OEB Level:The Complete FAQ Guide In 2025
Personnel in pharmaceutical and chemical manufacturing companies, especially those who are frequently contact with various chemicals, need to be careful when handling hazardous materials. Because there are many chemicals and substances that are very dangerous, known as highly effective active pharmaceutical ingredients.
OEB Level-sourced: virgool
In order to curb and eliminate the chances of personnel being exposed to hazardous compounds and improve their safety, OEB levels were developed and widely adopted. Following this OEB level guide, you may have a clear understanding of their safety standards. Take a look now!
1.What Does OEB Mean In Pharmaceutical Industry?
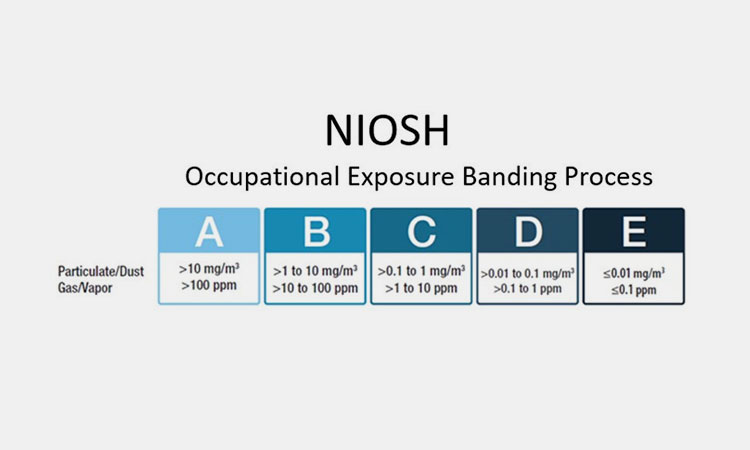
What Does OEB Mean In Pharmaceutical Industry-sourced: aiha
OEB, the full name is occupational exposure banding, also known as hazard banding, health hazard banding or exposure banding. It is a process of assigning chemicals to different levels or categories based on their toxicity and the risk of adverse health effects associated with exposure.
Based on the occupational exposure band, industrial hygienists, occupational and environmental health and safety professionals can predict the health of workers and take appropriate protective measures. This standard is developed and issued by NIOSH to help protect you or worker health exposed to chemicals at work.
2.What Is OEB Category?
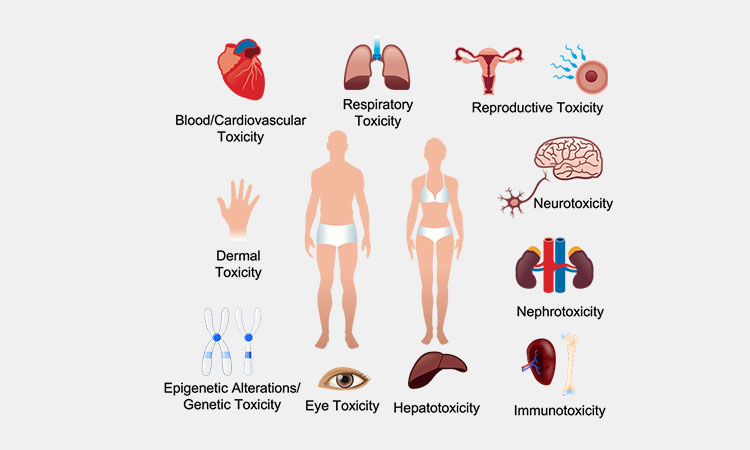
The OEB category is a toxicological or human health indicator of the reaction after exposure to the hazard. These include the following nine categories:
Eye Damage Or Irritation
Eye Damage Or Irritation-sourced: is
You may experience symptoms such as tearing, stinging, soreness, and inability to open your eyes if you have exposed to some chemicals. It may also cause diseases such as photoelectric eye inflammation, corneal damage, and dry eyes.
Skin Corrosion Or Irritation
Skin Corrosion Or Irritation-sourced: is
Skin corrosion and irritation refers to irreversible damage to your skin, including ulcers, bleeding, skin peeling, scabs, dermal necrosis, etc.
Respiratory Sensitization
Respiratory Sensitization-sourced: safetyplus
When you breathe substances into your lungs, it is prone to respiratory allergies, resulting in allergic coughs, allergic asthma, etc.
Skin Sensitization
Skin Sensitization-sourced: vecteezy
When exposed to the chemical substances, your skin will show a high reaction state under physiological or pathological conditions. The skin may show symptoms such as burning, stinging, itching, tightness, capillary dilation, etc.
Acute Toxicity
Acute Toxicity-sourced: uxwing
Acute toxicity refers to the poisoning effect caused by operators after contact with foreign compounds, and even causes death.
Specific Target Organ Toxicity
Specific Target Organ Toxicity-sourced: toxmsdt
It refers to specific, non-lethal target organ toxicity after a single exposure to some chemical substances and mixtures. All significant health effects that may impair function, reversible and irreversible, immediate or delayed.
Reproductive Toxicity
Reproductive Toxicity-sourced: is
Some chemicals may have adverse effects on reproductive functions of the parent such as germ cells, conception, pregnancy, delivery, lactation, as well as adverse effects on embryo-fetal development and postnatal development of the offspring.
Genotoxicity
It is a malignant effect that may cause DNA damage.
Carcinogenicity
Carcinogenicity-sourced: is
The carcinogenicity refers to the property of toxic chemicals or other chemical agents that can cause organisms to produce cancer cells due to the intake of this chemical.
To sum up:
It gives a total score based on each health effect. According to the severity of the most serious health result, the investigated substances are marked with A, B, C, D or E grades, where "A" means the least harmful and "E" means the most harmful.
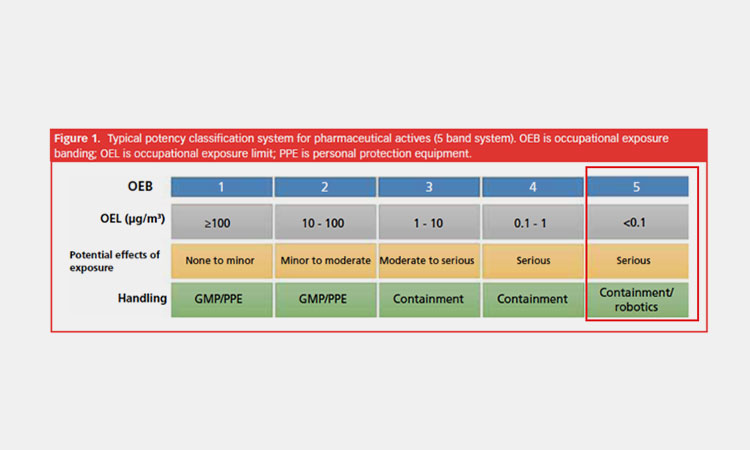
3.What Is OEB Classification?
What Is OEB Classification-sourced: selliliar
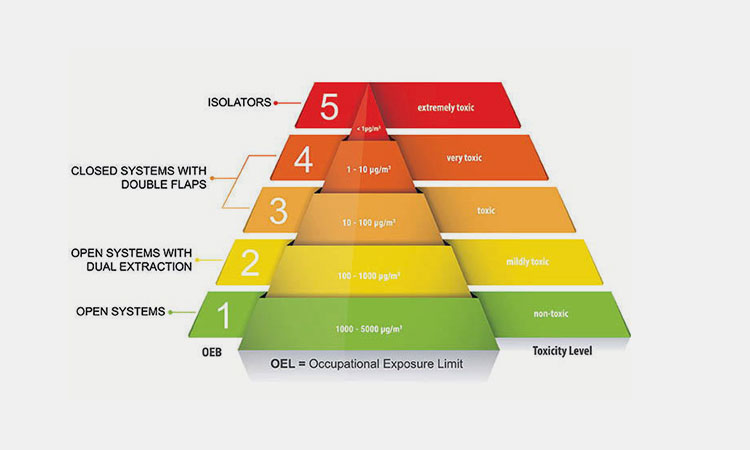
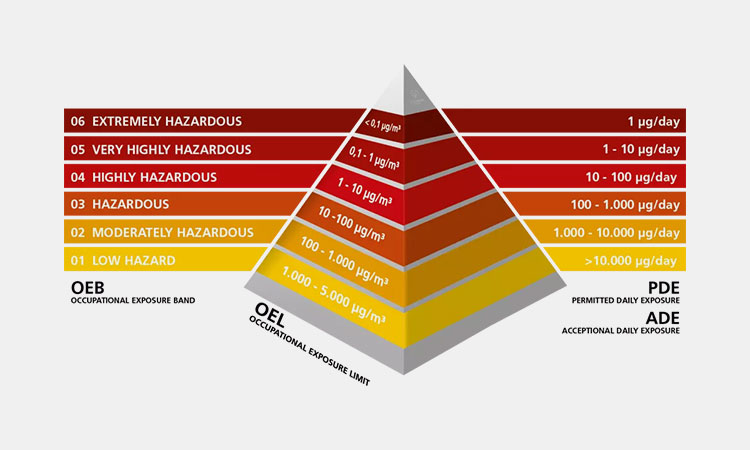
The OEB has 5 levels, A, B, C, D or E, depending on the substance being investigated. Each material identified by an OEB level has an associated target range for airborne particulate and vapor concentrations.
OEB Level 1 (A)
This level of toxicity does not pose a hazard to operators, as it is the lowest level. When handling this level of material, you need to work in a well-ventilated process room or suitable work environment.
OEB Level 2 (B)
OEB Level 2 materials pose a low risk of toxicity. However, in addition to the previous ventilation measures, you need to install special exhaust vents in the down-flow or cross-flow room to prevent dust transmission.
OEB Level 3 (C)
OEB Level 3 materials are mildly hazardous. You should take measures to prevent exposure during handling. This includes using flexible isolators and glove bags as a safe barrier, or using a continuous liner system to provide a suitable closed exhaust method.
OEB Level 4 (D)
OEB Level 4 materials are hazardous. You need to have a physical barrier in place when handling this material. You need to use isolators and restricted access barrier systems, or manipulate equipment and materials externally through glove ports.
OEB Class 5 (Class E)
OEB Class 5 materials are highly hazardous. A permanent physical barrier is required between you and the material. Within isolators and restricted access barrier systems, you need to perform closed material handling and transfers through glove ports and cannot handle materials openly.
Table 1: The OEB Level Guide
| OEB Classification | OEB Level | OEL Level | Hazardousness | Methods of Containment | Equipment To Use |
| 1 | > 100 mg | >1000-5000 µg/m3 | Non-hazardous | Open system with local extraction; | Ventilation containment |
| 2 | 10-100 mg | >100-≤1000 µg/m3 | Almost Non-hazardous | Down-flow booths, cone valve drum containment; | Single pass fume cabinets |
| 3 | 1-10 mg | >10-≤100 µg/m3 | Mildly Hazardous | Spilt valves, down-flow booths, cone valve drum containment, continuous liners; | VBEs, flowhoods |
| 4 | 0,1-1 mg | >1-≤10 µg/m3 | Hazardous | Isolaters, spilt valves, cone valve drum containment, continuous liners; | VEBs or DFBs with higher containment |
| 5 | < 0,1 mg | <1.0-0.01 µg/m3 | Highly Hazardous | Isolaters, spilt valves with dedicated extraction/washing, cone valve drum containment, continuous liners; | Isolators recommended |
| 6 | < 0,01 mg | 0.01-0.001 µg/m3 | Extremely Hazardous | Aseptic containment isolator with complete closed transfer; | Isolators |
4.Why Do You Need OEB Levels?
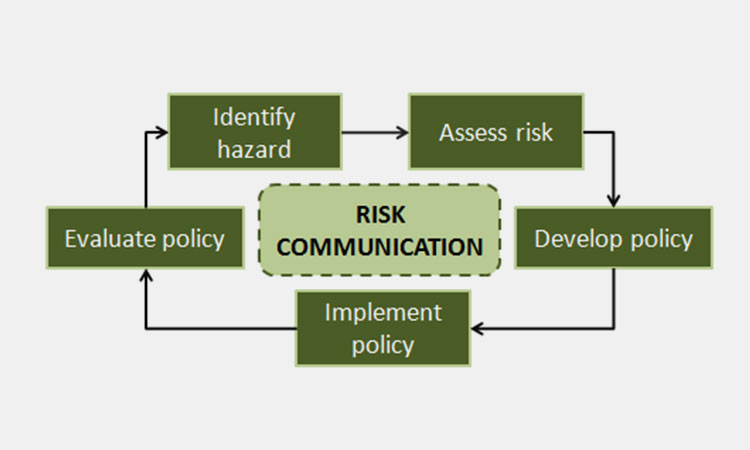
Why Do You Need OEB Levels-sourced: aiha
The OEB levels protect workers and prevent cross-product contamination. Furthermore, it provides you a systematic and standardized approach to assessing the potential risks associated with exposure to different substances.
Risk Communication
Risk Communication-sourced: researchgate
OEB levels help you more clearly and standardize the definition and communication of potential hazards associated with operators and substances. It facilitates effective communication and protection between different stakeholders including workers, employers and regulators.
Risk Assessment
Risk Assessment-sourced: purplesec
OEB levels prevent the risk of illness, injury, disability and premature death by assessing the risk of workers being exposed to potentially harmful chemicals. It also helps you conduct risk assessments for chemicals and chemical mixtures.
Risk Management
Risk Management-sourced: online
By classifying different substances into different levels, OEB levels help you develop appropriate control measures to minimize exposure, including engineering controls, personal protective equipment and other risk mitigation strategies to prevent workers from being exposed to potentially harmful chemicals in the workplace.
Improve Objectivity in Chemical Assessments
Improve Objectivity in Chemical Assessments-sourced: sciencedirect
Using a grading strategy, OEB levels can improve the consistency and objectivity of harmful chemical assessments, thereby providing recommendations for controlling the risks of chemicals used in a given task.
Avoid Impacts
Avoid Impacts-sourced: intelligent
The release of highly active drugs can seriously endanger the safety of operators. The formulation and implementation of OEB standards can help take reasonable and effective preventive management measures in the entire plant design, equipment selection, personnel and logistics flow, and production management.
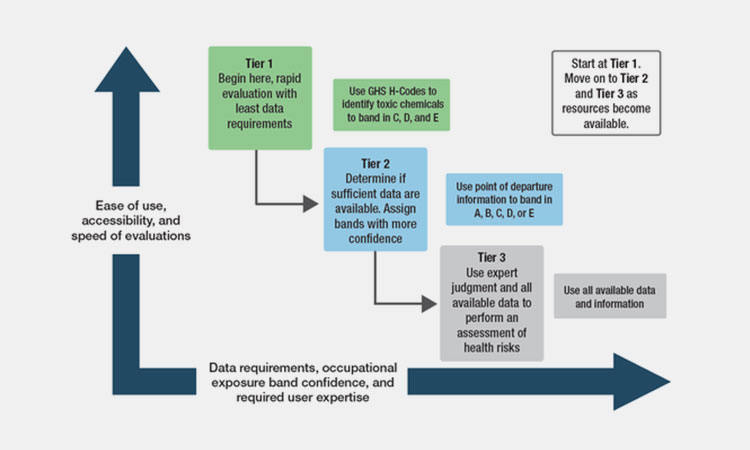
5.What Are The Appropriate Tier To Use OEB?
What Are The Appropriate Tier To Use OEB-sourced: wikipedia
During your work, you can use the exposure grading process based on the three-tier approach of the NIOSH occupational exposure grading process.
Tier 1
You need relatively little information about the material and only require simple professional training. It mainly provides a quick summary of the health effects related to the chemical of interest. You can quickly identify these materials.
Tier 2
You can check publicly available databases for related materials and extract relevant toxicological data. These information can be input into the grading algorithm.
Tier 3
Expert judgment is required to critically evaluate experimental data and discern toxicological results.
To sum up:
Once you are familiar with the appropriate tier process of the OEB, you can determine a method to measure whether the workplace exposure is within the range in the subsequent material processing. If your material results exceed the limit, you will take appropriate control measures.
6.What Are The Evaluation Criteria For OEB?
You can follow the evaluation criteria for OEB in below:
Product Dust
Product Dust-sourced: spray
The smaller the particle size of your material, the more likely it is that the powder will become airborne. This creates a greater chance of contamination. You need to consider operating in a well-ventilated space or with exhaust facilities.
Product Types
Product Types-sourced: clinicallab
If your product is cytotoxic or genotoxic and requires a range of 1-5 micrograms, you should consider operating in a fully enclosed space or an isolator. You may also need to use additional protective equipment (full air-supplied suits), etc.
Material Processing
Material Processing-sourced: labmanager
The longer you need to perform the process, the higher your potential exposure risk. The higher the amount of powder you handle at one time, the higher the risk.
7.What Is OEB 5 Compound?
What Is OEB 5 Compound-sourced: pharmtech
The OEB 5 compound refers to an active pharmaceutical ingredient assessed as the most severe category in the OEB E. It generally has the following characteristics:
Extremely Strong Medicinal Effect
The OEB 5 compound is extremely potent and the therapeutic dose is less than 0.5 mg/day.
Significant Adverse Reactions
Even at extremely low doses, the OEB 5 compound has significant adverse effects, including life-threatening or irreversible or severe sensitization.
Genotoxic
At relevant doses, the OEB 5 compound may have genotoxic, carcinogenic or reproductive effects.
Related Drugs
Some compounds other than oncology products may also be OEB 5 compounds. For example, vitamin D3, among others.
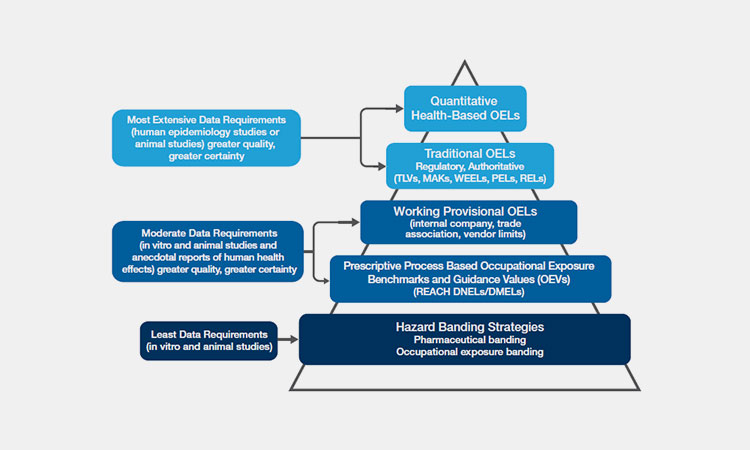
8.What Is Control Banding?
Control Banding-sourced: ohswa
The control branding is primarily used to objectively assess the hazards of chemical materials and to support risk management decisions in the absence of clear occupational exposure limits.
It primarily defines the range of air concentrations that are expected to protect worker health and help protect workers and emergency personnel from hazardous concentrations of airborne substances. It is the gold standard for protecting workers and emergency personnel from hazardous concentrations of airborne substances.
Table: The Control Banding For Exposures To Chemicals By Inhalation
| Band No. | Target Range of
Exposure Concentration |
Hazard Group | Control Methods |
| 1 | >1 to 10 mg/m3 dust
>50 to 500 ppm vapor |
Skin and eye irritants ; | Use good industrial;
hygiene practice and general ventilation; |
| 2 | >0.1 to 1 mg/m3 dust
>5 to 50 ppm vapor |
Harmful on single exposure; | Use local exhaust ventilation; |
| 3 | >0.01 to 0.1 mg/m3 dust
>0.5 to 5 ppm vapor |
Severely irritating and corrosive; | Enclose the process; |
| 4 | <0.01 mg/m3 dust
<0.5 ppm vapor |
Very toxic on single exposure, reproductive hazard, sensitizer; | Seek expert advice; |
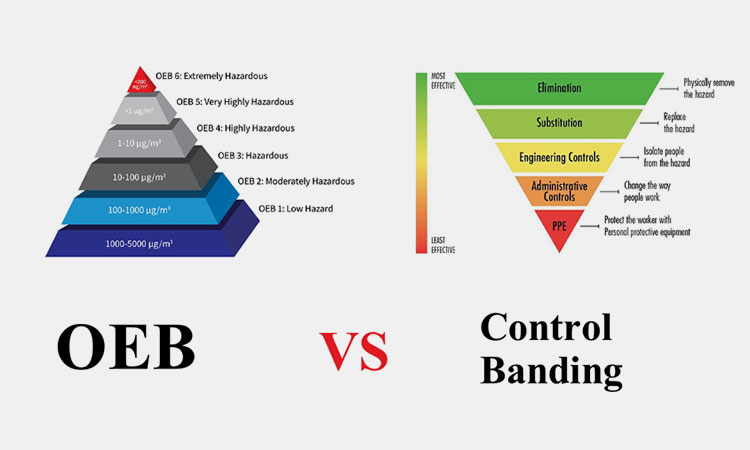
9.Is OEB the Same As Control Banding?
Is OEB the Same As Control Banding-sourced:ohswa
Different from the control banding, the OEB does not produce specific risk management and exposure control recommendations. Their specific differences are:
| OEB | Control Banding | |
| Definition Ranges | l It defines the dangerous range of hazardous substance concentrations that harm organisms; | l It defines the range of air concentrations that are expected to protect worker health; |
| Grading | l The OEB graded calculation an exposure limit range for comparison;
l You need to determine a method and measure the exposure; l To calculate whether the workplace conditions are within this range; |
l Control banding grade calculation requires specific measurement of the air concentration range for worker health;
l Once determined, a method must be developed and measured and analyzed; l And propose corresponding improvements and control measures to help reduce the risk goals; |
| Classification | l A, B, C, D, E;
l Grade A represents the lowest hazard and Grade E represents the highest hazard; |
l 1, 2, 3, 4;
l 1 represents the lowest dust concentration and 4 represents the highest dust concentration; |
| Grading Method | l The grading process adopts a three-tier approach;
l Tier 1, tier 2, tier 3; l Requires professionally trained users and experienced toxicologists to perform classification; |
l Calculate control methods based on GHS hazard statements;
l And retain air monitoring to verify that controls are effective; |
| Control | l OEB does not produce specific risk management and exposure control recommendations; | l Once control banding is determined, methods must be developed and measurements and analyses must be performed; |
10.What Is OEL?
What Is OEL-sourced: circularcanarias
OEL, known as occupational exposure limit, is a regulatory value. It indicates the level of exposure to a chemical in the air of the workplace that is considered safe. Specifically, it is the level of exposure that all employees can be exposed to for 8 hours per day and 40 hours per week without experiencing any harmful effects.
This guideline is that controlling exposure to hazardous chemicals in the workplace is a major strategy to ensure you a safe and healthy environment related to product safety and operator protection. After establishing the OEL, you need to evaluate the manufacturing environment to determine the appropriate level of control.
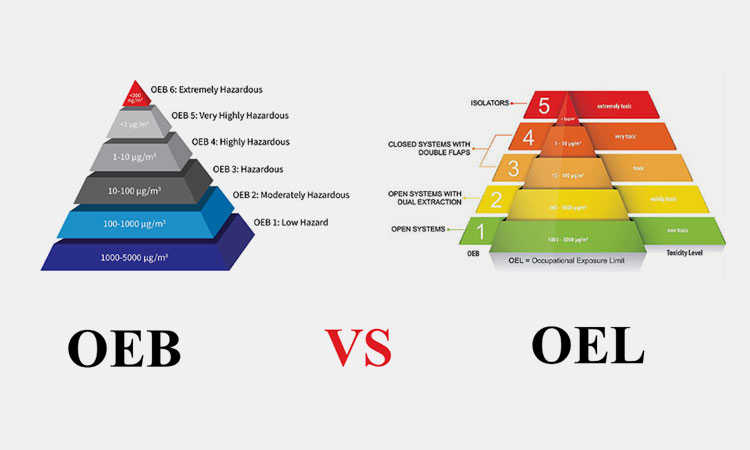
11.What Is The Difference Between OEB And OEL?
What Is The Difference Between OEB And OEL
OEB and OEL are two different concepts:
| OEB | OEL | |
| Full Name | Occupational Exposure Band | Occupational Exposure Limit |
| Explain | l The process of assigning chemicals to different grades or categories based on their toxicity and the risk of adverse health effects associated with exposure; | l The OEL, also called as PEL, is the maximum concentration of a harmful substance that a person can be exposed to without getting sick or hurt; |
| Purpose | l Select appropriate production facilities and operating procedures for each product production;
l Establish a classification standard to prevent adverse health effects from workplace exposure; |
l To help keep the workplace a relatively safe place, especially from toxic airborne chemicals; |
| Formulators | l They are established by authoritative organizations such as NIOSH; | l Such limits are established by EU and national regulatory agencies; |
| Scope of Application | l All toxic chemicals; | l Chemicals such as vapors, mists or dusts inhaled by workers; |
| Determination Methods | l Toxicological assessment;
l Occupational exposure limit (OEL) comparison; l Threshold assessment; |
l Collect data;
l Environmental assessment; |
12.What Is The Difference Between OEB And OHC?
OHC-sourced: ecampusontario
Follow the table below to figure out the differences between OEB and OHC:
| OEB | OHC | |
| Full Name | Occupational Exposure Band | Occupational Health Categorization |
| Explain | The process of assigning chemicals to different grades or categories based on their toxicity and the risk of adverse health effects associated with exposure; | Is a health-based risk assessment for appropriate manufacturing and worker handling of active pharmaceutical ingredients when limited information is available; |
| Scope of Application | All toxic chemicals; | All active pharmaceutical ingredients in nonclinical testing and early-stage new drugs in clinical trials; |
| Purpose | Select appropriate manufacturing facilities and operating procedures for each product production;
Develop a grading standard to prevent adverse health effects from workplace exposure; |
Effectively communicate the hazards and risks of active pharmaceutical ingredients to your workers or external contracting companies;
Provide you with a range of acceptable worker exposures and internally prescribed handling practices; |
| Features | The higher the OEB level, the more stringent the controls are; | The higher the OHC level, the more stringent the highest level of engineering, management, and personal protective equipment is required; |
| Formulators | They are developed by authorities such as NIOSH; | Pharmaceutical manufacturers and contract manufacturing organizations (CMOs) Jointly formulated; |
| Classification | "A" represents the least harmful, while "E" represents the most harmful; | Class 1 represents the least harmful compounds, while Class 4 or 5 compounds are considered extremely potent; |
13.What Are The Importance Of Implementing a OEB Strategy?
The OEB provides a systematic and standardized approach to assessing the potential risks associated with exposure to your different substances. To implement a OEB strategy is important due to the reasons:
Occupational Exposure Protection
Occupational Exposure Protection-sourced: cdc
The ultimate goal of the OEB strategy is to protect your workers and emergency personnel from the concentration of hazardous substances in the air, thereby protecting their health and ultimately implementing control measures in the workers' workplace.
Consistency and Objectivity
Consistency and Objectivity-sourced: cdc
Implementing an OEB strategy can improve the consistency and objectivity of chemical assessments. Due to incomplete hazard analysis, you may generally choose low-level controls. But by adopting an OEB strategy, you can define, prioritize and apply to a wider range of workplaces.
Data Organization
Data Organization-sourced: wikipedia
Through continuous improvement and supplementation, OEB helps organize chemical hazard data and identify gaps in the data, facilitating the development and implementation of subsequent control measures.
Prioritization
Through investigation and processing, OEB can help prioritize chemicals that may need more attention, such as those with results of D or E.
Simpler and Faster
Compared with OEL, OEB chemical classification requires less time and less data to develop than OEL, which has a simpler and faster effect.
Conclusion:
Through the complete guide of OEB level, you may properly use and deal with the active pharmaceutical ingredients (API) during your materials processing. In order to protect your workers health, there are more you need to know and learn about. If there are more you want to know about, do not hesitate to contact us!
Don't forget to share this post!
Vacuum Emulsifying Mixer Related Posts
Vacuum Emulsifying Mixer Related Products
Vacuum Emulsifying Mixer Related Videos
CONTACT US
Tell us your raw material and project budget to get quotations within 24 hours.
WhatsApp Us: +86 181 6426 8586

Want the best price & newest pharmaceutical machinery buying guide,tips and trends sent straightly to your box?Sign up for Aipak’s monthly newsletter,we’re free for your consultation and Offer you the most suitable solutions!
The Buyer's Guide
- Capsule Filling Buyer's Guide
- Blister Packaging Buyer's Guide
- Tablet Counting Buyer's Guide
- Tube Filling Buyer's Guide
- Cartoning Buyer's Guide
- Gummy Making Buyer's Guide
- CO2 Extraction Buyer's Guide
- Empty Capsules Buyer's Guide
- Suppository Filling Buyer's Guide
- Tablet Coating Buyer's Guide
- Tablet Press Buyer's Guide
- Softgel Encapsulation Buyer's Guide
Most Popular
- 7 Importance Of Pharmaceutical Packaging In Different Applications You Must Know
- 6 Advantages You Must Know About Tablet Counting Machine
- 8 Advantages of Blister Packaging You Must Know
- 6 Critical Applications of Automatic Capsule Filling Machine
- 6 Stations You must Know to Improve the Filling Quality of Automatic Capsule Filling Machine