Is Gelatin Same as Pectin?
Appetizing and longer shelf life of jams, jellies, candies, gummies, fruit spreads is attributed to gelatin and pectin. These are used as thickening agents for many food items and are colorless soluble substances.
Is Gelatin Same as Pectin?
People confuse these two emulsifiers and consider them one. However, gelatin and pectin are very much different from each other. They have different origin, structure, cooking method, nutritional properties and health benefits.
Let’s learn the differences between these two ingredients.
1.What Exactly Gelatin and Pectin are?
Gelatin is animal-based ingredient generally used as thickening agent, emulsifier, and stabilizing agent. It is a hydrocolloid that has good film-forming properties and has adhesivity.
Gelatin is naturally occurring and translucent powder. It is widely used ingredient to impart jelly-like feel to food items. This material is crumbly in dried form and mushy when wet.
Pectin is also used as thickening agent in jams, jellies, and candies although it is less commonly used than gelatin. It is a plant-based material and is suitable gelling agents for people on vegan, halal, or kosher diet.
It is light brown powdery substance and have subtle fruit like taste however it does not give any taste to recipes.
2.What is the history of gelatin and pectin?
Gelatin is used as food agent in Ancient Chinese and Ancient Egyptian civilizations. Around 8 thousand years ago, gelatin was used as glue.
However, its application as a functional food substance began when Frenchman Papin invented digestor in 1682. 200 years ago, people considered gelatin as the nutrition food material.
For hundreds of years, pectin was used in food manufacturing. Its gelling characteristics are known for some time.
But its commercial isolation began at the start of twentieth century. In 1825, chemist Henri Braconnot first prospered in separating pectin from fruits. First, dried apple pomance was used as source for pectin but later in 1920s and 1930s, commercial plants were built for extracting pectin both from apple pomace and citrus fruit skin.
3.Is Gelatin Same As Pectin?
No, They’re not same; whether it is gelatin or pectin, both are used as gelling agent in gummies preparation. But they’re not similar in many ways.
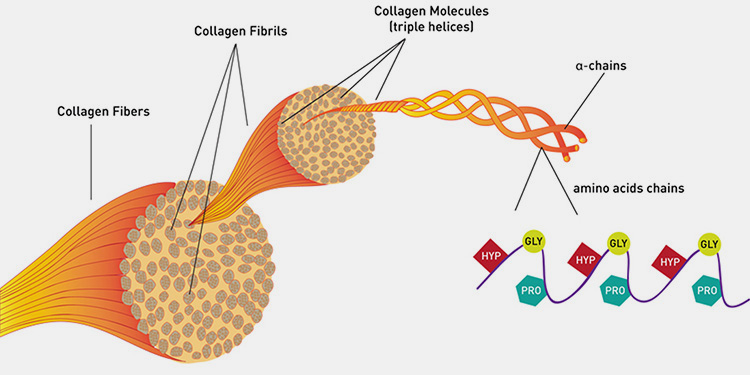
Animal sources such as their skin, bone, and connective tissues are used for making gelatin. It is the form of collagen obtained from boiling animal-based sources such as tendons, skin, ligaments of cows, pigs, cattle, horses, and fish. About 75% of gelatin is produced by hides of bovine and pork while 25% of gelatin comes from animal bone and meat chuck having cartilage.
Pectin is a water-soluble fiber usually present in cell wall of different plant. Pulp and skins of fruits are used for acquiring pectin. Fruits like apple, grapes, and citrus fruits have high quantity of pectin while pear and peaches have little concentration of pectin.
4.What is the Structural Core of Gelatin and Pectin?
Gelatin is a biopolymer acquired from denatured or hydrolyzed collagen. It consists polypeptide chain having18 amino acids. These chains are held together by hydrogen bonds. Gelatin has high number of glycine, proline, and 4-hydroxy proline reidues. Its molecular formula is C102H151N31O39.
Pectin is a heteropolysaccharide, a complex carbohydrate made solely from d-galacturonic acid units that are bonded together by -(1–4) glycosidic linkages. Side chain of pectin also has neutral sugar such as xylose, galactose and arabinose. It also contains sodium, potassium, calcium, and ammonia and has weight of about 150,000 Daltons.
5.How do you get Gelatin?
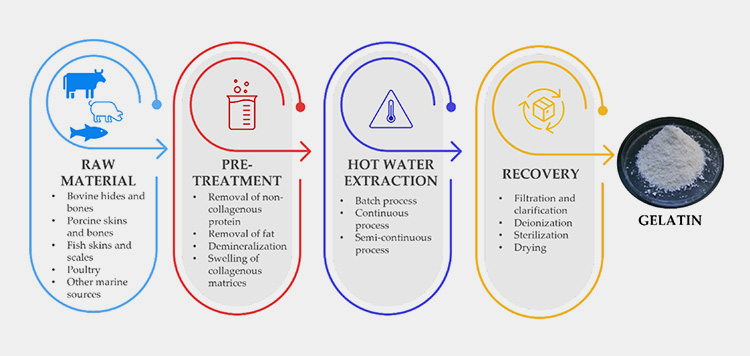
For industrial extraction of gelatin, the animal parts are first cut into small fragments.
- Then these are washed with high pressure water. Oils are removed from these pieces by placing them in hot water and then these chucks roasted at temperature of 100°C.
- These roasted animal pieces are placed in container of acid or alkali for 5 days to separate mineral and microbes from them. This process also releases collagen from fragments.
- After chemical treatment, animal parts are boiled and liquid containing gelatin is extracted via tube.
- This liquid is then sterilized and filtered for removing pieces of skin or bone. Afterwards, water is evaporated and solid gelatin is shaped into sheets and grounded into powders.
6.How do you Get Pectin?
Commercially pectin is produced using fruit which are harvested after drying. After drying, these fruits are placed in water solution containing enzyme, that is used for isolation of pectin from fruits. These enzymes separate protopectin from fruit peel by hydrolysis.
Chucks of fruit skin are removed from the pectin suspension by filtration which ensures good quality of pectin. The resultant pectin syrup after filtration is precipitated by addition of alcohol (S:E, 1-2HR), and then purified by second filtration for isolating pectin. This purified pectin is then dried at 50 degrees -and pulverize into powders.
7.What is the Setting Temperature of Gelatin?
Gelatin set at lower and cooler temperature. This setting temperature is few degrees than room temperature around 20°C(70°F). At temperature of 20°C, gelatin takes longer time for setting and does not have firm texture.
However, if gelatin is placed in fridge at temperature of about 0-10°C, it will be firmer and set more quickly in approximately 6-10 hours.
Setting temperature of gelatin is generally depended upon the ingredients such as sugar, salt, and water used in gelatin formulation.
Moreover, setting temperature of gelatin also depends upon its initial temperature, degree of hotness, environmental temperature and quantity of gelatin. Sheet of gelatin set more rapidly than bowl of gelatin.
8.What is the Setting Temperature of Pectin?
Unlike the setting temperature of gelatin, pectin typically set at much higher temperature. The gelling properties activate at about 80-85°C. Gradually boiling pectin increases its ability to set.
Setting of pectin occur at temperature of 104°C. At this temperature, pectin molecules are crosslinked together to take gel like appearance.
Sugars and acids usually affect the gelling or setting temperature of pectin. Furthermore, this temperature is also correlated to type of pectin. Rapid-set pectin set faster than slow-set pectin but this setting usually occurs at high temperature.
9.Is Gelatin is Nutritionally Beneficial Than Pectin?
As both gelatin and pectin are obtained from different source that’s why these two have different nutritional profile. Pectin is a water-soluble polysaccharide and is rich in fiber and about 34% of daily fiber requirement is covered by consuming pectin.
1 ounce of packet pectin has 106 calories. Moreover, pectin is a good source of cooper, iron, and zinc. Some nutritional benefits of pectin are:
- Carbohydrate- 45 g
- Fiber- 4 g
- Zinc- 2mg
Although gelatin contains less calories than pectin about 94 calories per 1 ounce packet, it is more nutritional beneficial than gelatin. It is an excellent source of protein satisfying about 42% of daily protein need for men and covering 52% of daily protein for women. It has 18 amino acids and 17 of which are essential amino acids except tryptophan.
Gelatin is a rich source of selenium and phosphorus. Nutritional facts of gelatin are:
- Protein- 24g
- Phosphorus- 141mg
- Glycine- 27%
- Proline- 16%
10.Is Gelatin Consistency More than Pectin?
Viscosity is defined as difficulty in flow of material while blooming is gel strength or firmness. Both these terms have a role in determining thickening effect of gelatin and pectin.
It has been observed that gelatin is more elastic and viscous than pectin. It is water soluble and its gelling nature contributes in its consistency. Food grade gelatin has blooming range of about 80-300 while the viscosity in the range of 20-40 mps.
Higher blooming means more firm consistency. These characteristics make gelatin an excellent thickening agent.
Pectin has lower gel strength and usually require sugar, salts and acid for its setting resulting in its reduced firmness and consistency. Pectin has softer and squishier consistency.
11.Is Gelatin Tastier than Pectin?
Unlike pectin, gelatin has no taste and smell and is regarded as flavor neutral. It usually takes on the flavor of dish in which it is added. It can be added in dishes for thickening purposes without changing flavor of dishes.
However, pectin has a subtle bitter taste usually depended upon fruit from which it is extracted. Sugars added in dishes to balance slight bitter flavor of pectin. Pectin often has advantage over gelatin because of its taste boosting characteristics since it pop up taste of dishes.
Manufacturers prefer using pectin in confectionaries since it promotes flavor release of confectionaries and desserts .
12.Is Gelatin and Pectin Gives Same Texture?
Texture and feel of food give magical properties to its taste, appearance, and smell. Texture of food is impacted by various factors such as softness, fluidity, hardness, and flexibility. Mouthfeel is perception of senses is also determined by its graininess, wetness, and dryness.
The texture of gelatin and pectin is very different from each other. Gelatin have chewy and firm texture while pectin is shorter and softer in texture.
Gelatin forms gel when its molecules interact and cross-link with each other. This characteristic of gelatin will result in its blooming thus giving gelatin firm and elastic texture.
Gelatin is often employed in culinary for adding shape and texture to desserts and candies. Gummies manufactured from gelatin have stretchy and stringy texture.
Pectin forms spreadable gels thus have soft and tender texture. Pectin gels are called jellies and these polysaccharide jellies form thick solutions when they changed into solid. They have softer bite but have brittle texture and are not elastic, chewy and stretchable. Pectin is preferred in dishes due to its creamy and smooth texture.
13.What is More Economical? Gelatin or Pectin?
Purchase cost is differential factor that is given due consideration when choosing gelatin or pectin. The buying cost of gelatin is significantly less than pectin as process for gelatin extraction is more optimized and animal materials are easily available.
There is difference of 1:5 in cost of gelatin versus pectin. Gelatin is $5 to $6 per pound while price of pectin id about $25 per kg.
But halal or kosher based gelatin is more costly than its pectin counterpart.
Special storage and transport conditions products like cooling rooms, air conditioning and ice packs are required for gelatin products which increases operational expenses. Pectin products do not need these special conditions for storage
14.What is More in Demand? Gelatin or Pectin?
Gelatin is best stabilizing and gelling agent and is favorite choice among manufacturer due to its excellent gelling characteristics and versatility. It is high in demand as it is utilized for manufacturing vast array of products from softgel capsules, to marshmallows, to gummies etc. Moreover, melt-in-mouth characteristics of gelatin and its shiny appearance make it winner in the eyes of manufacturers. It creates products with vibrant and transparent colors that is well liked by children and adults.
However, animal-based origin of gelatin creates difficulty for manufacturers due to certification for required for halal and Kosher. Pork gelatin is the most popular type of gelatin but porcine based products are not consumed by Muslim and Kosher people due to religious faith.
Due to these obstacles, now brands owners are using pectin for improving consistency of their products. Plant-based pectin is favored by vegan or vegetarian consumers as well as Muslim and people on Kosher diet.
Manufacturer are also switching to pectin because it also has significant advantage over gelatin as it has high melting point (>35%) and does not easily melt at room temperature which is why pectin-based products do not lose their integrity on high temperature. This reduces product wastage and lowers distribution cost.
Demand for pectin is increasing because of customer preference and its benefit of higher melting point.
15.Is Gelatin Safe as Pectin?
Pectin is considered as safe substance as it is made with plant and fruit sources which does not carry risk of disease. Although pectin is considered as safe for human consumption by FDA. Some experts caution against consuming gelatin in higher amount.
Since gelatin is acquired from animal sources, it may be contaminated with animal disease causing microbes. Ingesting gelatin is linked with increased risk of acquiring transmissible spongiform disease. This disease is caused virus that enters human body by consuming gelatin that is infected by animal-borne disease bovine spongiform encephalopathy or mad cow disease.
Hence gelatin has low safety profile than its pectin counterpart.
16.Is there any Substitute for Gelatin?
Since gelatin is derived from animal sources, it is not well-received by people around the world. Hence, there are different substitutes of gelatin for vegan people such as:
Agar Powder
It is produced from seaweed and red algae. It works quite similarly to gelatin but it gummier than gelatin creating creamier results. It is not a 1:1 substitute for gelatin.
Pectin
It requires sugar for setting thus it is only used instead of gelatin in sweet desserts such as jams, jellies, etc.
Xanthan gum
It is used as food additive to provide stability and texture to bakery products. It is artificially synthesized in laboratories
Carrageenan
It is manufactured from dried seaweed called carrageenan. Texture of carrageenan is more soft and melts quickly in mouth hence often used in pudding.
Vegan Jel
This product is created from numerous ingredients such as vegan gum, tapioca dextrin and calcium phosphate. It is best alternative for gelatin because its thickening action and taste profile is similar to gelatin.
17.Is There any Substitute for Pectin?
Accessibility of pectin is problem in far flung areas of the world therefore, there are numerous ingredients which can be used as substitute for making dishes if you do not have pectin on hand. These substitutes are:
Citrus Peel
White part or pit of citrus fruit skin is excellent substitute of pectin. This part is packed with natural pectin and is often used instead of pectin for making jams and marmalades.
Gelatin
It is good alterative for pectin as it is readily available and instantaneously dissolve in warm and hot waters.
Cornstarch
For acquiring gel like consistency, cornstarch is used in place of pectin. It stabilizes ingredients and has silky and smooth flavor profile.
Agar
It has similar texture to Jello when dissolve in water. It is carbohydrate in nature but agar is used in less amount than pectin in various dishes. The ratio of pectin to agar is 1:3.
Conclusion
Gelatin and pectin are thickening agent and often in food materials for improving texture. Gelatin is animal-based while pectin is derived from plants. Gelatin is protein while pectin is a polysaccharide. Chewy texture of gummies and marshmallows is attributed to gelatin. Pectin is more economical than gelatin but gelatin has high nutrition content than pectin. In short, gelatin and pectin are not same but vastly different from each other.
Don't forget to share this post!
Gummy Making Machine Related Posts
Gummy Making Machine Related Products
Gummy Making Machine Related Videos
CONTACT US
Tell us your raw material and project budget to get quotations within 24 hours.
WhatsApp Us: +86 181 6426 8586
Want the best price & newest pharmaceutical machinery buying guide,tips and trends sent straightly to your box?Sign up for AIPAK’s monthly newsletter,we’re free for your consultation and Offer you the most suitable solutions!
The Buyer's Guide
- Capsule Filling Buyer's Guide
- Blister Packaging Buyer's Guide
- Tablet Counting Buyer's Guide
- Tube Filling Buyer's Guide
- Cartoning Buyer's Guide
- Gummy Making Buyer's Guide
- CO2 Extraction Buyer's Guide
- Empty Capsules Buyer's Guide
- Suppository Filling Buyer's Guide
- Tablet Coating Buyer's Guide
- Tablet Press Buyer's Guide
- Softgel Encapsulation Buyer's Guide
Most Popular
- 7 Importance Of Pharmaceutical Packaging In Different Applications You Must Know
- 6 Advantages You Must Know About Tablet Counting Machine
- 8 Advantages of Blister Packaging You Must Know
- 6 Critical Applications of Automatic Capsule Filling Machine
- 6 Stations You must Know to Improve the Filling Quality of Automatic Capsule Filling Machine