Oral Solid Dose Manufacturing: The Complete FAQ Guide In 2025
Are you interested in uncovering broad-spectrum insight about oral solid dose manufacturing? This is the challenging phase of pharmaceutical sciences and yet demanding too. What are the complexities and types of types of machinery utilized when planning oral solid dose manufacturing? You’re at the right place because, in this blog, you will be opening the horizon for orally ingested products and attaining therapeutic effects. Come on reader, have a look at our expert’s suggestions and details described in the blog ‘Oral Solid Dose Manufacturing: The Complete FAQ Guide In 2024’.
1.What is oral solid dose manufacturing?

Oral solid dose manufacturing- Picture Courtesy: Evonik Health Care
This is the manufacturing of oral solid doses for the administration of medication for users as this is the most conventional and affordable way of therapeutic agent. Various pharmaceuticals and related companies strive day and night for oral solid dose manufacturing to make a safe and effective way of taking medicine with intact and correct formulation.
This includes tablets, capsules, lozenges, etc that are solid in texture and disintegrate in favorable sites of action to reach your blood circulation. However, it involves the inclusion of active pharmaceutical ingredients with multiple excipients to make your product very stable. Also, this is not a one-step process, rather various series of steps and machines are involved to bring oral solid doses to the market.
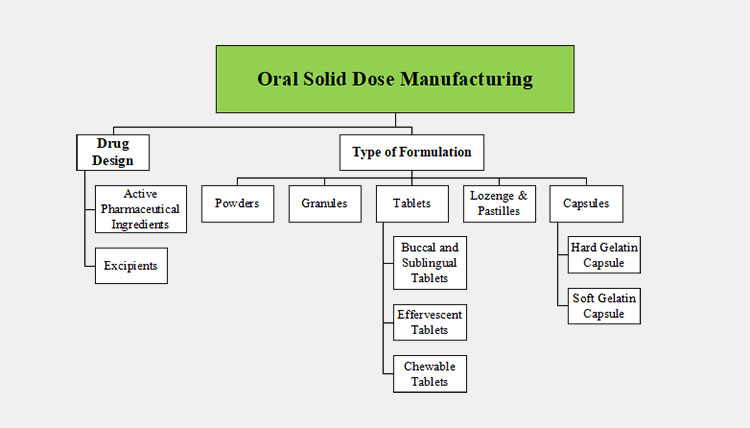
2.What are the key regions of oral solid dose manufacturing?
When designing the oral solid dose manufacturing in any area of the production sector, you must go through the following key steps:
Key Regions of Oral Solid Dose Manufacturing
Drug Design
This is the first step that you have to ensure that what is the desired type of dose formulation in your mind, and its bioavailability, disintegration, and user compliance. Every oral solid dose manufacturing principle is based on these two objects.
It is included with choices of two things:
Active Pharmaceutical Ingredients
Active Pharmaceutical Ingredients
Your indication and therapeutic needs can be controlled by a major entity known as active pharmaceutical ingredients or APIs. This might be related to either the neurological system, heart system, nephrological system, reproductive system, inflammation, etc. So, the major therapeutic agent must be decided in the selection method.
Excipients
Excipients
This is considered an inactive substance that does not actually play any role in inducing a therapeutic response. Instead, it is used to improve the strength, release action, and stability of oral solid dose manufacturing. This is involved in incorporating fillers, binders, disintegrants, etc.
Type of Formulation
This is a long series of oral solid dose manufacturing, where you will need to click on the specific formulation type. This means that you must know what exact product the oral solid dose is intended to formulate. There are various oral solid dose types that you must be aware of.
Powders
Powders
The dry powder is the fundamental element behind every formulation you prepare. These are mainly prepared by crushing and sifting to improve the flow characteristics. However, they possess free-flowing and non-free-flowing properties upon which to design the formulation. The powders themselves have various types such as loose powders, transparent powders, compact powders, settling, and finishing powders that are prepared as oral solid dose manufacturing.
Granules
Granules
This is oral solid dose manufacturing where solid agglomerates are prepared from small, tiny particles to improve flowability and regular particle shapes. You can either manufacture these granules and other formulations of oral solid dose or can consume them directly by taking them with the help of water.
Tablets
Tablets- Picture Courtesy: Picture Courtesy: jidabarr
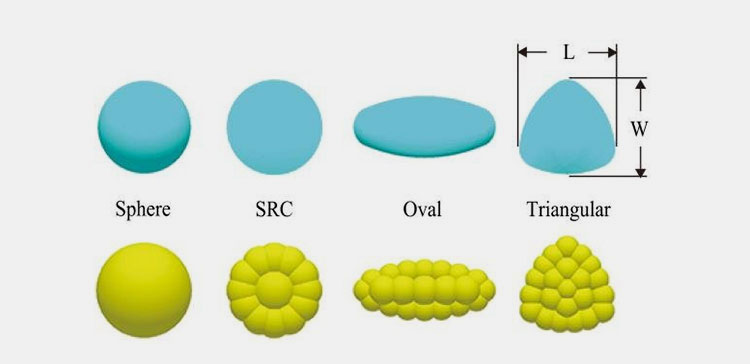
This is a very conventional medication with a hard texture and is designed with various shapes. You commonly see the circular or oval shape of a tablet, but it is also presented in triangular, rectangular, star, etc shapes that mainly hold the unit dose or more than one medication.
It is available in various types such as:
Buccal and Sublingual Tablets
Buccal and Sublingual Tablets- Picture courtesy: GoodRx
These are the types of tablets that you place either in between your gums and cheeks or buccal administration or place just under the tongue or sub-lingual to attain rapid circulatory response and therapeutic effects. Such medication is capable of dissolving faster as it reacts via mucosal membranes to enter the bloodstream without affecting from action of the stomach.
Effervescent Tablets
Paramount safety products
These are comparatively larger than standard tablets and capable of fizz when you put them in water due to the presence of citric and tartaric acids as well as carbonates which form bubbles to release carbon dioxides once react with water. These tablets are mostly facilitated with pleasant smell and taste and many patients love them due to high compliance.
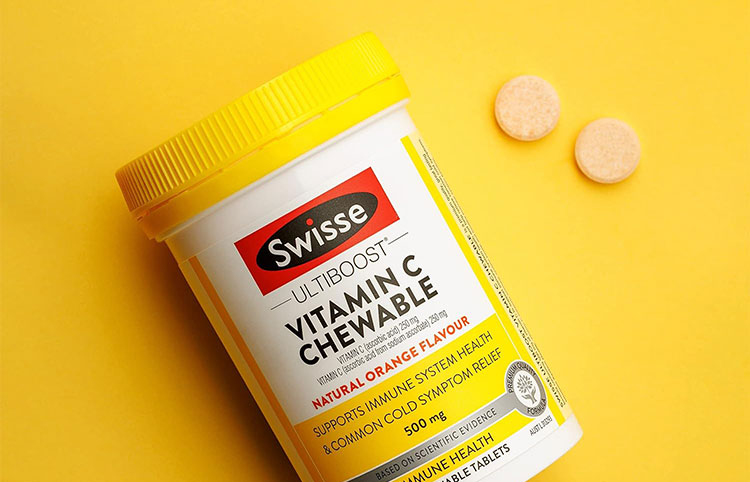
Chewable Tablets
Chewable tablets
These are intended to be chewed once you put them in your mouth to swallow. They are mostly designed to chew without taking it directly to get therapeutic actions and are recommended for special populations. Many nutraceutical products are designed to have chewable properties to provide you with maximum efficacy. However, you often do not require water to disintegrate the tablet as upon chewing it starts breaking down into small pieces and starts producing its dissolving action.
Lozenge & Pastilles
Pastilles: Picture courtesy: William Curley
This is the type of oral solid dose manufacturing intended for gradual and steady dissolving properties when placed in the mouth. They are mostly sweet with various fruity flavors along with active ingredients. Due to the presence of sugars, gums, and substances facilitating cohesiveness ensuring slow dissolution of the medicine.
Similarly, the pastilles are soft textured lozenges that have properties to dissolve slowly in your mouth. They have a soft jelly-like texture that has basic ingredients like glycerol, gelatin, and acacia, to improve elastic texture.
Capsules
Capsule- Picture courtesy: Life Vision Healthcare
Flexible and gelatinous capsules are the second most applicable type of oral solid dose. They are easy to swallow and offer taste-masking effects with other properties. Just like tablets, they are also presented in various shapes. Such as oval, round, star, and hard intact shell (head and body) but these shapes are mainly depending on the types of capsules you intend to prepare. For instance,
Hard Gelatin Capsule
Hard gelatin capsule
These are hard-shell capsules mainly composed of a head and body; you can fill either powder granules or pellets in them and secure the material by enclosing the head. This is considered the most common and easy oral solid dose manufacturing type.
Soft Gelatin Capsule
Soft gelatin capsule- Picture Courtesy: Pharma Frenchi
Some liquid formulations such as oils, suspension, and viscous products are dispensed in soft shell capsules which are hermetically sealed and keep your product safe and intact. This is known as a soft gelatin capsule that requires technical expertise and different machines when meant for capsule oral solid dose manufacturing.
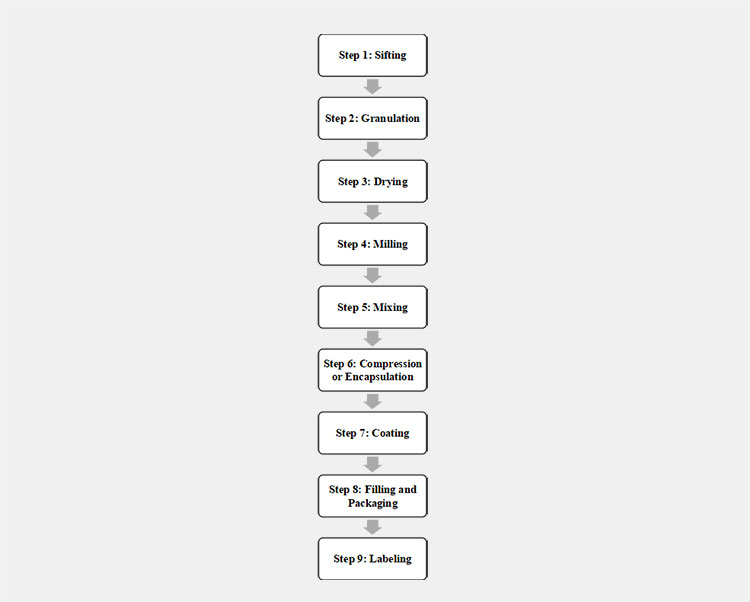
3.What are the process steps of oral solid dose manufacturing?
Oral solid dose manufacturing – Picture courtesy: Within3
The process steps of oral solid dose manufacturing are mainly based on 9 stages. For instance:
Steps of Oral Solid Dose Manufacturing
Step 1: Sifting
Sifting- Picture courtesy: Fryer
Every oral solid dose manufacturing starts with a sifting process. This step ensures the clear and uniform sieving of the materials with a specified mesh number. Every formulation in the pharmaceutical industry must be passed through a screener to allow quality raw materials. This is mainly based on wirable mesh with particular aperture sizes that upon vibration improve the movement of the materials where too large sizes remain on the top layer while maintaining cGMP requirements.
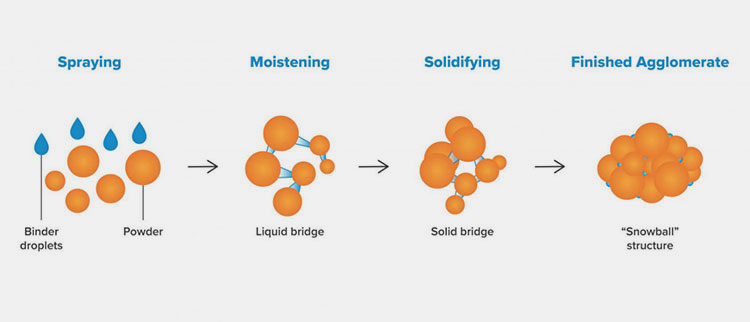
Step 2: Granulation
Granulation
First, understand the concept of granulation, it is the process of combining powder particles to form a uniform-shaped particle known as a granule. The granulation process itself is categorized into dry granulation and wet granulation.
Dry Granulation
Dry Granulation
Dry granules mean, there won’t be any involvement of water during the making procedure. This is simply based on implementation forces that might be compaction forces by the application of a roller compactor to produce a dense granule without the involvement of additional binding agents.
For oral solid dose manufacturing, this is an essential step as it ensures dust reduction and allows a better process by improving the powder's flowability. Moreover, maintaining a consistent particle distribution is required for various formulations. Also, this helps expand the bulk density of medicine thus allowing it for specific body absorption.
Wet Granulation
Wet Granulation
As the name suggests, here you will need the involvement of water content with solids to get granules. Two things would be implemented in wet granulation, first ‘water’, second ‘high or low shear forces. These two entities combined together to allow high-compressed granules production. In this case, you may find particles belonging to various sizes and ranges where the joining of them will be attained by spraying an aqueous solution or binding agents.
Moreover, the reason for wet granulation is also similar to dry granulation such as it lets you reduce the chances of dust formulation, improving the flowability ratio of your materials, ensuring high compactness of particles, improving the bulk density of the powders, etc.
Step 3: Drying
Drying- Picture courtesy: CurTec
This is a critical and essential method which is actually the vaporization of water content present in the material especially those materials that are subjected to wet granulation and makes it possible to wipe off moisture inside the substances.
Here, the gas is utilized as a carrier source which helps in the drying of material and elimination of water with the help of hot air application. Also, drying is required when you have used a liquid substance either volatile in nature or any liquid.
With the help of a vacuum, and internal heat conduction is the main principle source used to vaporize the water content safely.
Step 4: Milling
Milling
Milling is the application of forces and mechanical energies over the particles to make them reduced in size into smaller particles. This is mainly achieved by grinding the substances, comminution, or pulverization. This process is needed to improve the dissolution or distribution of particles used in oral solid dose manufacturing. It is performed on APIs as well as on excipients for optimized delivery of the medications.
Moreover, this is a simple step as well as with cost-effective units but ensures improved bioavailability and improves the various pharmaceutical parameters required for effective therapeutic response.
Step 5: Mixing
Powder and bulk solids
None of the product is possible if mixing or blending is ignored. Yes, this is true as the proper particle distribution is only acquired when you thoroughly blend them, and this can be achieved with the help of the mixing and blending method.
However, in oral solid dose manufacturing, it is one of the crucial steps that help in the combining of particles to produce an effective product.
Before final production, the combination of APIs and excipients is exactly delivered when it is passed through successful mixing which is indeed not an easy task if performed manually. For example, fillers, various binding agents, diluents, lubricants, and many more substances blending is properly established by this mixing to produce a stable product.
Step 6: Compression or Encapsulation
Compression or Encapsulation- Picture Courtesy: Lucky pharma
The final oral solid dose manufacturing is created for your production line which is mainly performed by compression or encapsulation procedure. This is mainly achieved by compression and encapsulator machines such as tablet press machines, and capsule filling machines to produce oral solid dose manufacturing with accurate and correct dosage.
The mixed or blended materials are combined and form tablets with simply compressed force where the upper and lower punch firmly unit to produce an oral solid dose.
Similarly, in the encapsulation step, the amount to be introduced in capsules is fairly measured and placed in the capsule body followed by the placement of the head. Whereas the soft gelatin capsules are produced filled and sealed by the same unit that we have discussed in the later part of the article.
Step 7: Coating
Coating
The taste, appearance, release properties, and flavor of the oral solid dose manufacturing are involved with the coating step which applies a coating solution over the produced medication. This step is essential and helpful in the enhancement of the quality, stability, and therapeutic properties of your products by ensuring greater protection.
The coating solution is mainly of two types either sugar coated or film coated which is prepared by incorporation of various polymers with other ingredients such as flavorants, colorants, etc. However, several layers are applied over the oral solid dose so the final appearance and releasing pattern are optimized. Various types of products can be formed by coating application such as extended release, sustained release, etc.
Step 8: Filling and Packaging
Filling and Packaging- Picture Courtesy:sigmasoftgel
Your product can be accurately counted and packed by the implementation of the filling and packaging step. The oral solid dose manufacturing can be either following blister packaging, bottle packaging, strip packaging, etc. This is an important step that ensures the oral solid dose is protected against external factors, physical damage, as well as other factors such as moisture, light, etc.
Step 9: Labeling
The label printers
Your brand name, information about oral solid dose, manufacturing date, expiry date, how to use, dosage information, colorful and attractive presentation, etc are the important and final steps included in oral solid dose manufacturing and are done by labeling. This step promises that the medication deals with essential details that every customer looks for. However, this is achieved by using various different categories of labeling units available in the market.
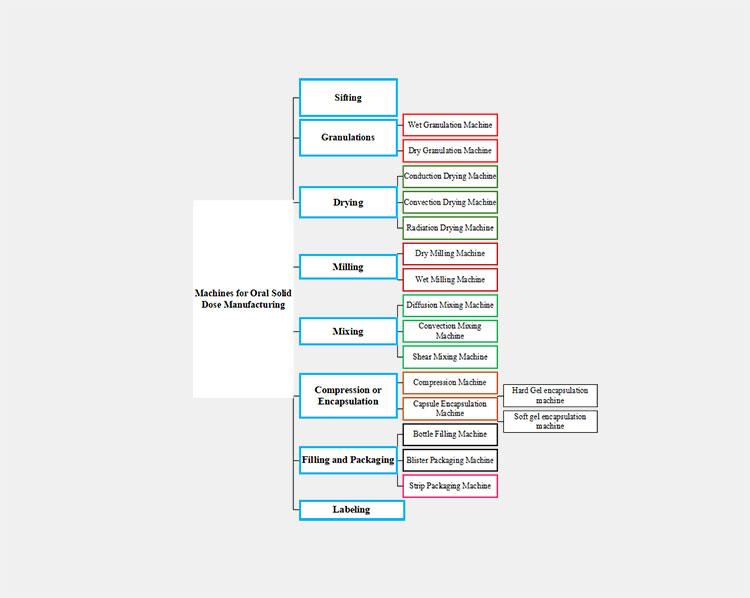
4.What are oral solid dose manufacturing machines?
A wide array of machines is involved in oral solid dose manufacturing, specially engineered to perform a specific job related to preparation, processing, and, packaging. Let’s go into the details of every oral solid dose manufacturing machine and look into their functions and examples.
Machines for Oral Solid Dose Manufacturing
Machine for Sifting
| The sifter machine of oral solid dose manufacturing operates on the mechanism of screening and grading different types of particles depending on their sizes, densities, or, other properties by passing the raw feed through a mesh screen or sieve. The mechanical energy provided by vibratory, rotational, and horizontal motion aids in the dispersal of particles across the sieve.
This fluidity and gravitational forces are integral in penetrating smaller-sized particles through the aperture of the screen whereas, larger lumps or impurities are left on the screen. These oversized particles are eliminated as rejected or coarse waste from a machine. Its examples include vibratory, centrifugal, or gyratory sifter. |

Allpack Vibratory Sifter |
Machines for Granulations
It is one of the core machines in oral solid dose manufacturing. Its function is to agglomerate the powders into larger granules to boost compressibility for tableting or encapsulation. There are two main types of granulation machines- wet granulation and dry granulation machines.
Wet Granulation Machine
| The wet granulation machine is normally used for combining or compacting fine powders into cohesive granules with the addition of a liquid binder.
First, the drug components (active ingredients and excipients) are fluidized and mixed using impellers or heated air. Afterward, the binder or granulating fluid is either sprayed or poured into the powder bed. The binder serves as glue to bind and adhere particles together and so, the powder mix is then transformed into solid granules by nucleation, growth, and, consolidation. Lumps are broken in the wet granulation machine via chopper blade and mechanical agitation. High-shear granulators, fluid bed granulators, and spray granulators are categorized as wet granulation machines. |

AIPAK Wet Granulation Machine |
Dry Granulation Machine
| In this kind of granulating machine, the fine powders are compacted into granules without incorporating granulating fluids.
The dry granulation machine only performs the task of agglomeration of dense forms, such as flakes, with the assistance of mechanical pressure. Powder mixtures are introduced into the compaction machine where counter-rotating rollers or die cavities are utilized for applying high pressure for the compaction of powders into a solid mass called ribbon or slug, respectively. Slugging machines or roller compaction machines are examples of dry granulation machines. |

Roller Compaction- Picture Courtesy: Pharmaceutical Networking |
Machine for Drying
As the name suggests, this equipment is pivotal in the evaporation of moisture or watery materials using dry heat, airflow, and mechanical agitation. Its main classification is:
Conduction Drying Machine
| In conduction drying machine, the granules or powder mixture for oral solid dose manufacturing occurs through direct contact with heated air.
The materials are placed on the heated surface. This results in a direct flow of heat from surface to materials. As a result, the feed absorbs heat and the moisture found inside the feed is moved to the surface of the material by the increase in energy. This leads to evaporation of moisture that is then discharged from the machine using ventilation systems. Drum dryer, plate dryer, and static are included in the conduction drying machine. |

AIPAK Static Vacuum Dryer |
Convection Drying Machine
| In this machine, the materials are heated by indirect heat contact. Heated air or gas is employed to convey heat to feed for drying.
Usually, at the start, the temperature of the air is increased via heating elements or steam exchangers. Later, this heated air is introduced into the drying chamber with the aid of a fan or blower. The air flows over a powdery or granular bed and distributes heat to feed, thus moisture particles with high energy begin to move upward and evaporate. Afterward, the moisture-loaded air is discharged from the outlet through exhaust pipes or a ventilation system. Tray dryers, fluidized bed dryers, rotary dryers, spray bed dryers, etc are types of convection dryers. |

AIPAK Fluid Bed Dryer |
Radiation Drying Machine
| It is the type of dryer in which high-energy radiations like infrared rays or UV radiations are utilized for directly heating the material.
The feed to be dried absorbs the electromagnetic energy of radiation, which leads to an increase in the thermal movement of molecules in the raw feed. This results in the production of heat, so that water content is vaporized from the surface. Infrared dryers or microwave dryers are examples of radiation dryer machines. |

Infrared Drying Machine- Picture Courtesy: FoodTechProcess |
Machines for Milling
This equipment plays a significant part in the size reduction of solid lumps or agglomerates through the techniques of slicing, pulverizing, or crushing. It is divided into two fundamental categories:
Dry Milling Machine
| This device does not utilize any type of liquid or fluid to fragment feed into smaller pieces. It incorporates physical measures, for instance, impact, compression, shear, or attrition to crush feed.
The dry matter is loaded into the milling component through a hopper or feeder part. Then, the material is exposed to various crushing or compression forces using blades, hammers, and rollers, for milling. In other types of dry milling machines, shear forces to cut particles or attrition forces grounded with the frictional force are applied. A sieve estimates the final size of particles. The oversized particles are transferred back to the milling chamber for further size reduction. It includes hammer mill, pin mill, ball mill, jet mill, roller mill, and universal mill. |

Allpack Pulveriser Machine |
Wet Milling Machine
| It is a specialized device typically used for size reduction of materials with the help of a liquid medium. It is involved in homogenization, emulsification, and slurry preparations. Using mechanical forces and liquid fluid, effective milling and mixing is achieved.
A blend of solid feed and liquid phase is transferred to the milling chamber and a consistent slurry mixture is formed by carefully controlling the ratio of solid-liquid. After that, mechanical forces, for instance, shear, and impact are exerted on the material as it travels through the milling chamber. These forces are exerted by the rotor-stator, grinding media, etc. The liquid phase averts the particle agglomeration and assists in consistent pulverization. Screens are incorporated at the end to ensure only materials of preferred size are offloaded from the miller. It includes a colloid mill, bead mill, rotor-stator mill, and high-shear mixer. |

Allpack Colloid Mill |
Machine for Mixing
For mixing two or more substances, the industrial mixing machine is utilized in oral solid dose manufacturing. It ensures the homogenous distribution of components in the mixture. Its types are detailed below:
Diffusion Mixing Machine
| This instrument favors gentle and homogenous mixing of powders and granules. It is based on diffusion mixing action in which particles are randomly dispersed in different directions due to the tumbling action of equipment. By rotation of the mixing vessel, the material particles lift and cascade down with gravity.
The particles are mixed in random patterns through their tumbling. This leads to diffusive mixing in which particles are fragmented and then mixed with others. Its subtypes are: V-blender, double-cone blender, drum blender, bin blender, octagonal blender, and others. |

|
Convection Mixing Machine
| Its mixing principle is based on the conventional movement of particles in which materials are lifted and folded, resulting in their homogenous distribution. Materials are displaced by the motion of paddles, ribbons, or screws and then recombined in large portions.
These agitators form a convection flowability of particles with their upward motion. With pushing and falling, the feed is evenly intermixed. Its kinds are ribbon blender, paddle mixer, screw mixer, and plow shear mixer. |

|
Shear Mixing Machine
| The materials are uniformly intermixed in the shear mixing machine with the application of shear forces.
The latter is responsible for breaking or crushing the lumps of particles and distributing these particles evenly into a mixture. A high-speed agitator or rotor rotates closely to a mobile stator, generating high-intensity shear forces. In the gap between these two blades, material particles are moved and broken down into smaller particles with shear forces. It also emulsifies immiscible liquids and mixes feed until uniform size distribution is attained. It is comprised of high-shear mixer and low-shear mixer. |

|
Machine for Compression or Encapsulation
They are the core instruments involved in the manufacturing of tablets and capsules. They include:
Compression Machine
| It is also called a tablet press machine. It holds the task of compacting or consolidating powders or granules into compact or solid tablets. The feed is filled into a die cavity through a feeder component.
After filling, the upper punch is moved down to press the material into tablets and then the end tablet is discharged from the equipment with the upward motion of the lower punch. Its examples are single-punch tablet press machines or rotary tablet press machines. |

|
Capsule Encapsulation Machine
This instrument fills or loads powders, granules, pellets, mini-tablets, liquids, pastes, or gels into shells of capsules.
Hardgel Encapsulation Machine
| It makes two-piece hard gel capsules by separating their caps and bodies and filling various types of drug materials inside the empty capsules. Finally, caps and bodies are joined together. | 
|
Softgel Encapsulation Machine
| It forms a one-piece softgel capsule by encapsulating semi-solid or oily liquids inside the softgel capsules.
The gelatin solution is formulated, heated, and loaded into the machine that transforms into two thin threads with rotating dies. After that, fill material is injected between two threads of ribbons. Finally, using heat or pressure, the gelatin ribbons are sealed and then separated into individual capsules with cutters. |

|
Machine for Coating
| This machine is involved in post-oral solid dose processes and covers the surface of medicine with a smooth and consistent layer of film, or sugar.
Oral solid doses are first loaded in the drum or pan while the spray nozzle disperses the coating fluid on the rotating oral solid dose. After, the heated air is blown into a rotating chamber to air dry the coating layer. There are various categories of coating machines, such as sugar machines, film coating machines, fluidized bed coaters, etc. |

|
Machine for Filling and Packaging
This machine loads tablets, capsules, powders, and, granules into containers or film pockets to easily distribute and deliver them to patients. After product loading, the filled containers are either capped using various caps or sealed with hermetic airtight seals with the help of film. Its fundamental categories are:
Bottle Filling Machine
| It is an important machine for packing oral solid dose in bottles. It also seals the bottles by closing them with caps.
The bottle is filled with the filling nozzles using auger fillers, multi-head fillers, etc. After filling, caps, for instance, screw caps, press-on caps, or other closures are placed on bottles and tightly twisted by torque or capping head. Some caps are secured by pressing them on bottles. |

|
Blister Packaging Machine
| It forms a blister cavity in which oral solid doses are filled. The plastic film is softened at high temperatures and molded into the desired cavity using a molding device. Then products are fed into cavities and then these pockets are sealed by aluminium film with the application of heat or pressure. | 
|
Strip Packaging Machine
| It encloses tablets or capsules into strip-like packages in between two webs or layers of packaging film made of Aluminium, paper, or plastic. Heated rollers or sealing plates are employed to seal two layers. | 
|
Machine for Labeling
| This device is employed at the post-packaging stages, and it sticks or prints the information or product label to the oral solid dose bottles, boxes, or, jars.
It fixes labels either around the whole circumference of the packaging container, its front or back panel, or its top end. This device has a guiding system that places the container for correct labeling orientation. The labels are unwound from film and the labeling head or press smoothly applies them without causing their creasing or misalignment. |

|
5.What are the critical challenges associated with oral solid dose manufacturing?
Whether it is pharmaceutical, nutraceutical, or any other industry, formulating oral solid dose manufacturing may impose certain challenges. However, with thorough research, and expertise, I consider you will be capable of dealing with these challenges easily. Here, I have talked about some common pitfalls with easy approaches that will present flexibility in your production process.
Non-standard shapes and sizes
Oral solid doses with different shapes and sizes
In traditional oral solid dose manufacturing, you were supposed to make regular-shaped tablets and capsules, but today times have changed, and requirements have changed. You are now subjected to make various shapes, and sizes of oral solid dose manufacturing. For that, it is quite substantial to have an optimized manufacturing protocol and make a broad strategy and need to bring advanced types of machinery with a series of dies, and mold, with a balanced running approach.
Sticky oral solid dose products
Stickiness- Picture Courtesy: Nutribear Gummies
Stickiness and moisture trapping are critical problems that can affect the quality and stability of the oral solid dose. Especially when you are dealing with gummies or any softer products such as soft gel capsules, you might encounter sticky surface problems that might be due to high temperatures and humidity.
Various machine body construction with premium quality stainless steel is the remedy. You can have production under a controlled environment with simultaneously good machines can be an easy solution to avoid the problem by preventing the adhering of products with machines contact or related materials.
Cross-contamination
Cross-contamination- Picture Courtesy: Elohealth
Formulation oral solid dose manufacturing may sometimes meet the cross-contamination problem. This is not only challenging but can result in the overall production of the batches which ultimately results in withdrawal. You need to have critical monitoring over maintenance and cleaning of the machines by having daily, weekly, and monthly check-ups. This is the simple and easy gateway to prevent big problems, it will not only keep your productivity protected but can extend the machine’s life.
Conclusion
Oral solid dose manufacturing is considered the lifeblood of pharma-based industries. While it is very important to understand insight about APIs, and excipients when it comes to manufacturing them. Not only this but knowing about machine learning and its proper utilization can help you to improve your business with achieving market differentiation. However, this is a challenging task but at the AIPAK team, we are the experts in offering a vast range of machines involved in oral solid dose manufacturing for over a decade. We are always continuously helping pharma and related companies by offering them tremendous solutions ensuring excellent quality and conformities in them throughout production. If you looking to find solutions for oral solid dose manufacturing, please contact us to discuss how we could assist you.
Don't forget to share this post!
Granulator Machine Related Posts
Granulator Machine Related Products
Granulator Machine Related Videos
CONTACT US
Tell us your raw material and project budget to get quotations within 24 hours.
WhatsApp Us: +86 181 6426 8586

Want the best price & newest pharmaceutical machinery buying guide,tips and trends sent straightly to your box?Sign up for AIPAK’s monthly newsletter,we’re free for your consultation and Offer you the most suitable solutions!
The Buyer's Guide
- Capsule Filling Buyer's Guide
- Blister Packaging Buyer's Guide
- Tablet Counting Buyer's Guide
- Tube Filling Buyer's Guide
- Cartoning Buyer's Guide
- Gummy Making Buyer's Guide
- CO2 Extraction Buyer's Guide
- Empty Capsules Buyer's Guide
- Suppository Filling Buyer's Guide
- Tablet Coating Buyer's Guide
- Tablet Press Buyer's Guide
- Softgel Encapsulation Buyer's Guide
Most Popular
- 7 Importance Of Pharmaceutical Packaging In Different Applications You Must Know
- 6 Advantages You Must Know About Tablet Counting Machine
- 8 Advantages of Blister Packaging You Must Know
- 6 Critical Applications of Automatic Capsule Filling Machine
- 6 Stations You must Know to Improve the Filling Quality of Automatic Capsule Filling Machine