How to Mix Pharmaceutical Powder
Powder is not only a solid dosage form, but it is the beginning point of other dosage forms. In a simpler term, it is a core of practicing pharmacy. To mix pharmaceutical powder, pharma industry must have a sound knowledge of it. Mixing of pharmaceutical powder is a key component for the quality and good performance of the product. These processes are highly implemented in the field of pharmaceutical, food, healthcare, and chemical industries.
Powder mixers are classified according to mechanisms of mixing, such as diffusion, convection & shear. Moreover, their selection is based on properties of powdered particles such as shape, particle size and their concentration. By considering such factors minimizes the chances of particle segregation. This deep review features curated content about pharmaceutical powder mixing to improve your knowledge and process hurdles when manufacturing pharmaceutical products.
Table of Contents
Ⅰ.Importance of Pharmaceutical Mixing in the Pharma Industry
- Good Performance Product
In pharmaceutical industries, products must require a thorough mixing prior to later steps of production. Commencing these steps are essential to obtain top quality performance formulation with uniform distribution of particles without batch-to-batch variation.
- Greater Efficiency
Manufacturing products in pharmaceutical industries are always sought to improve efficiency and potency. A good quality mixing possibly mixes a batch material thoroughly and greatly improves the efficiency of production.
- Safe and Hygienic Medication
To manufacture a safe and hygienic medication with minor concentration of active pharmaceutical ingredient. You must consider pharmaceutical mixing to achieve easy and flexible configurable homogeneity, product stability and even particle distribution.
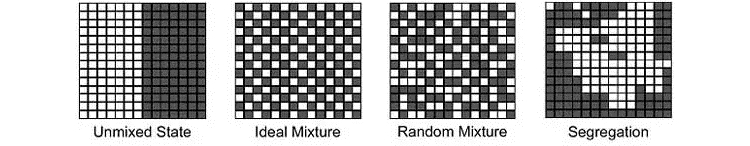
II.Different States of Powder Mixing
Mixing is shuffling type procedure that involved the groups of large and small as well as individual particles. For mixing it is essential to cease the movement of mix so that system may exist in static equilibrium without being segregated.
III.Processes in Pharmaceutical Mixing
There are three kinds of mechanism linked with motion of particles in pharmaceutical mixing. These mechanisms are discussed below:
a.Shearing
It is defined as the motion of one layer of particles with respect to another layer of powder particles. The particles in layers moving with different speeds in rotary vessels, cause shear mixing.
This type of mixing occurs due to motions of particles layers and not by motions of particles separately. The mixing rate of shearing is intermediate and involves microscopic blending.
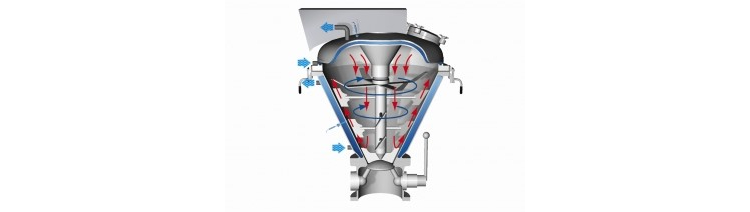
This kind of mixing is referred as movement of large collective of particles from one place to another. This process is usually performed by paddles and baffles.
Mixing rate of connective is fast and involves large-scale macroscopic mixing. But to accomplish homogenous mixing more time is needed.
c.Diffusive Mixing
Diffusive mixing is the mixing due to haphazard movement of powder grains. The volume of powder is enhanced due to shearing and convective forces, which result in high mixing of every particle.
The rate of this type of mixing is low but it usually lead to microscopic mixing.
IV.How to select tablet counting machine manufacturer from China?
There are four main types of pharmaceutical mixing which are as follows:
1.Spatulation
This kind of pharmaceutical mixing involves the merging little amount of powder by using spatula. This mixing is done on the piece of parchment, balm slab, or in mortar.
Advantages
- It is useful for mixing powders that have similar mass.
- There is no wastage of material during this kind of mixing.
- Spatulation is convenient if two solid powders are mixed to form liquid blend.
Limitations
- Particle size is not decreased in this technique.
- Large particle sized powders are not blended efficiently by spatulation.
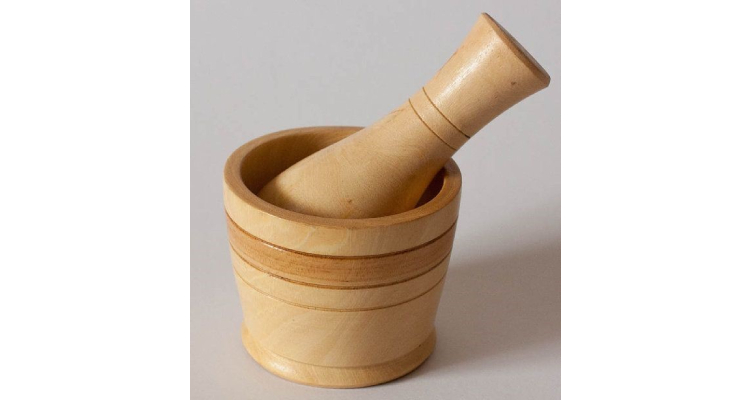
2.Trituration
It is a technique mixing of hard powder by mincing or pulverizing them inside mortar and pestle. This techniques mix powders by reducing their size.
Two kinds of mortar and pestle are used in trituration.
- If you want to simply mixing two powders together without diminishing their grain size then you should select glass mortar.
- If small sized particles are desired, then you should use wedgewood mortar. This mortar is preferred for milling and pulverization as it has coarse interior.
Advantages
- This technique creates fine sized particles.
- Therapeutic effects of powders are enhanced by trituration.
Limitation
- Trituration is a laborious process and does not have much efficiency.
- Hard metals are difficult to mix by trituration.
3.Sifting
In this technique in which lightweight powders like magnesium oxide and charcoal are mixed together by the means of sieve. This method is used to mix powders which are otherwise difficult to mix with trituration.
Sifting technique is utilized for exclusion of large masses and lumps from powder blend.
Usually ordinary kitchen sieve are employed for mixing the powders but standardize pharmaceutical sieves are also available in market.
Advantages
- Sifting instrument is easy to use and has high efficiency.
- Sifting method produces lightweight and fluffy powders.
Limitation
- Sifting is only utilized to mix dry powders.
4.Tumbling
In the tumbling process, the powders are mixed with each other by agitating and moving them in a closed vessel. It is appropriate method of mixing powders if the powders are of different densities.
The powder particles move freely in space of container and should not fall from the sides of vessels.
Generally tumbling is used for large-scale blending and it is accomplished by the means of mixer. These mixers assist in achieving homogenous mixture in adequate time and with accurate speed.
Advantages
- Tumbling is precise and reproducible mixing of powders.
- Tumbling is useful for blending abrasive sensitive powders.
- This is suitable for gentle mixing.
Limitations
- This kind of mixing is costly.
- These are not suitable for blending of segregating powders.
Ⅴ.Principle of Pharmaceutical Mixing
- If you are mixing powders having different densities, first put the lightweight powder in mixing container and then place the high density powder on lightweight powder.
- If powders are in various particle sizes such as granules or fine powder, ground each of powders individually before mixing them together.
- Use the formula of geometric dilution if you are blending small quantity of a drug to bulk amount of powder.
Principle of Geometric Dilution
Geometric dilution is generally used when uneven amounts of powders are mixed. This includes mixing of small quantity powder with same amount of other powder. Then resultant powder is mixed with equal amount of large quantity powder. This procedure is repeated until the powders are finely mixed.
ⅤI.Factors Influencing Pharmaceutical Mixing
Some of the factors influencing the rate of pharmaceutical mixing are detailed below:
A.Particle Size
The smaller sized particle powders are more effectively mixed than the powders having large sized particles. Also increasing the particle size can cause segregation.
B.Nature of Particles
The powders having smooth surface particles are more easily mixed than powders having coarse particles.
C.Particle Shape
If particle of powders have spherical shape then this results in uniform blend.
D.Particle Charge
The attractive forces due to electrostatic charges of particles decrease the mixing rate.
E.Quantity
The powders in small quantities are generally easily mixed.
F.Speed of Impeller
Impeller rotating with low speed results in more homogeneous blend than the impeller with high speed.
VII.Challenges in Pharmaceutical Mixing
Broadly two problems pose the challenge in the pharmaceutical mixing. These are
- Agglomeration
When the particle size of the powders reduced then cohesiveness occurs between the particles, leading to the agglomerate or clump assembly.

This problem is solved by using various dispersing techniques like rigorous connective and shearing. Similarly particle size minimizing approaches like sifting and pulverization are also employed for effectively decreasing agglomeration.
- Segregation
Segregation is the alteration in mixture size distribution or separation of blended solids that were previously homogenously mixed. It is also referred to as unblending. Segregation happens due to unequal sized particles and particle shape.
Remedy
Segregation cannot be prevented but can be curtailed by using convective mixing.
Conclusion
In a nutshell, mixing of pharmaceutical powder require good understanding about particle properties that allow the perfect composition of the mixing, equipment design, and sampling techniques to get perfect quality mix.
If you want to know the basic applications of powder, types of equipment involved in powder filling processing, DIYs, and FAQs, click AIPAK Powder Application to find more informative resources you look for.
Don't forget to share this post!
Powder Filling Machine Related Posts
Powder Filling Machine Related Products
Powder Filling Machine Related Videos
CONTACT US
Tell us your raw material and project budget to get quotations within 24 hours.
WhatsApp Us: +86 181 6426 8586
Want the best price & newest pharmaceutical machinery buying guide,tips and trends sent straightly to your box?Sign up for AIPAK’s monthly newsletter,we’re free for your consultation and Offer you the most suitable solutions!
The Buyer's Guide
- Capsule Filling Buyer's Guide
- Blister Packaging Buyer's Guide
- Tablet Counting Buyer's Guide
- Tube Filling Buyer's Guide
- Cartoning Buyer's Guide
- Gummy Making Buyer's Guide
- CO2 Extraction Buyer's Guide
- Empty Capsules Buyer's Guide
- Suppository Filling Buyer's Guide
- Tablet Coating Buyer's Guide
- Tablet Press Buyer's Guide
- Softgel Encapsulation Buyer's Guide
Most Popular
- 7 Importance Of Pharmaceutical Packaging In Different Applications You Must Know
- 6 Advantages You Must Know About Tablet Counting Machine
- 8 Advantages of Blister Packaging You Must Know
- 6 Critical Applications of Automatic Capsule Filling Machine
- 6 Stations You must Know to Improve the Filling Quality of Automatic Capsule Filling Machine
Tell us your material or budget,we'll reply you ASAP within 24 hours