Industrial Blender Vs Mixer: Which One You Really Need?
Mixing and blending are vastly dissimilar from each other, but people often confuse both of them. Mixing usually involves high-shear agitation while gentle dispersion of materials occurs in blending. Similarly, industrial mixers and blenders are often considered similar machines.
But they have distinct working, uses, shear forces, and operational scales. Today, industrial mixers and blenders are the most optimized solution for mixing tasks, saving operational expenses and time. However, manufacturers are often confused about which one- an industrial blender or mixer- is ideal for their mixing and blending needs.
So, to understand the distinction between both these machines and their compatibility with different jobs, we recommend reading this informative blog post “Industrial Blender Vs Mixer: Which One You Really Need?”. Buckle up your seat belts for an interesting ride.
1.What is an industrial blender?
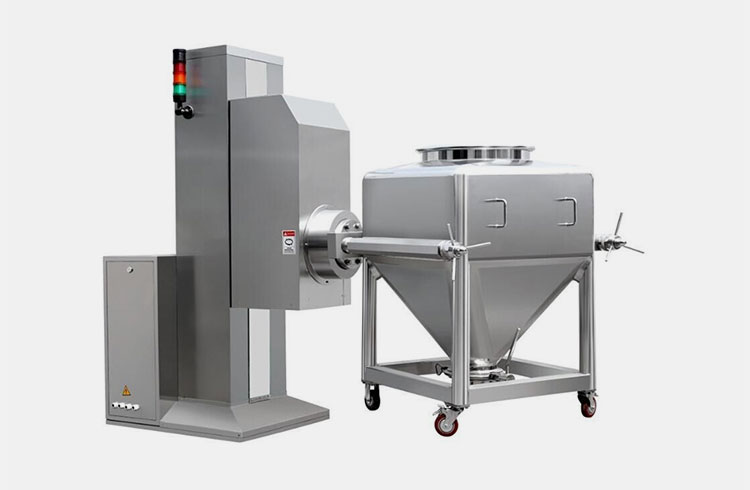
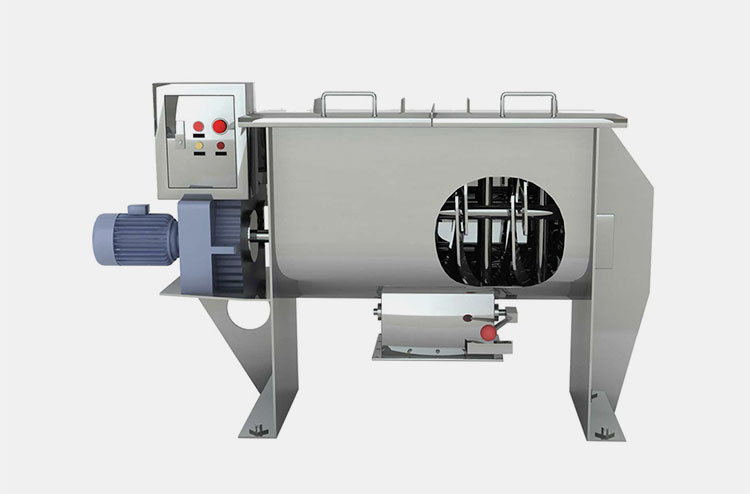
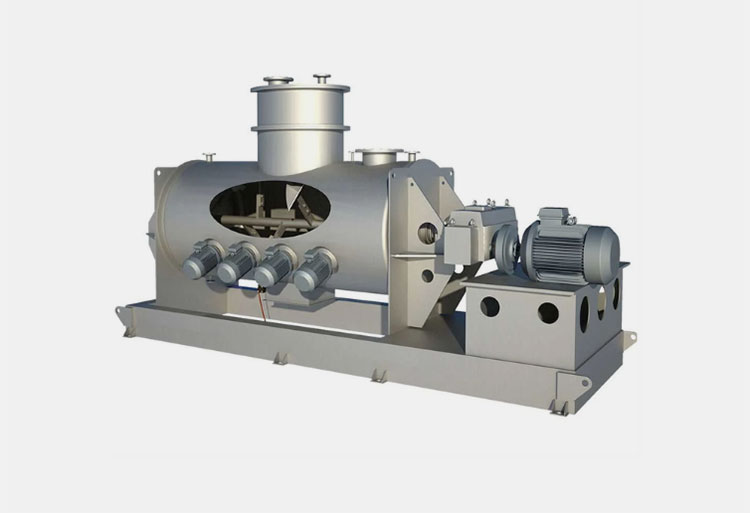
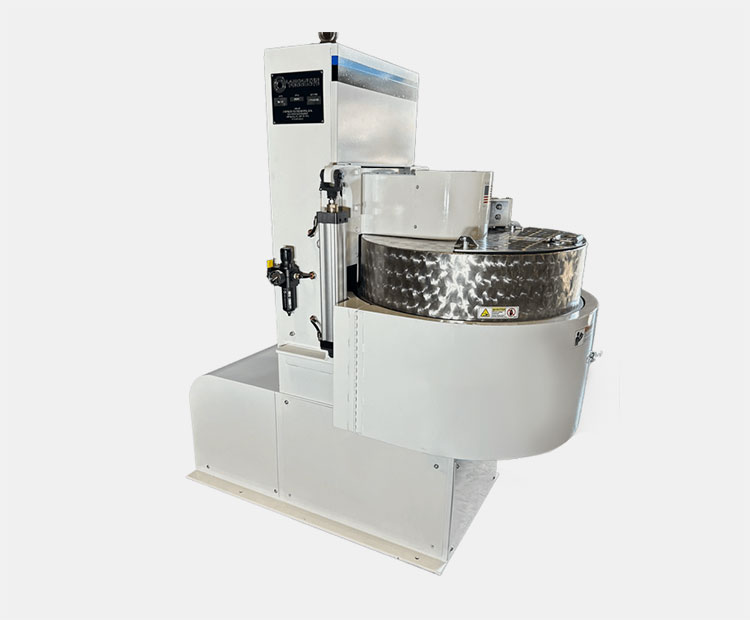
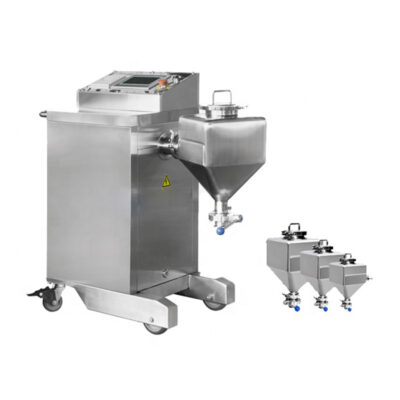
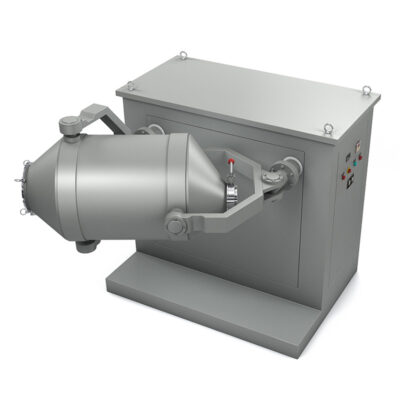
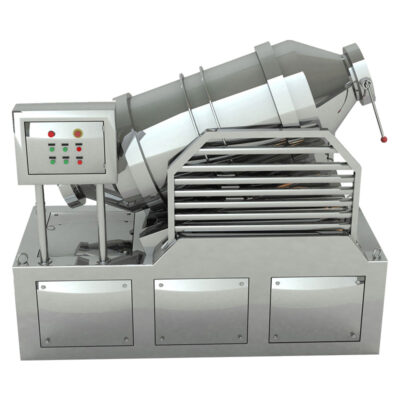
AIPAK Industrial Blender
The industrial blender is defined as a large vessel, ideal for blending product batches. Blending is a gentle process involving the homogenous distribution of two or more substances. It includes a uniform amalgamation of solid-solid or a tiny amount of liquid with solid.
An industrial blender is often best for delicate blending and involves minimal contact of ingredients with blender blades. This device is effective in achieving uniform quality and smooth texture of end products.
This device creates inseparable distribution, and the resultant mixture is a new product with distinct properties.
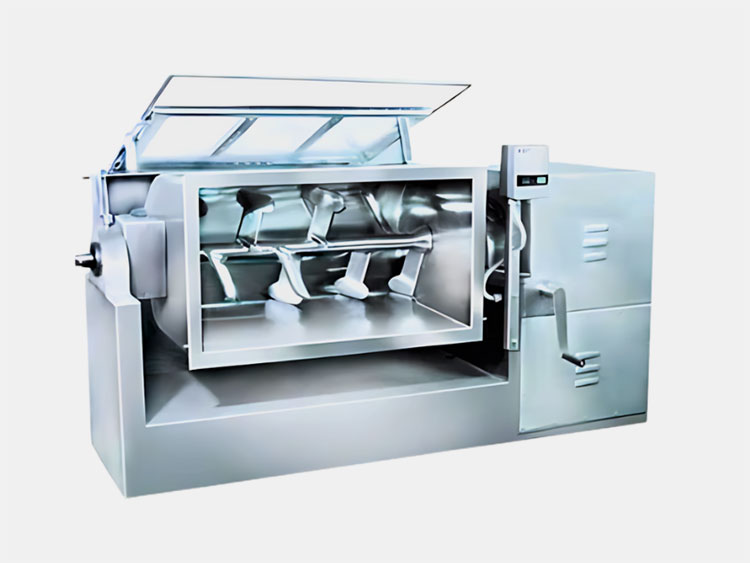
2.What is an industrial mixer?
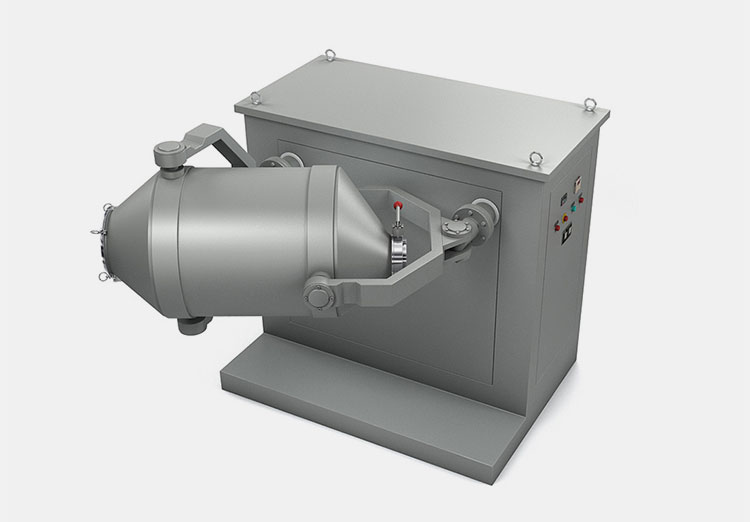
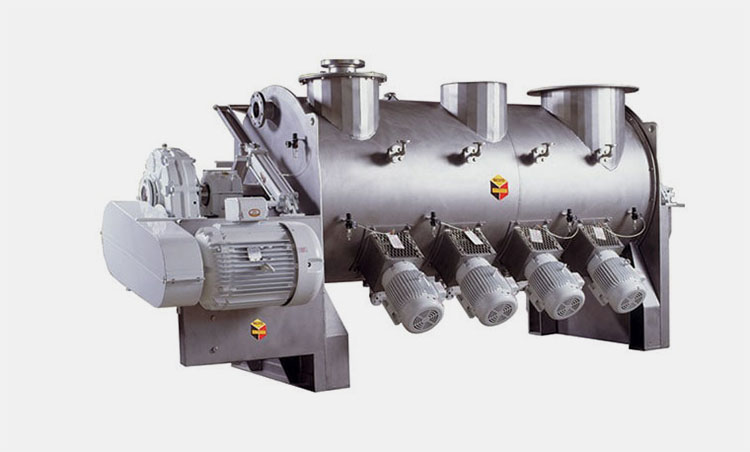
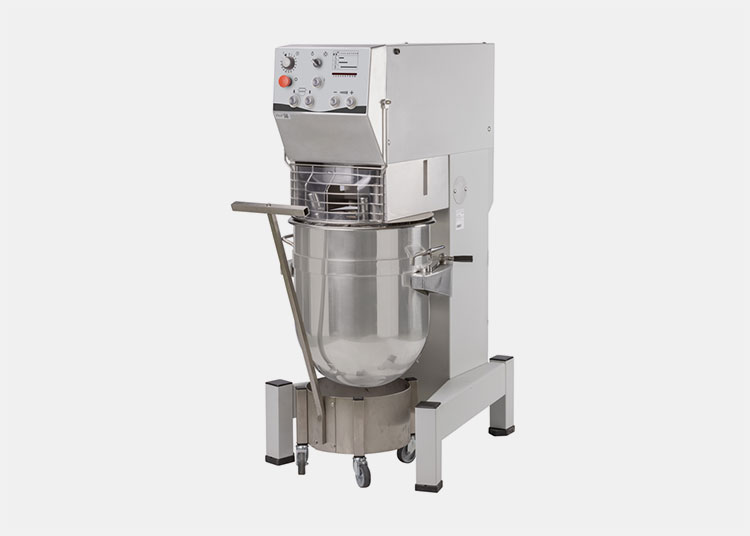
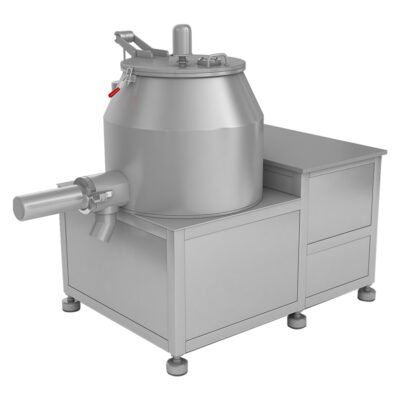
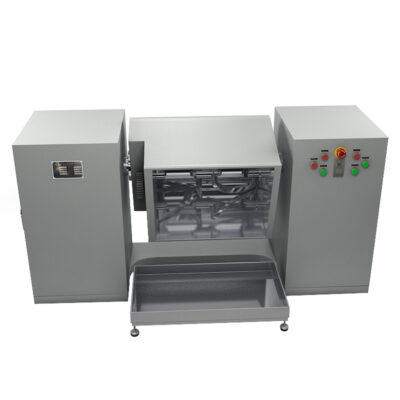
AIPAK Industrial Mixer
The industrial mixer is a large-scale device, routinely utilized in industries for combining two or re materials for uniform distribution. This machine achieves mixing through physical agitation, beating, whipping, whisking, or stirring.
It uses aggressive operativity to amalgamate two or more ingredients. It creates a turbulent flow of feed to create it’s even consistency. Solid-liquid as well as liquid-liquid materials are mixed in an industrial blender. It is jacketed for both heating and cooling processes.
3.Industrial blender vs mixer
There is much confusion about the differences between an industrial blender and a mixer in the manufacturing sector. In literature, usually, these terms are mentioned interchangeably. However, there is a gigantic distinction between these industrial machines. Let’s discuss the differences between an industrial blender and an industrial mixer so you can understand their distinction clearly:
Mechanism
Mechanism- Picture Courtesy: GangBen Mixer Manufacturer
Connective and tumbling movements are performed in the industrial blender to get a uniform blend of materials. In connective blending, the materials are scattered and moved along the entirety of the device using blades or paddles to produce a homogenous blend.
In tumbling blending, the blending vessel rotates, leading to tumbling of materials along with it. This motion is prevalent in tumbling blenders, resulting in the flow of materials and blending through gravitational force.
On the other hand, the industrial mixer generally employs vigorous agitation or rotational forces to mix materials from every direction. Some types of industrial mixers consist of rotating blades that rotate about a fixed central support and also spin about their axis at the same time, causing dual mixing motion for homogenous mixing.
Purpose
Purpose
An industrial blender and an industrial mixer have dissimilar purposes in the industries. The primary purpose of an industrial blender in the manufacturing sector is dry blending. It deals with ingredients- mostly in a solid or dry state. This equipment blends materials with little to no liquid.
The industrial mixer is valuable in wet mixing. It typically mixes one or more liquid ingredients, forming slurries, pastes, or liquid mixtures. It also dissolves and suspends solid ingredients in liquid solvents.
Use
Use- Picture Courtesy: SupHerb Farms
An industrial blender is mostly used in applications related to blending powders. This machine is perfect for processing and mixing free-flowing powders and granules for tablet and capsule manufacturing. In the food industry, it is involved in the blending of spices, juice instant powders, sugar, flour, seasoning, etc.
It homogenizes dry chemicals, fertilizers, plastic granules, and resins in the chemical industry. These chemicals need a consistent and uniform distribution of particles in the blend.
Conversely, industrial mixer performs the mixing of liquid carriers to form syrups, ointments, and creams in the pharmaceutical industry. In the food industry, this machine is known for its use in bakery sectors and kneads doughs, batters, and mixes sauces and dressings.
It is implicated in the mixing of dispersions and suspensions in the chemical and paint industry and the stirring of lotions, creams, and gels in the cosmetic industry.
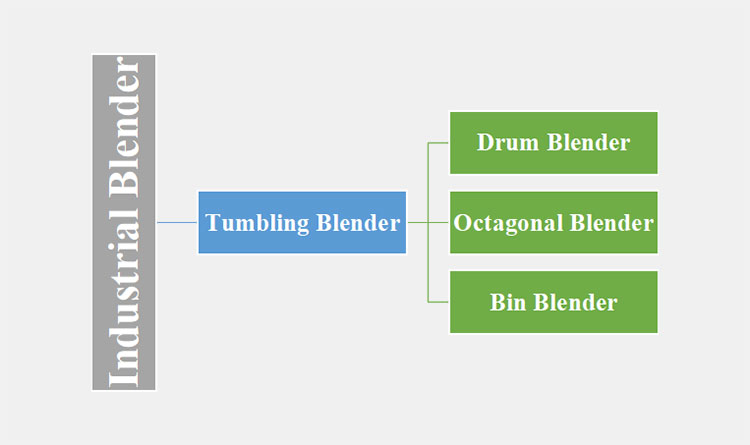
Types of machines
The types of industrial blender are:
Tumbling Blender
It is also named a gravity blender because it blends various feed types by rotation of its entire vessel. This leads to the tumbling and cascading of materials, guaranteeing uniform blend consistency. It depends upon gravity for blending instead of mechanical agitation, which allows gentle blending action. The types of tumbling blenders are mentioned below:
Drum Blender
Drum Blender- Picture Courtesy: Servolift GmBH
As the name indicates, this industrial blender features a gallon-type drum. The blending is carried out by the rotation of the drum about its axis. The materials fall over each other with the spin of feed, leading to simple yet efficient blending.
The drum spins completely for tilting and distributing materials evenly. Due to its complete slanting, there are no dead zones in this blending vessel. The substances are introduced and offloaded by the same opening in the drum blender.
Octagonal Blender
Octagonal Blender
It features an eight-sided shape structure. The central part of this structure has a rectangular shape and its ends are attached to firm stands.
The octagonal structure rotates, causing continuous tumbling of material, which leads to a smooth blend. This octagonal blending chamber has a slower rotational speed than other industrial blenders. It offers medium blending action; thus, blending does not exert excessive strain on materials.
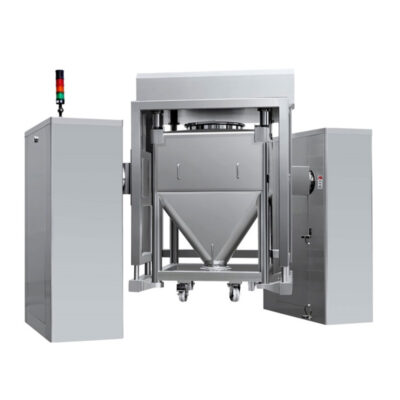
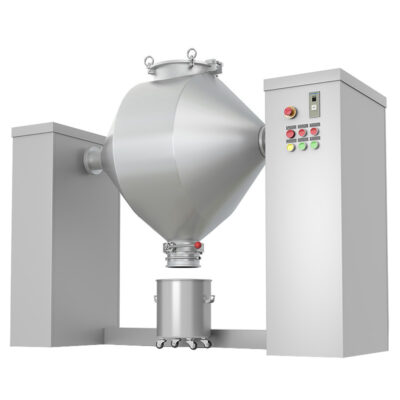
Bin Blender
AIPAK Bin Blender
It is also called a pharmaceutical blender or IBC blender. It is a unique kind of free-fall blender and is usually utilized when large-volume feeds are processed. Sometimes, it is also utilized when a fixed-clamped blending vessel is needed to attain uniform blending results. The bin-like blending device has different types of configurations, such as square, rectangular, round, or double-cone. Moreover, this bin is also designed with a symmetrical or asymmetrical V shape.
The bin shell is easily carried out, thus providing ease in loading and discharging, as there is no need for separate containers for housing blends.
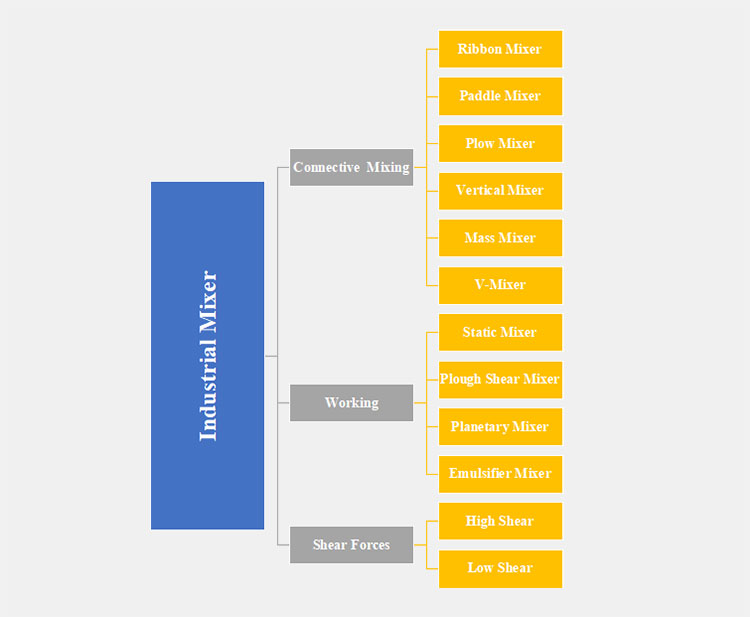
Industrial Mixer
This mixing device is categorized into different types, depending upon the mixing, working and shear force production. The classification of industrial mixer is penned below:
Connective Mixer
This type of industrial mixer employs mechanical agitation to disperse and homogenize feed. It is equipped with an internal agitator or bladelike structure that fluidizes materials within the mixer, producing a smooth and consistent mix. Different kinds of connective mixers are mentioned below:
Ribbon Mixer
AIPAK Ribbon Mixer
It is usually configured as a horizontal U-shaped trough or vertical-shaped device in which one or more middle shaft is mounted. This shaft has various helical ribbon blades for folding and distributing materials. It is a light-duty shear mixer and is valued for its dry and pre-processed feed mixing.
The motor drives the shaft that in turn rotates the helical ribbons for scattering, folding, and lifting feed, which form a thorough and uniform mix.
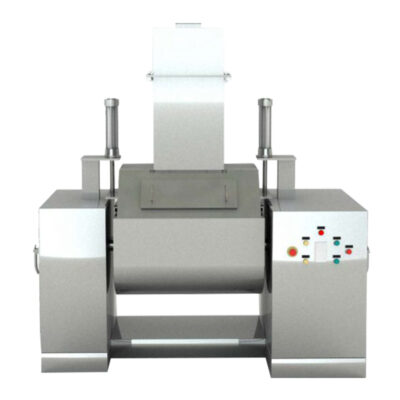
Paddle Mixer
Paddle Mixer- Picture Courtesy: PreMix
It has an identical construction to that of a ribbon mixer; however, a paddle mixer consists of paddle blades rather than ribbons. It has a U-shaped chamber and centrally mounted shafts with radiating arms. Numerous tiny paddles are present on these arms and have a star-shaped arrangement. These paddles are the core components, responsible for moving the feed within the mixing chamber.
The paddles of this mixer move in radial and tangential directions to boost the throughput of mixing.
Plow Mixer
Plow Mixer-Picture Courtesy: Scott Equipment Company
It has a U-shaped trough or cylindrical device that has a centrally located rotor with wedge-like plow blades to lift and distribute materials, creating a fluidized motion to attain high mixing efficiency. These plow blades use gravitational force to lift, force, and push materials away from the walls of the mixing chamber into free space in a zigzag direction.
They are integral in separating and cascading the materials in a three-dimensional pattern and moving the feed in a back-and-forth direction along the entire span of the mixing vessel.
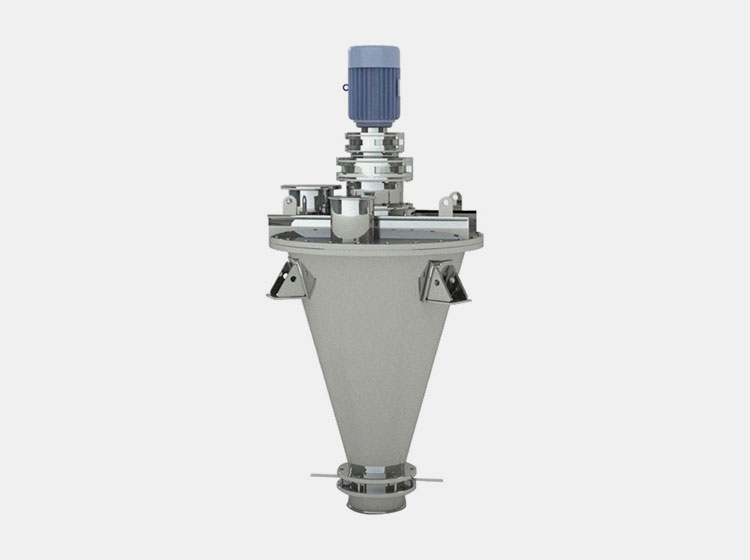
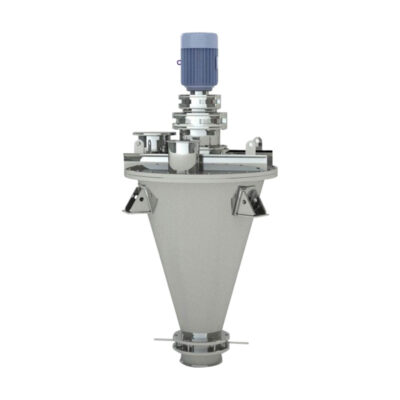
Vertical Mixer
AIPAK Conical Screw Mixer
It is also termed a conical screw mixer because it features a conical-shaped or tapered auger mixing vessel with a rotation screw. This instrument is vertically oriented and has a centrally located shaft or screw. The rotating screw-like component has a pivotal role in lifting feed from the bottom part to the top portion and via gravity materials fall, producing an efficient and uniform mix.
The materials are introduced from the inlet found at the top and discharged from the bottom outlet- controlled by a discharge valve.
Mass Mixer
Mass Mixer- Picture Courtesy: Ramashary Pharma Machinery Pvt
It has a rectangular structure and has a main shaft with paddle-like blades. The main shaft has a straightforward rotational pattern and moves at low speeds for gentle mixing. It has a connective mixing motion aided by the consistent movement of paddles and causes a vortex of feed for even dispersal and mixing of materials.
Upon completion of the mixing cycle, it is tilted to remove end products.
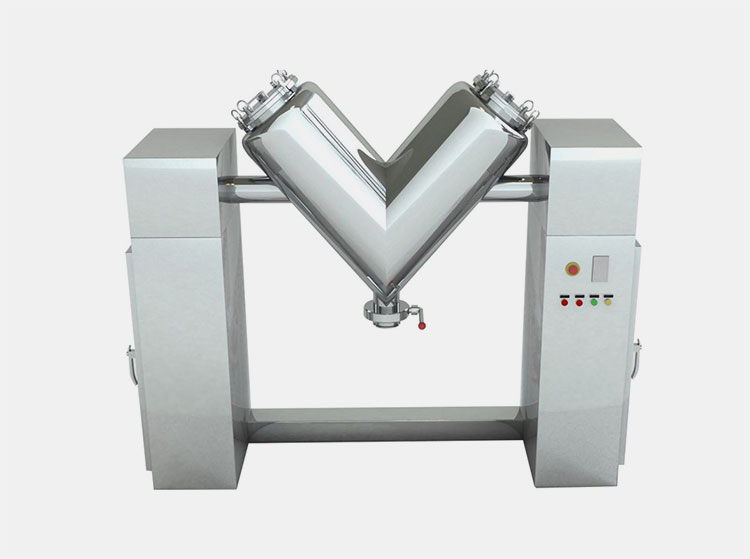
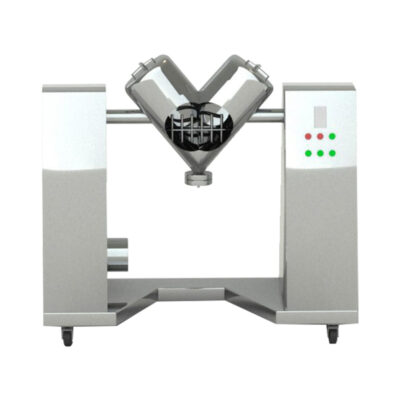
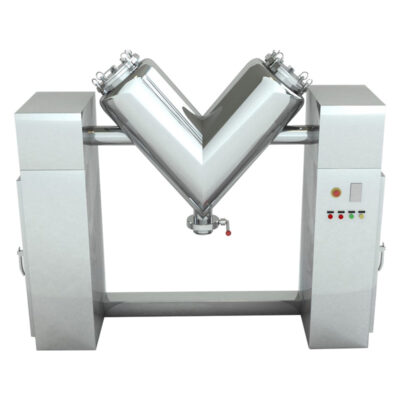
V-Mixer
AIPAK V-Mixer
This blender is also called a twin-shell mixer, as it is designed with two interconnected cylindrical vessels that join together at the bottom to create a V-shape. The cylindrical vessels are supported by a rod-like structure. It is rotated at 70-90° to create a flowing movement of ingredients from one shell to another. This leads to gentle yet thorough mixing.
There are two inlets present on each shell for loading and accessing the device while a discharge outlet is located at the bottom position, where two shells are connected.
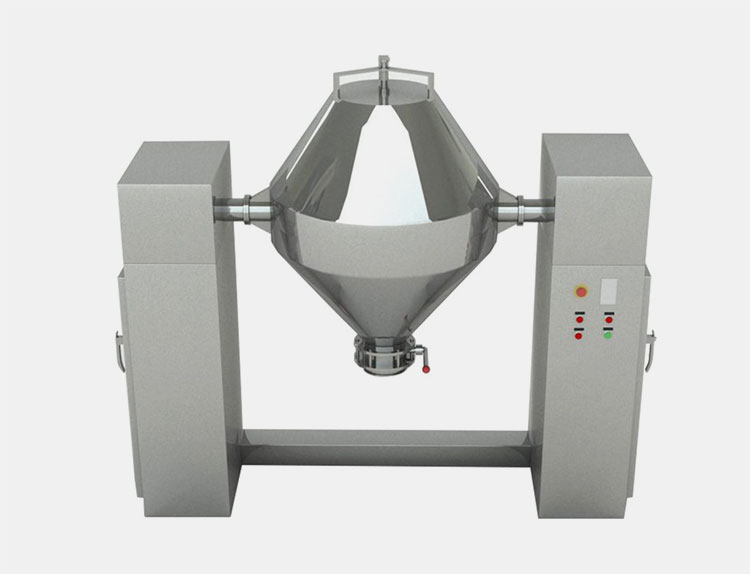
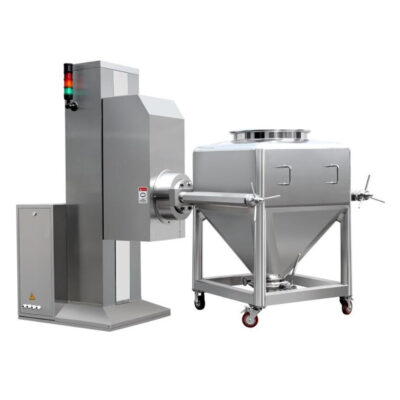
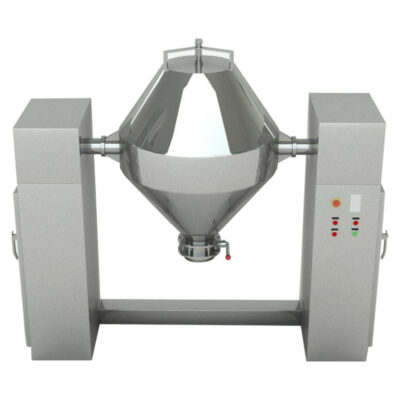
Double Cone Mixer
AIPAK Double Cone Mixer
It is a highly renowned type of industrial mixer and is equipped with two cone-shaped vessels that are joined in the opposing direction. The double cone structure rotates around the horizontal axis, supported by the shaft.
It executes a full 360° consistent rotation to achieve a homogenous mix. With rotation and gravitational force, the ingredients are steadily mixed. There are no dead areas in this industrial mixer due to its unique configuration.
According to Working
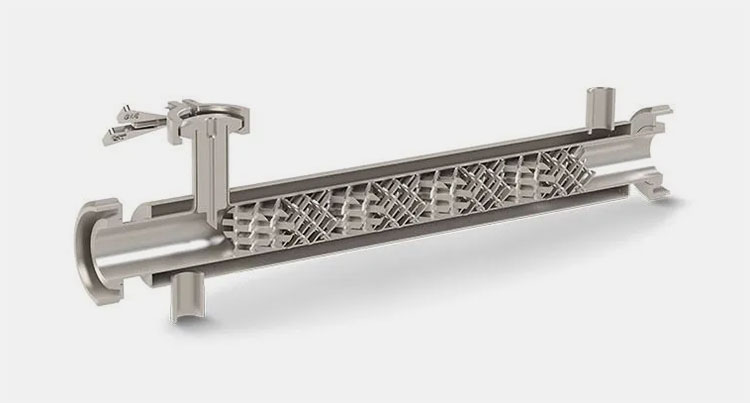
Static Mixer
Static Mixer- Picture Courtesy: primix
Unlike other industrial mixers, the static mixer is composed of immobile parts, and mixing action is carried out by fixed or static elements present in the mixing chamber rather than agitating blades. Turbulence is developed by these elements to ensure smooth and even mixing.
The materials are fluidized by their division or breaking down and recombination, creating even mixing. It is used for liquid-liquid and liquid-gas mixing.
Plough Shear Mixer
Plough Shear Mixer- Picture Courtesy: Asha Industry
It is an ideal type of industrial mixer that is preferred for fast and effective mixing. It has a specialized type of agitating device- ploughs or plows. These agitating tools are welded on a horizontal shaft that is fitted inside the cylindrical device.
The mixing zone is developed by the movement of plows, which lift and stir feed in a three-dimensional motion. Consequently, materials are in continuous circulation, producing a uniform mixture.
Planetary Mixer
Planetary Mixer- Picture Courtesy: Dito Sama
It is a type of heavy-duty industrial mixer, effective for mixing thicker consistency feed. It consists of a removable bottom bowl. There are spray nozzles and viewing ports present in this bowl structure. It has two or three multi-hinged blade-like structures located at the top of the mixing bowl, which exhibit both rotational and revolving motion concurrently.
The ingredients move up and down in the inner cylinder, bringing about a complete and uniform mixing performance in a short period.
Emulsifier Mixer
Emulsifier Mixer- Picture Courtesy: Ginhong
An emulsifier mixer is a specialized kind of industrial mixer and is suitable for forming mixtures of immiscible liquids, such as oils and water. It creates a stable emulsion with its high-intensity mixing. Strong forces are developed with fluidity of materials, which break down the molecular composition of one material into tiny droplets and evenly distribute them throughout the entirety of other liquids.
According to Shear Forces
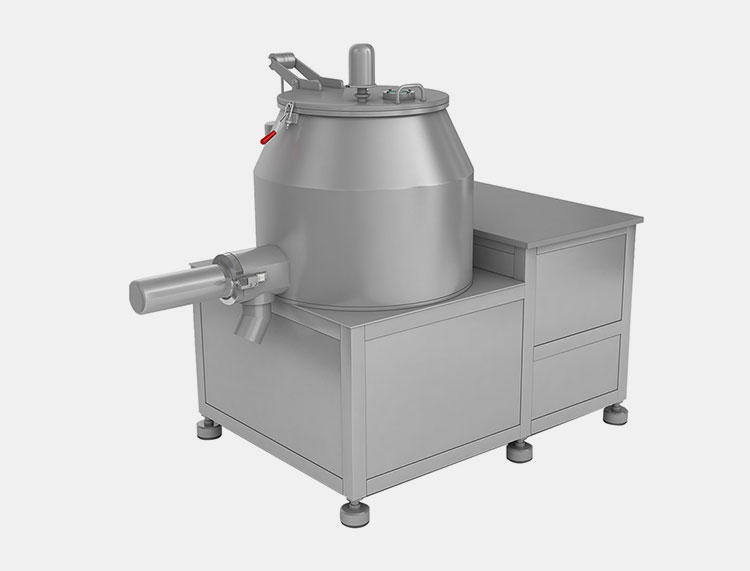
High-Shear Mixer
AIPAK High Shear Mixer
It is also known as high-shear mixer or high-shear homogenizer. It is an industrial mixer, preferred in industrial settings for its excellent emulsification, homogenization, dispersing, and, grinding action. In this equipment, the agitation shafts or rotors rotate in a stationary mixing vessel.
This device runs at high rotor speed and produces high-shear forces by high rotational velocity and turbulent flow of fluidized materials. These shear forces apply stress on materials and result in the fluidizing of materials in opposite directions within the sample plane.
Low-Shear Mixer
Low-Shear Mixer- Picture Courtesy: Lancaster Products
It uses a mixing propeller- fitted in the mixing vessel for all-purpose mixing. It is also equipped with a hydrofoil impeller, appropriate for low-shear mixing. Due to the unique configuration of the low-shear mixer, there is a minimal number of shear forces produced in it, thus this industrial mixer is effective in maintaining the structural integrity of mixing components.
Many types of low-shear mixers are portable and provide ease of mobility. It operates at reduced speeds, consequently limiting the forces and stress exercised on materials.
Flexibility
Flexibility
An industrial blender is considered a less versatile machine, as it is developed for exclusively processing solid-type ingredients. It has limited capability to blend wet or cohesive materials.
On the contrary, the industrial mixer is regarded as a highly flexible mixing machine since it is easily adapted to handle a wide range of substances belonging to all ends of the spectrum like liquids, pastes, semi-solid, powders, and, solids. This equipment comes with interchangeable mixing components to mix several types of raw feed.
Production Scale
Production Scale- Picture Courtesy: JW Consulting Engineers
An industrial blender and a mixer have diverse utility in different types of production sizes. An industrial blender is highly recommended in mass-scale productions. It performs well in high-throughput operations. It can efficiently blend bulk batches of materials, consequently facilitating large-sized facilities. However, if this machine is scaled down to process smaller batches, then its blending efficiency is reduced.
The industrial mixer is frequently utilized in small- and large-sized batches and continuous productions. It has versatility in handling different batch sizes.
Design and Cost
Design and Cost- Picture Courtesy: HosokawaMicron
An industrial blender has less upfront purchase cost and its maintenance and cleaning are less time-consuming and exhausting since it has a straightforward design and minimal number of mobile components.
Conversely, the industrial mixer is typically pricier due to its complicated construction. It often includes customizable accessories, leading to complex and routine maintenance requirements and more operational expenses.
Energy-Consumption
Energy Consumption
An industrial blender has characteristically limited energy consumption in contrast with an industrial mixer. This is due to its low-intensity blending and no need for excessive mechanical forces. This instrument works on the principle of connective or tumbling motion, therefore, it does not require excessive power for its operation.
Alternatively, the industrial mixer has high energy demand, as it works by producing intensive mechanical forces with agitation or paddling to evenly distribute materials. Moreover, it mixes highly viscous liquid materials that need excessive power for mixing because they are resistant to flow.
Let’s summarize the differences between an industrial blender and a mixer in the table below:
| Feature | Industrial Blender | Industrial Mixer |
| Mechanism | Tumbling or Connective Motion | Agitation or intense rotational movement |
| Purpose | Dry blending | Wet Mixing |
| Type of Materials | Dry and free-flowing powders or granules with minute quantities of liquids | Moderate or heavy viscosity materials, sticky, agglomerates, lumpy materials, semi-solids, pastes, and slurries |
| Ingredients Profile | Starting materials have less variability in particle size, viscosity, and texture. | Materials have more complicated ingredient profiles with huge variations in their fluidity, particle, size, and texture. |
| Application | Blending of pharmaceutical powders, spices, sugar, seasoning, and, plastic resins | Kneading of doughs and batters, mixing of paint emulsions, stirring of creams, gels, lotion, and ointments |
| Intensity of Mixing | Less intense blending | More vigorous and aggressive mixing |
| Shear Forces | Low-shear force | Excessive shear and mechanical forces |
| Use | Blending | Mixing, homogenization, emulsion, wet milling |
| Flexibility | Less flexible | More versatile |
| Production Scale | Usually processes bulk-volume of batches. | Suitable for both small and large batches. |
| Design and Cost | Simple design, easy maintenance, and low upfront cost | Complicated design, difficult maintenance, and high investment cost |
| Energy-consumption | Less energy use | More energy consumption |
4.When should you choose an industrial blender over a mixer and vice versa?
Various industrial applications require different types of mixing equipment. The choice between an industrial blender and an industrial mixer is heavily based on the characteristics of the materials being processed and the resultant mixture. Some of the factors that influence the selection of an industrial blender over an industrial mixture and vice versa include:
Material Characteristics
Material Characteristics
If your processing material has free-flowing characteristics, then it is best to opt for an industrial blender. Moreover, this blending device usually processes materials having smaller particle sizes. It also blends non-cohesive or non-sticky materials that do not clump or agglomerate during blending.
If materials have more moisture content or have a semi-solid texture, then they are typically mixed using industrial mixers. It is a model mixing device for mixing slurries and pastes components in which solid particles are dispersed in a liquid base.
Sometimes, the mixing of ingredients- having discrepancies in texture, size, and viscosity- is needed in industrial operation, so this challenging task is efficiently handled by an industrial mixer. Heavy-duty and intensive mixing is a highly desired feature of an industrial mixer. Industrial blenders are less flexible in accomplishing this task due to a lack of intense mechanical performance.
Low-Viscosity and High-Viscosity Materials
Low-Viscosity and High-Viscosity Materials- Picture Courtesy: SilverChef
If you are dealing with low-viscosity materials having more flow, such as powders and granular feed, then the gentle blending action of an industrial blender is more suited for this task.
If you are involved in production, where sticky, thick, or highly viscous feed is processed then you should select an industrial mixer. It is because an industrial mixer is developed to easily process ingredients having medium to thicker consistency, while it is difficult for industrial blenders to handle thicker consistency materials.
Gentle and Aggressive Mixing
Gentle and Aggressive Mixing- Picture Courtesy: Dough Tech
If you do not want to damage or degrade the physical structure of fragile and delicate materials, then you should choose an industrial blender over a mixer. An industrial blender is pivotal in preserving the integrity of ingredients and does not cause their fragmentation. It is normally important for processing substances that are prone to breakage and need mild blending action.
Industrial mixers are appropriate for processing applications, where aggressive, intense, or vigorous mixing is needed. If your starting materials have a high number of agglomerates, lumps, and clumps, then you should pick an industrial mixer.
High shear forces are developed during the mixing of products with an industrial mixer, consequently it can easily break or fragment large agglomerates.
Emulsification
Emulsification- Picture Courtesy: MICHELIN Guide
If your industrial applications generally require the formation of emulsions or thoroughly homogenizing mixture then an industrial mixer- for instance, a high-shear mixer or planetary mixer- is best for the job. By fragmenting and size reduction of particles, this equipment yields a uniform and stable mixture. It is used for wet milling and its use goes beyond simple blending.
The industrial blender does not produce a high level of shearing forces, so it is unable to form an emulsion.
Conclusion
An industrial blender is associated with the gentle mixing of delicate powders and granules, whereas an industrial mixer is an exemplary device for mixing thicker viscosity, non-free flowing, semi-solid, or liquid-based material. The latter uses high shear forces and intense agitation to uniformly mix diverse types of substances, on the other hand, an industrial blender operates on less intensive tumbling and connective movement. These industrial devices also differ in their design, processing, uses, purpose, maintenance needs, and energy consumption. Hopefully, this blog post has cleared up confusion about the use of an industrial blender and a mixer. If you require optimized blending and mixing solutions for your production, then we, AIPAK, are always at your disposal to cater to your needs.
Don't forget to share this post!
Bin Blender Related Products
Bin Blender Related Posts
Bin Blender Related Videos
CONTACT US
Tell us your raw material and project budget to get quotations within 24 hours.
WhatsApp Us: +86 181 6426 8586
Want the best price & newest pharmaceutical machinery buying guide,tips and trends sent straightly to your box?Sign up for AIPAK’s monthly newsletter,we’re free for your consultation and Offer you the most suitable solutions!
The Buyer's Guide
- Capsule Filling Buyer's Guide
- Blister Packaging Buyer's Guide
- Tablet Counting Buyer's Guide
- Tube Filling Buyer's Guide
- Cartoning Buyer's Guide
- Gummy Making Buyer's Guide
- CO2 Extraction Buyer's Guide
- Empty Capsules Buyer's Guide
- Suppository Filling Buyer's Guide
- Tablet Coating Buyer's Guide
- Tablet Press Buyer's Guide
- Softgel Encapsulation Buyer's Guide
Most Popular
- 7 Importance Of Pharmaceutical Packaging In Different Applications You Must Know
- 6 Advantages You Must Know About Tablet Counting Machine
- 8 Advantages of Blister Packaging You Must Know
- 6 Critical Applications of Automatic Capsule Filling Machine
- 6 Stations You must Know to Improve the Filling Quality of Automatic Capsule Filling Machine