How to Prepare for GMP Validation?
GMP is a series of basic requirements for various factors that affect the quality of drug production to ensure that drug quality is foolproof. GMP validation plays an important role in ensuring drug quality, improving enterprise production efficiency and market competitiveness, meeting regulatory requirements, and promoting continuous improvement.
Do you know the reason for GMP validation failure? How to avoid verification failures? How to prepare for GMP validation? Next, let's explore the knowledge about GMP validation together.
1.What Is GMP Validation?
GMP Validation - Sourced: Angstrom Technology
The full name of GMP is Good Manufacturing Practice, which is an important standard for ensuring drug quality and production standards. Validation is an important component of GMP. Validation is a mirror that verifies the implementation of GMP. It faces the entire process of drug production and can effectively reduce costs, optimize processes, and achieve expected production goals. It can provide reliable quality assurance for drugs and enable enterprises to achieve better economic benefits.
2.What Is the Significance of Validation?
Why is validation necessary? What are the benefits of validation?
Ensuring product quality
Ensure Product Quality - Sourced: Corporate Vision
GMP requires pharmaceutical manufacturers to have good production equipment, reasonable production processes, sound quality management, and strict testing systems to ensure that the final product quality meets regulatory requirements. Through validation processes, reliable guarantees can be provided for product quality, reducing the risk of product defects and non-conforming products.
Meeting regulatory requirements
Meeting Regulatory Requirements - Sourced: insBlogs
In many countries and regions, the production of drugs and food products must pass GMP validation, which is a necessary condition for pharmaceutical enterprises to operate legally.
Realizing economic benefits for enterprises
Realizing Economic Benefits For Enterprises - Sourced: TIAA
Validation improves the stability and reliability of the process, thereby reducing the incidence of non-conforming products, reworked products, and waste. At the same time, it also improves the quality of the product, reduces claims due to adverse reactions or quality issues, and invisibly reduces product costs and improves the company’s reputation.
3.What Are the Difference Between Qualification and Validation?
Difference Between Qualification and Validation - Sourced: Pharma Gyan
In GMP, qualification and verification are certifications. Simply put, qualification means checking whether the final product meets the customer’s usage requirements, that is, using performance data to prove whether we have manufactured the correct product. And validation is the recognition that the prescribed requirements have been met by providing objective evidence.
Purpose
Purpose - Sourced: David Daniel Books
Qualification is usually carried out before the operation or process to ensure compliance with the prescribed standards and requirements. For example, in the pharmaceutical industry, qualification of raw materials and equipment is a prerequisite for producing qualified drugs.
And validation is to confirm whether the control measures, including the prerequisite plan, operational prerequisite plan, and HACCP plan, have achieved the expected level of hazard control as a whole, and whether a safe final product can be obtained. It is necessary to determine whether the entire system operates effectively.
Scope
Qualification is usually carried out for a single operation or process, such as equipment installation and debugging.
The scope of validation is much larger, including the implementation of prerequisite plans, whether the input of hazard analysis is continuously updated, whether the hazard level of the final product is within an acceptable level, and the implementation and effectiveness of other procedures required by the organization.
Implementation timing
Qualification is carried out before the implementation of control measures included in the operational prerequisite plan and HACCP plan, including the implementation after planning changes, while validation is the activity carried out during or after the implementation of overall control measures, that is, after a period of implementation.
4.What Are the Types of GMP Validation?
GMP validation is not a simple process and involves many types, including the following:
Process validation
Process validation - Sourced: Olanab Consults
To verify a production process that can operate continuously and stably according to approved process parameters, and produce products that meet the specified standards, usually using the specified commercial batch, with at least three consecutive successful batches for validation. Process validation is crucial for confirming the effectiveness of production processes, and it is also a systematic engineering involving collaboration among multiple departments.
Cleaning validation
Cleaning Validation - Sourced: PharmaLex
Verifying that the cleaning method or procedure for equipment, such as capsule filling machine, in direct contact with the product can effectively clean the equipment to ensure that the product is not contaminated by product residues, cleaning agents, and microorganisms from production equipment or systems.
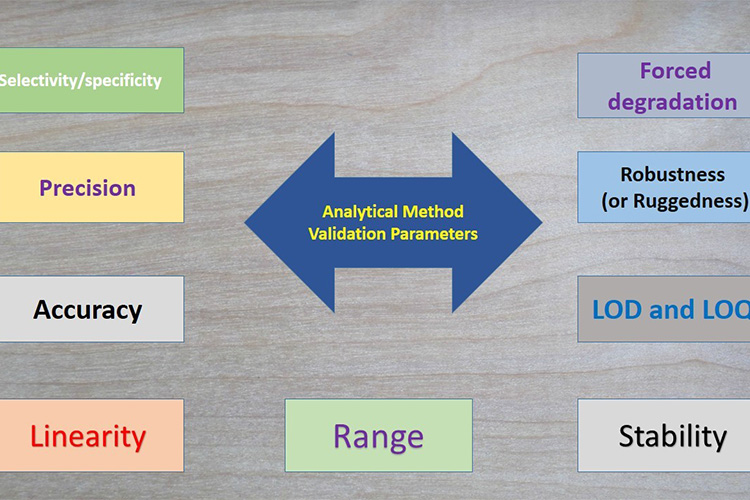
Validation of analytical methods
Validation of Analytical Methods - Sourced: LinkedIn
Regarding the inspection method, although it only has a few words in GMP, its role in the qualification and validation system cannot be underestimated. Only validated or confirmed testing methods can be considered as methods that can output accurate test results, and their importance and complexity are detailed in ICH Q2 “Validation of Analytical Methods”.
Computerized system validation
A computerized system is a complex system, and in order to confirm its effectiveness, it is necessary to validate it, which is another complex process.
Transport validation
For materials and products that have special requirements for transportation conditions, it is necessary to confirm whether their transportation conditions comply with approved documents, quality standards, or enterprise requirements. Speaking of GMP guidelines (second edition), placing it under validation rather than confirmation may be due to its focus on transportation conditions, which are intangible.
5.What Factors Cause Validation Failure?
Validation Failure - Sourced: Pharma GxP
The failure of validation can affect the overall work efficiency and even the economic benefits of the enterprise, so we need to analyze the reasons for verification failure and pay attention to these issues in future work.
Failure to consistently involve all stakeholders
Successful projects come from the continuous participation of a stakeholder team. Business department leaders, quality personnel, IT, QC laboratories, and engineering departments, etc. It ensures continuous adjustment and cooperation to address challenges arising from constantly changing situations such as scope changes and human errors.
Lacking of real-time project status
The executive management often complains that they do not have real-time updates on the current status of all projects. Unfortunately, they only realize the key issues when there is a significant or irreversible impact on costs, plans, and scope. Therefore, these changes must be displayed in real-time in a concise and clear manner.
Lacking of project risk management
Lacking of Project Risk Management - Sourced: DRMcNatty & Associates
During the project initiation and team building process, the team is unable to proactively identify, analyze, and mitigate project risks related to scope, plan, and budget. Doing so in advance can prevent passive handling of project risks, thereby providing management with visibility into the project team's loss of control. It is wise to develop and publish a project risk management plan and provide risk training to the entire project team.
6.How to Prepare for GMP Validation?
GMP validation is crucial for the development of enterprises, so how to prepare validation to avoid serious failures?
Conducting a thorough risk assessment
Conducting a Thorough Risk Assessment - Sourced: Financial Crime Academy
All validation require a risk assessment to determine the risks of new or changed systems and their potential impacts on products and safety (operators and customers). Determining validation requirements based on identified risks, and the scope and degree of validation are determined by risk assessment.
The testing during the validation process should focus on the identified areas of risk to the equipment, process, or product. Risk analysis runs through the validation lifecycle of products/equipment. Fault Tree Analysis (FTA), Design Failure Mode and Effects Analysis (DFMEA), and Process Failure Mode and Effects Analysis (PFMEA) are commonly used risk analysis methods that can be chosen.
Advance planning
Validation is generally coordinated by the verification leader and guided by the verification team for implementation. The validation team members include chemists, microbiologists (if necessary, sterile assurance engineers and program analysts must also be included), quality engineers, engineering department engineers, and process engineers.
Preparing personal
Prepare Personal - Sourced: Quantified AI
The GMP validation work requires active participation and collaborative efforts from various functional departments within the enterprise. Therefore, an organization must be established to lead this work.
The finished product members include technical backbones from various energy harvesting departments. Under the leadership group, several small specialized teams can be set up to be responsible for the renovation, improvement, and organization of hardware and software systems. Only by fully preparing personnel and entering the substantive initiation stage of GMP validation work.
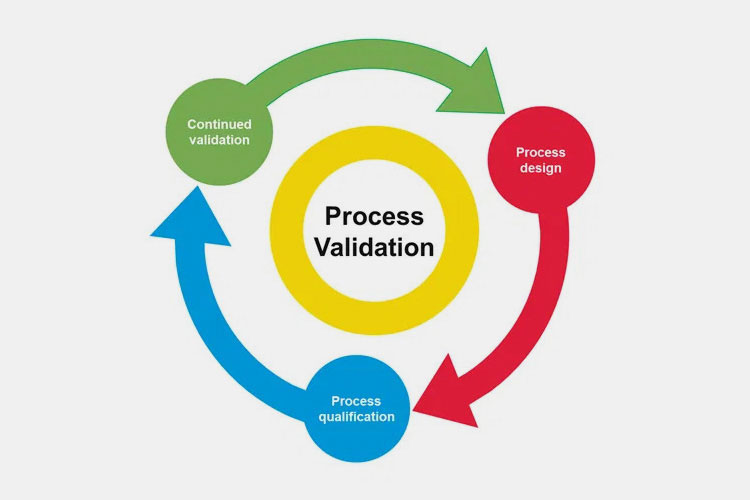
7.What Are the Phases for GMP Process Validation?
Manufacturing safe and high-quality pharmaceutical products requires good manufacturing processes. Simply put, this is the goal of process validation, which is to ensure that drugs always meet quality standards. The method to achieve this goal is through three stages of process validation.
Phase 1: Process design
Process Design - Sourced: Nobpreneur.com
Process design is the core activity of the research & development phase. The main goal of process design is to determine the appropriate process for commercial production of products.
From a regulatory perspective, an important component of this stage is meticulous and comprehensive record keeping. The regulatory authorities need to review how the developer conducted the research and development process during the process design phase to ensure that the key projects mentioned above have been thoroughly researched and reasonably concluded.
Phase 2: Process qualification
Process Qualification - Sourced: ValGenesis
Evaluate and validate the process of early design during the process confirmation phase to ensure that it can reproduce consistent and reliable quality levels. It involves collecting and evaluating data related to various aspects and stages of the manufacturing process.
The implementation of the PPQ protocol should not begin until all necessary departments within the organization, including the quality assurance department, have approved it. Another important component of this process is developing emergency plans for situations where problems arise.
Phase 3: Continued process verification
Continuous process validation involves continuous validation during the production process of commercial products to ensure that the processes designed and confirmed in previous stages can continue to provide consistent product quality as expected.
One of the main goals of this stage is to detect, analyze, and solve the so-called process shift problem. The so-called process drift is based on the observation that the Sigma level of the production process gradually decreases with the continuous progress of production.
8.What Is the Process of GMP Validation?
Do you know what processes verification needs to go through? Next, let's take a detailed look.
Project plan
The project plan is the foundation of all activities and should include at least the project objectives, project scope, participants, project content, and project schedule.
Risk assessment
Conduct risk assessment on the product process of project design and provide basic information for drafting the URS of equipment. At the same time, the risk points of risk assessment are also the standard source for future equipment confirmation and the source of future process control points.
URS
URS - Sourced: Pharmaguddu
The basis for drafting URS needs to be based on regulatory requirements, industry standards, process requirements, and commercial requirements. URS is usually drafted by the equipment usage department and reviewed by relevant departments. But for new projects, R&D personnel should at least participate in the URS review of some key process equipment.
Equipment risk assessment
The main purpose of the equipment risk assessment here is to determine the scope and depth of equipment validation based on its purpose and technical requirements, in preparation for drafting the validation master plan. The scope of risk assessment here is limited to the impact of equipment on product quality and technical difficulty.
DQ (Design Qualification)
DQ (Design Qualification) - Sourced: Pharma Engineering
If there is a deviation, there is no need to follow the GMP deviation investigation procedure for immediate remediation and investigation of the cause of the deviation. The CAPA procedure should be followed, only the investigation needs to be conducted.
IQ (Installation Qualification)
Installation qualification includes but is not limited to the following: confirming that components, instruments, equipment, piping engineering, and services are installed correctly according to engineering drawings and design specifications.
OQ(Operation Qualification)
The content of OQ should include confirmation of instrument calibration; Environmental conditions for equipment use; A feasible standard operating procedure (SOP) should be developed for new equipment, at least in draft form; Confirmation before equipment operation and use; Interlocking braking and safety control detection; Confirmation of confidentiality function of PLC (Programmable Logic Controller) system; Check the jog operation function; Inspection of motor rotation direction (motor debugging); Alarm confirmation/line confirmation.
Conclusion
Only after validation can it be considered qualified. GMP validation is crucial for both products and businesses, therefore, we need to avoid validation failures. After reading this article, do you know how to prepare for GMP validation? If you have any further questions, please feel free to contact AIPAK at any time.
Don't forget to share this post!
Blister Packaging Machine Related Posts
Blister Packaging Machine Related Products
Blister Packaging Machine Related Videos
CONTACT US
Tell us your raw material and project budget to get quotations within 24 hours.
WhatsApp Us: +86 181 6426 8586
Want the best price & newest pharmaceutical machinery buying guide,tips and trends sent straightly to your box?Sign up for Aipak’s monthly newsletter,we’re free for your consultation and Offer you the most suitable solutions!
The Buyer's Guide
- Capsule Filling Buyer's Guide
- Blister Packaging Buyer's Guide
- Tablet Counting Buyer's Guide
- Tube Filling Buyer's Guide
- Cartoning Buyer's Guide
- Gummy Making Buyer's Guide
- CO2 Extraction Buyer's Guide
- Empty Capsules Buyer's Guide
- Suppository Filling Buyer's Guide
- Tablet Coating Buyer's Guide
- Tablet Press Buyer's Guide
- Softgel Encapsulation Buyer's Guide
Most Popular
- 7 Importance Of Pharmaceutical Packaging In Different Applications You Must Know
- 6 Advantages You Must Know About Tablet Counting Machine
- 8 Advantages of Blister Packaging You Must Know
- 6 Critical Applications of Automatic Capsule Filling Machine
- 6 Stations You must Know to Improve the Filling Quality of Automatic Capsule Filling Machine