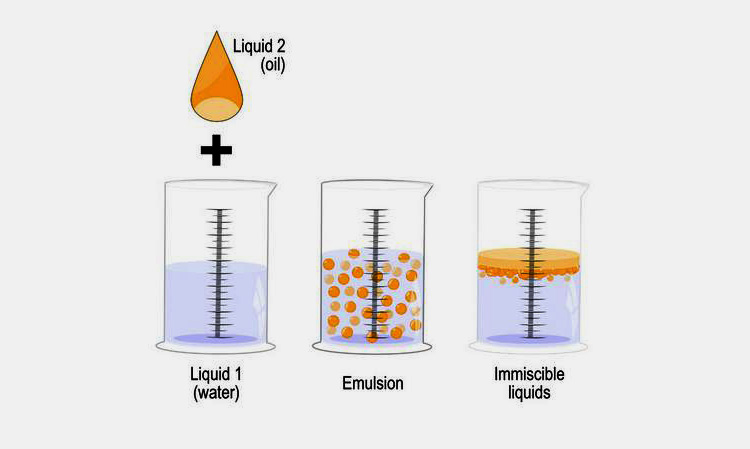
Do you know what happens when you mix water with oil? Why do oil and water form two separate layers? How immiscible liquids are mixed perfectly?
The phenomena of mixing two immiscible phases e.g., oil and water are known as ‘Emulsion’. The pharmaceutical emulsion is found everywhere around the manufacturing world. Whether from medicine to nutraceuticals, cosmetics to foods, beverages to crude oil; pharmaceutical emulsion is crucial for the best quality of the product. In this article, we will talk about deepening the science behind this phenomenon. How to form, break, classify, emulsifying agents, and much more!
1.Pharmaceutical Emulsion- How it Derived?
History doesn’t help to tell you how early pharmaceutical emulsions were derived or when humans picked up mixing and stirring intentionally for the first time. But all we know is that mixing is associated with the longest history that begins over 30,000 years ago. Isn’t surprising?
Researchers have picked the grinding tool in Italy, Russia & Czech demonstrating the first grinding roots, wild grasses were treated using water.
The emulsion word is taken from the Latin word “emulgere” which means to milk out. Emulgere is a combination of two words that are “ex” (means out) and “mulgere” (means milk). Milk is a kind of emulsion formed from fats and water together with various other polar and non-polar chemicals.
2.Significance of Pharmaceutical Emulsion in Industrial Applications
Pharmaceutical emulsion occupies a central place in several industries due to its valuable attributes such as
| Pharmaceutical Industry
|
In pharma sectors emulsions are employed due to their palate boosting properties. They also improve therapeutic efficacy by maintaining dosage of drugs. These solutions are nontoxic and are directly administered to patients. |
| Agriculture Industry
|
They act as a delivery mechanism for various insecticides and pesticides in agriculture industry. These emulsions also enhance sprayability of pest controlling chemicals. |
| Cosmetic Industry
|
Various kinds of emulsions are used for moisturizing, softening, and smoothing hairs and skin in the cosmetic industry. These emulsions act as conditioning agents for hairs because they consist of positive charges. |
| Chemical Industry
|
Paints and inks are liquid-in-liquid emulsions and are composed of waterproof films and pigments that dry instantly without changing colors. They are inflammable and thus are widely used as coloring agents for walls and wood. |
| Food Industry
|
Milk, salad dressing, ice creams, and peanut butter are types of emulsions. Emulsion affects the physical appearance of food and imparts characteristic mouthfeel of various edibles. |
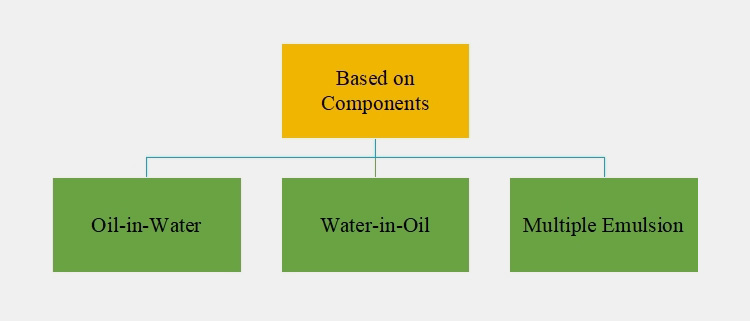
3.Types of Pharmaceutical Emulsion
Pharmaceutical emulsions are classified in different categories on the basis of the following characteristics:
- On the Basis of Components
- On the Basis of Particle Size
Classification on the Basis of Components
There are three types of pharmaceutical emulsions on the basis of component:
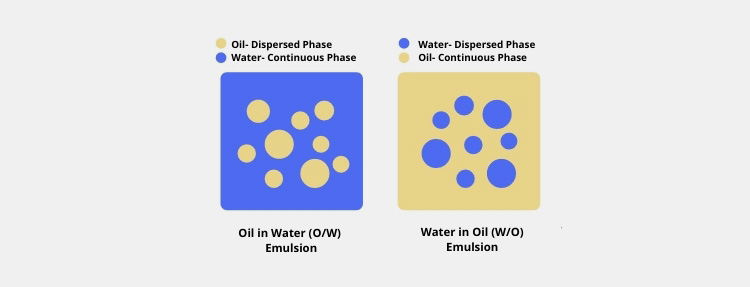
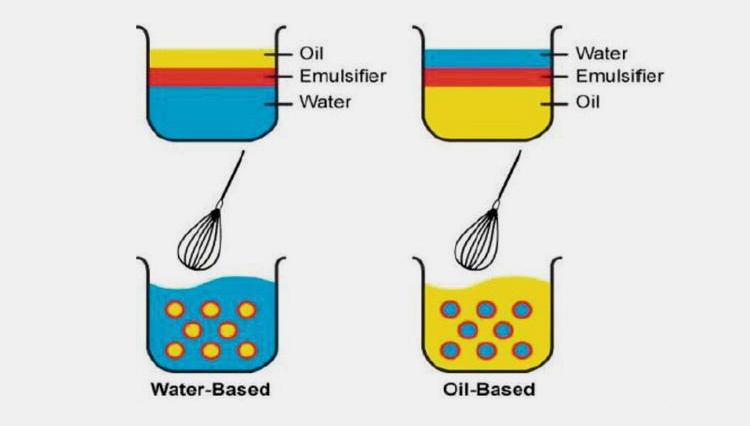
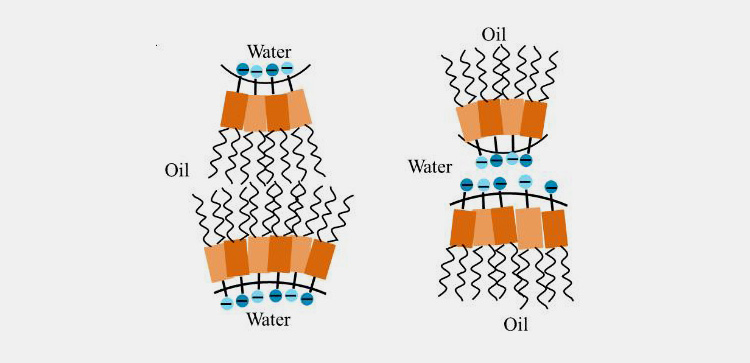
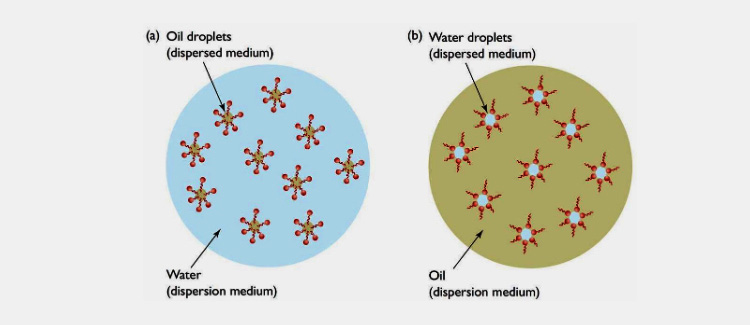
Oil-in-Water
In this kind of emulsion, the oil droplets are suspended in an aqueous medium. The oil is dispersed media while water is continuous media in the case of oil-in-water emulsion. These are employed for lowering the bitter taste of oils and they offer cooling effect if used externally.
Water-in-Oil
In a water-in-oil emulsion, the aqueous media is dispersed in hydrophobic oil media that act as a continuous phase. Margarine or butter is an example of a water-in-oil emulsion. These emulsions are usually employed for drug delivery when compared with oil-in-water emulsions.
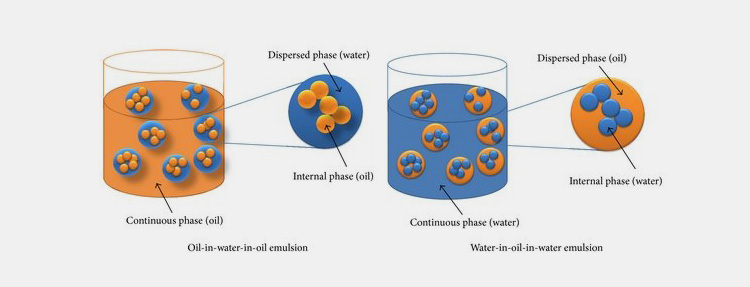
Multiple Emulsions
These are formed by various dispersed media and are called emulsion of emulsions or double or triple emulsions. They are produced by suspending either water-in-oil emulsion or oil-in-water emulsion in another continuous media. This continuous media is either water or oil.
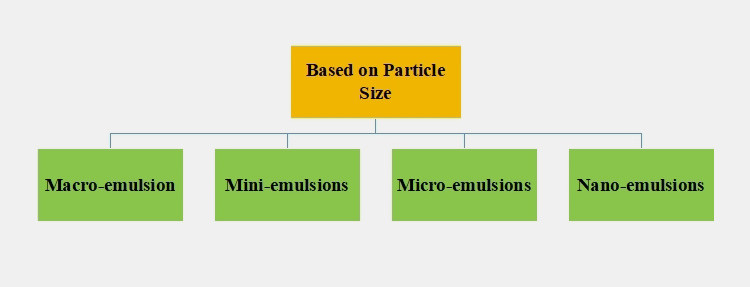
Classification of the Basis on Particle Size
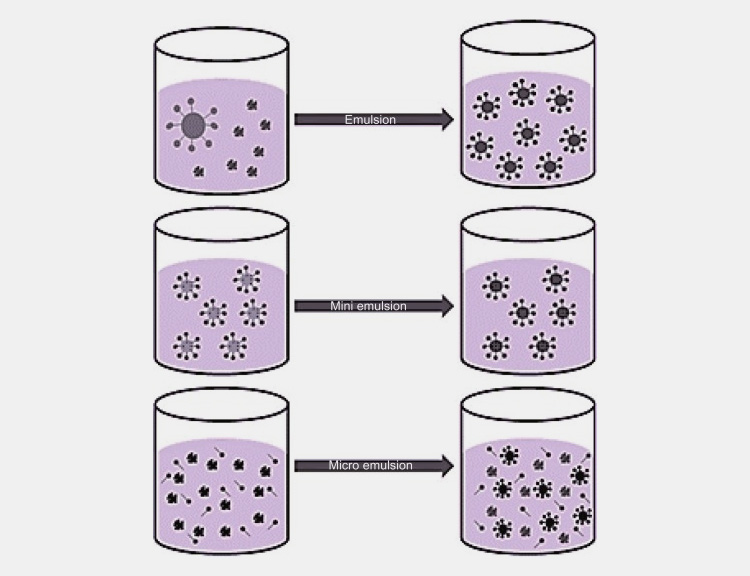
There are four kinds of emulsion based on particle size:
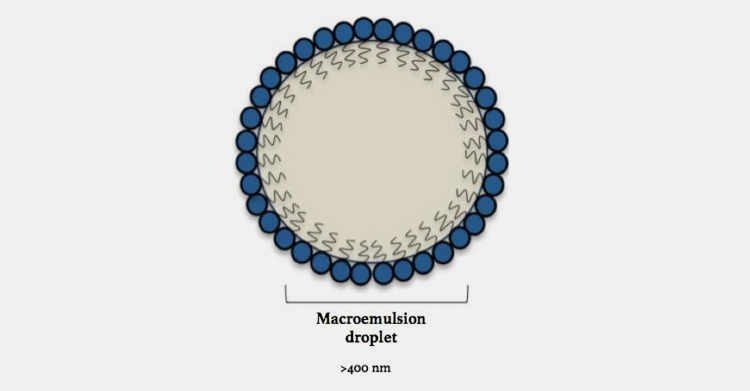
Macro Emulsions
This category of emulsion has a large particle size, usually greater than 10 mm. Macroemulsions are thermodynamically unstable and have a milky appearance. They are more inexpensive than microemulsions and are used as skincare and sunscreen products.
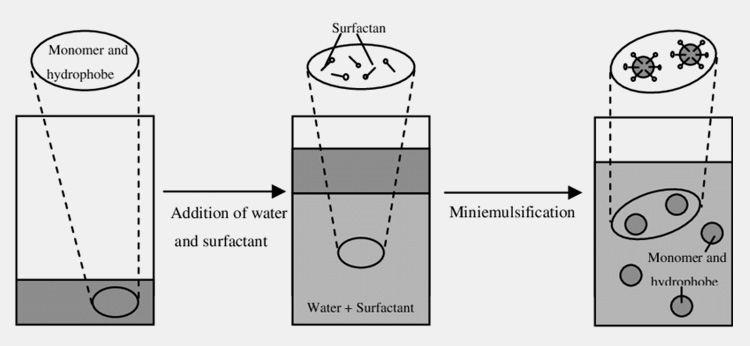
Mini Emulsions
These are the special kind of oil-in-water emulsions that are distinguished by their particle size (0.1–10 µm) and enhanced stability over several hours. They are formed by the high shearing of oil and water along with surfactants. They are employed as a vehicle for delivering water-insoluble nutrients.
Micro Emulsions
They have a particle size between 100-600 nm. These emulsions are bicontinuous kinetically stable and translucent formulations. Microemulsions are frequently applied for administrating hydrophobic and hydrophilic drugs through tropical or transdermal routes.
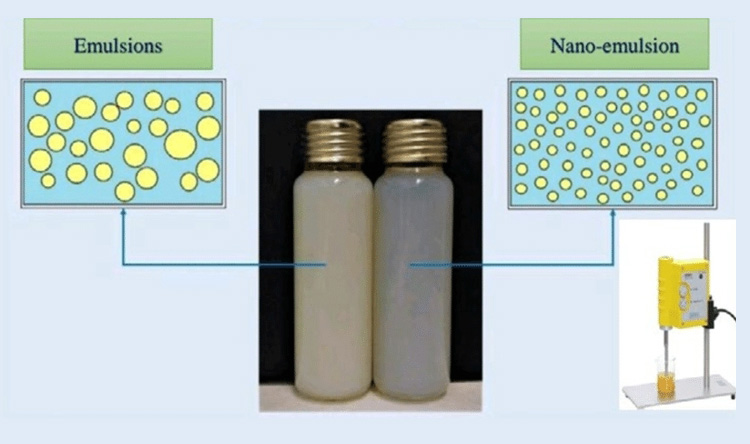
Nano Emulsions
These have a particle size of 10–100nm and are transparent formulations of oils and aqueous solutions. They are utilized for drug delivery due to their easy encapsulation, stability, and impulsive emulsification.
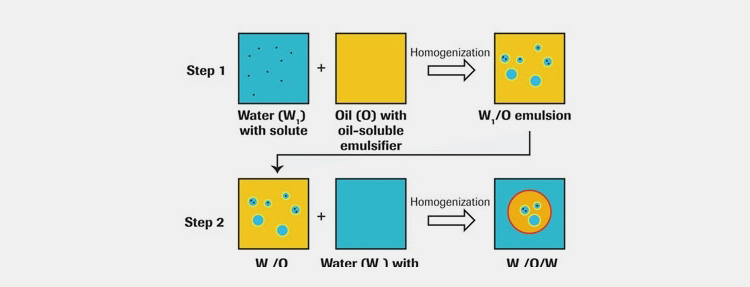
4.How is Pharmaceutical Emulsion formed?
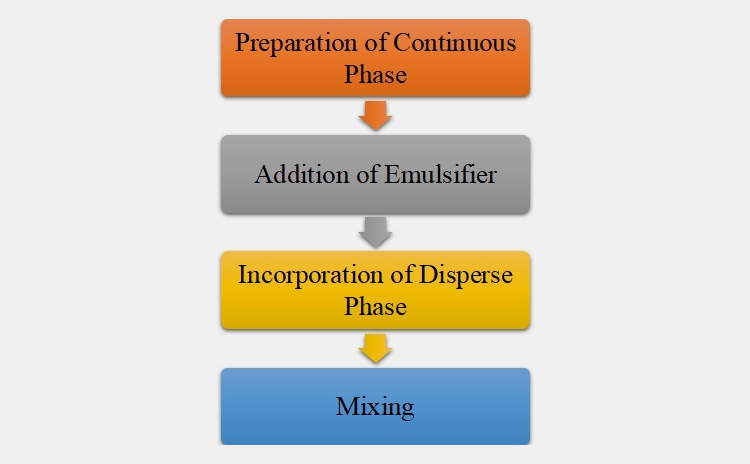
The steps included in formation of pharmaceutical emulsions are given below:
Preparation of Continuous Phase
In the first stage, continuous media whether oil or water is prepared.
Addition of Emulsifier
Afterward, an emulsifier is added in the continuous phase for boosting the stability of an emulsion.
Incorporation of Disperse Phase
The dispersed phase is poured gradually in a mixture of emulsifier and continuous phase with forceful shaking.
Mixing
Vigorous agitation is done for coating dispersed smaller droplets with suitable amount of emulsifier.
5.How does Pharmaceutical Emulsion Break?
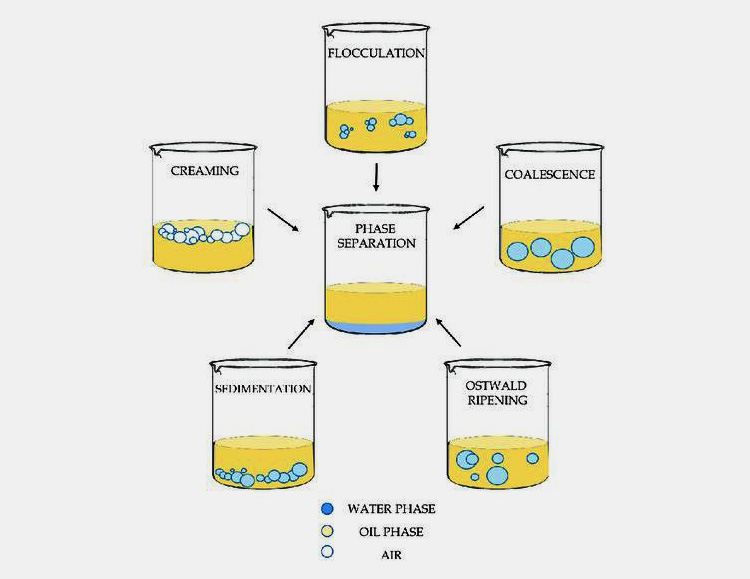
Pharmaceutical emulsions are disrupted by four different approaches which are described below:
Flocculation
It is a process in which emulsion particles combine to form larger particles due to attractive forces between them resulting in unstable assembly. This happens due to gravity and stirring force which reduces repulsion between particles.
Creaming/Sedimentation
This separation process of emulsion takes place due to differences in the density of particles. The particles rise on the top part due to centripetal force.
In sedimentation, heavier water droplets settle down at the bottom of the emulsion and this process usually occurs in water-in-oil emulsions.
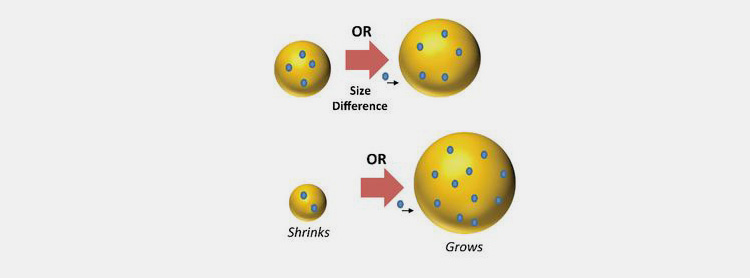
Coalescence
In this emulsion destabilization step, the little droplets of the discontinuous phase collide with each other to produce larger droplets consequently escalating the mean size of particles over time.
Coalescence takes place when droplets come in contact with each other and their interfacial film layer degrades.
Ostwald Ripening
It takes place when small particles dissolve and accumulate on top of larger droplets. This usually happens in an inhomogeneous system during the time course and leads to a thermodynamically unstable phase.
6.Mechanism of Pharmaceutical Emulsion
Various theories encompassing chemical and physical mechanisms have been proposed regarding formation of emulsions. These are:
Repulsion Theory
It states that an emulsifier builds a film covering on a globular liquid phase that results in repulsion between globules. This opposition force is the reason for droplets' suspension in continuous media.
Viscosity Modification Theory
According to this speculation, emulsifying agents for instance acacia, polyethylene glycol, carboxymethylcellulose, etc. augments the viscosity of droplets in the dispersed phase.
The viscosity plays a significant role in producing and sustaining the distribution of particles in a continuous phase.
Surface Tension Theory
This speculates that interfacial tension has an important role in determining the stability of the emulsion. If there is low surface tension between phases, then the resulting emulsion is more stable.
7.Properties of Pharmaceutical Emulsion
Some useful attributes of pharmaceutical emulsions are:
Uniformity
A good pharmaceutical emulsion should have uniformity in drug dosage between various batches as well as between packaged bottles.
Size Distribution
Dispersed media in pharmaceutical emulsion should have fairly constant particle size throughout the lifetime of the product.
Drug Concentration
Drug concentration is lost due to drug crystallization and evaporation of continuous phase so solubilizers and surfactants are incorporated in emulsion for preventing concentration drop.
Flowability
An ideal emulsion should have optimal viscosity for flowing out of an open bottle and injection needle
Resuspendability
A pharmaceutical emulsion that is separated into two phases should be easily redispersed upon light shaking.
Palatability
The taste of bitter drugs is boosted by the addition of sweeteners, flavors, coloring agents, etc., and then dispensing them as pharmaceutical emulsions.
8.Pharmaceutical Emulsifying Agents
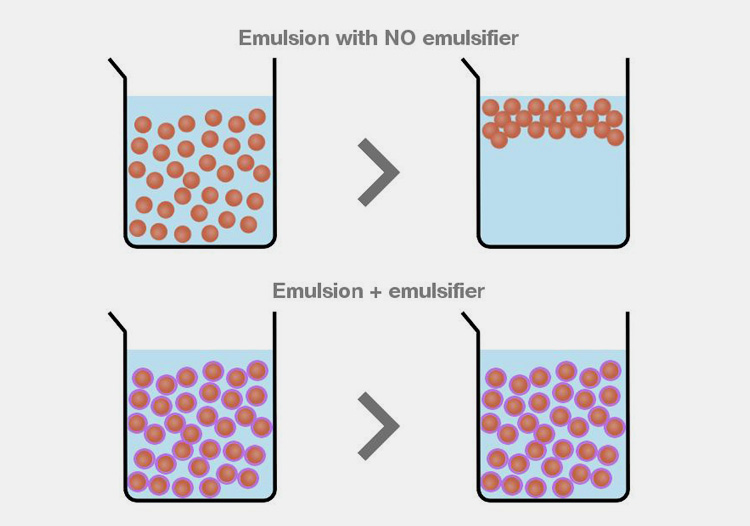
These are the stabilizing agents that are added to emulsion for maintaining their stability during the course of time. They are also called emulsifiers and emulgents. The function of these surface agents is to enhance the kinetic constancy of pharmaceutical emulsions.
These agents also inhibit the major size change in droplets over time. Emulsifying agents also promote the thermodynamic stability of emulsion by lowering interfacial tension between two phases.
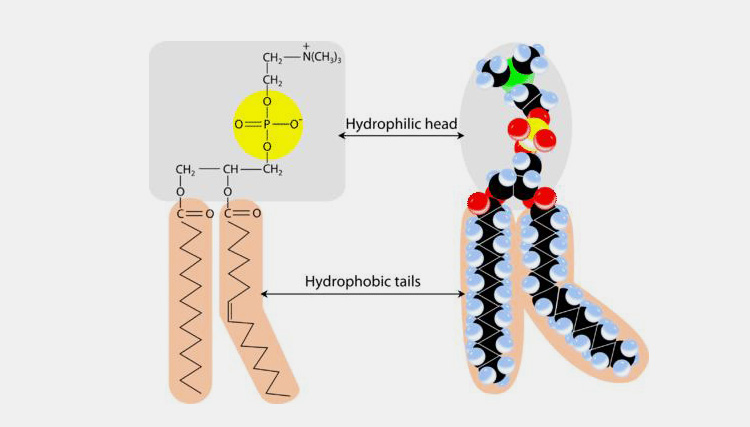
Structure of Emulsifier
These are amphipathic molecules meaning they have both polar (hydrophilic) and non-polar (hydrophobic) ends. Due to this, emulsifying agents are more or less soluble both in water and oil.
Characteristics of Pharmaceutical Emulgents
- They should be non-toxic
- These agents should have little taste, odor and color of their own
- They should be compatible with other excipients
- Emulsifying Agents should not have an impact on the efficacy of active drug.
CommonEmulsifiers Used in Pharmaceutical Emulsions
- Acacia
- Sodium Lauryl Sulfate
- Tragacanthin
- Methyl cellulose
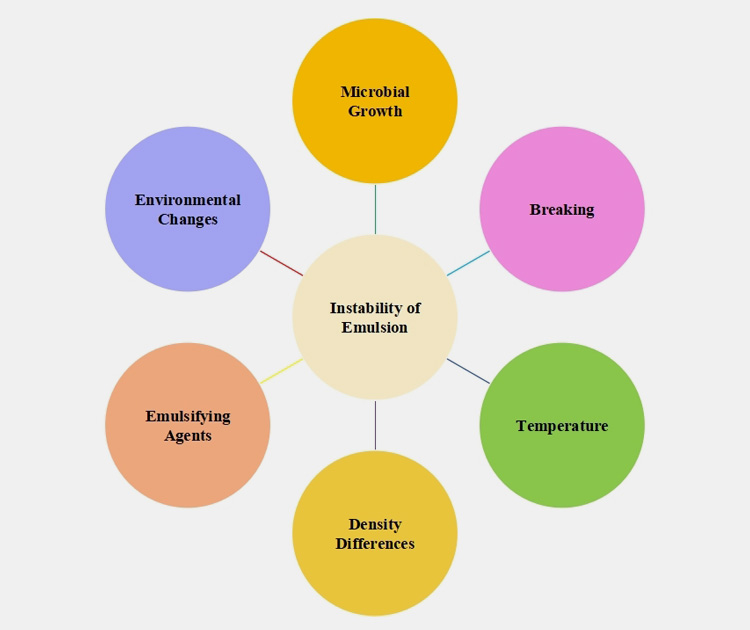
9.Instabilities of Pharmaceutical Emulsion
Pharmaceutical emulsions have reduced stability due to immiscible nature of liquids as well as tension forces between them. This instability is caused by the number of factors such as:
Breaking
This happens when two media form distinct layers due to the addition of chemicals such as table salt or acid in emulsions. Sometimes stirring or centrifugation also causes the breaking of emulsion.
Density Differences
The size and density differences of particles in two phases lead to instability of emulsion. If particles of one phase are lighter than the other then these droplets will float at the top of the second phase.
On the other hand, if droplets of the dispersed phase are heavier than the continuous phase then they will settle at the bottom of latter.
Emulsifying Agent
The pharmaceutical emulsions also lose their stability if incorrect or no emulsifier is added in them. The emulgent inhibits the aggregation of droplets in a continuous phase.
If an unsuitable emulsifying agent is added which is more attracted to one phase then it will break contact with other phase consequently unbalancing the emulsion.
Temperature
Higher temperature elevates the viscosity of hydrophobic molecules causing aggregation of droplets consequently destabilizing the pharmaceutical emulsion.
Environmental Changes
Fluctuations in environmental conditions such as variation of light and pH cause the instability of emulsions. Furthermore, oxidative or hydrolytic surroundings will result in the rancidity of oils thus lowering the stability of emulsions.
Microbial Growth
An increase in microbial populations also degrades emulsion since an emulsifier is a suitable agent for the growth of microbes like bacteria, fungi, and yeast.
10.Let’s Make Emulsion- Which Emulsions Equipment Do You Need?
Choosing the right kind of pharmaceutical emulsifier is the crucial step in manufacturing an emulsions line. If you’re thinking to invest in adding emulsifying equipment, then consider the following list below:
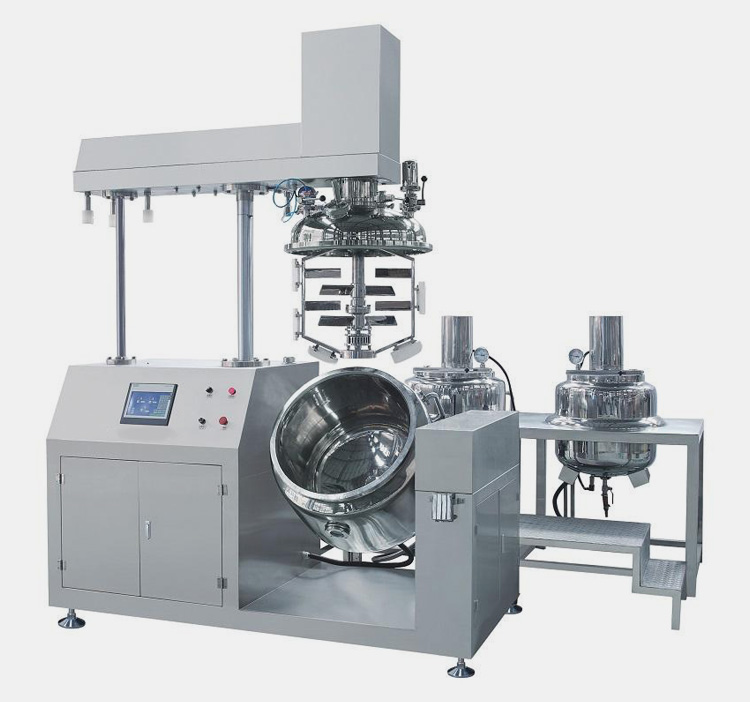
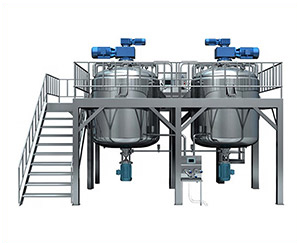
Vacuum Emulsifying Mixer
Aipak Vacuum Emulsifying Mixer
This mixer is comprised of mixing blades considerably perfect for material with high viscosity and for emulsification. The scrapers help in cleaning stuck material on the inner side of the bowl and protect from dead corners. The machine produces high mixing via continuous vacuum homogenization.
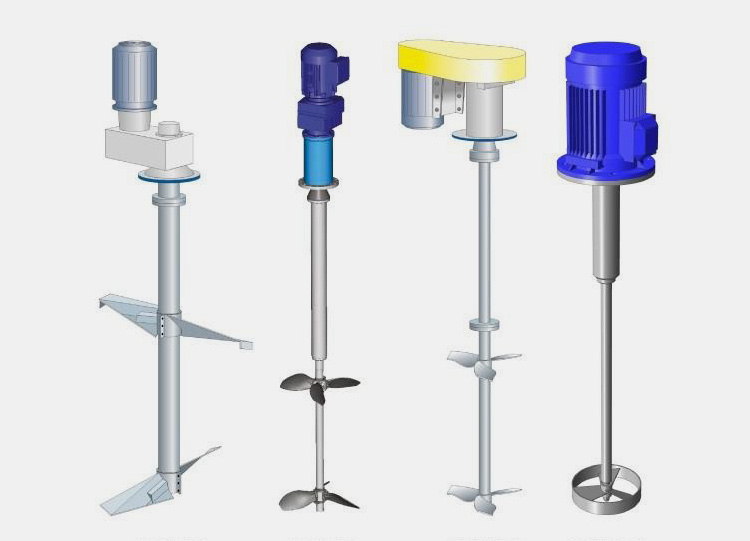
Jet Flow Agitator
The agitator is suitable for the homogenization, dispersion, emulsification, and mixing with the help of a rotor-stator system. This ultimately results in appropriate mixing of high viscosity media that greatly enhances of emulsification process.
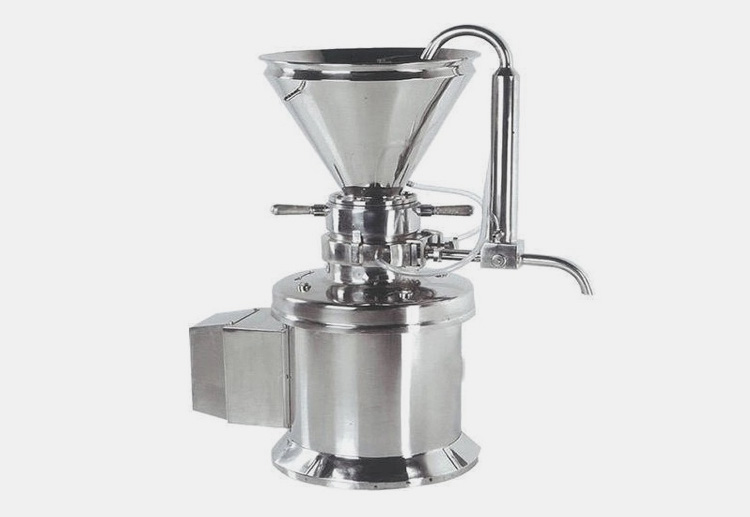
Colloid Mill
A colloid mill is the better choice for creating ultra-fine emulsion and high-quality dispersion. The machine creates pressure shocks that help in the distribution of extremely small particles.
Inline Batch Mixer
Inline Batch Mixer emulsifies powders into liquids and processes high-viscosity products without aggregation. The machine is designed for processing homogenization, suspension, emulsions, and wet milling. The unit also works at elevated temperatures.
Conclusion
Pharmaceutical emulsions have diverse applications ranging from creams to enemas and oils. They are formed from two phases (continuous and disperse phase) that are typically water and oils. Special agents called emulsifying agents are needed for retaining the stability of the emulsion. Before selecting an emulsifier, it is essential to calculate its hydrophilic-lipophilic balance and hydrophilic-lipophilic difference. For more technical details or equipment involved in making perfect emulsion; Please contact us Right Now!
Don't forget to share this post!
Vacuum Emulsifying Mixer Related Posts
Vacuum Emulsifying Mixer Related Products
Vacuum Emulsifying Mixer Related Videos
CONTACT US
Tell us your raw material and project budget to get quotations within 24 hours.
WhatsApp Us: +86 181 6426 8586
Want the best price & newest pharmaceutical machinery buying guide,tips and trends sent straightly to your box?Sign up for Aipak’s monthly newsletter,we’re free for your consultation and Offer you the most suitable solutions!
The Buyer's Guide
- Capsule Filling Buyer's Guide
- Blister Packaging Buyer's Guide
- Tablet Counting Buyer's Guide
- Tube Filling Buyer's Guide
- Cartoning Buyer's Guide
- Gummy Making Buyer's Guide
- CO2 Extraction Buyer's Guide
- Empty Capsules Buyer's Guide
- Suppository Filling Buyer's Guide
- Tablet Coating Buyer's Guide
- Tablet Press Buyer's Guide
- Softgel Encapsulation Buyer's Guide
Most Popular
- 7 Importance Of Pharmaceutical Packaging In Different Applications You Must Know
- 6 Advantages You Must Know About Tablet Counting Machine
- 8 Advantages of Blister Packaging You Must Know
- 6 Critical Applications of Automatic Capsule Filling Machine
- 6 Stations You must Know to Improve the Filling Quality of Automatic Capsule Filling Machine