Everything You Need to Know About Drug Delivery System
Your life resonates around medicines! From neonates to geriatrics, your body is always exposed to drugs for treatments. Some of you might be spending time figuring out how they produce therapeutic effects inside the body. How are they designed in a particular way that alleviates unwanted responses of human physiology? Or What exactly myth is behind the drug delivery system?
Everything You Need to Know About Drug Delivery System is specially designed to provide important information, broad classifications, and future direction about the drug delivery system.
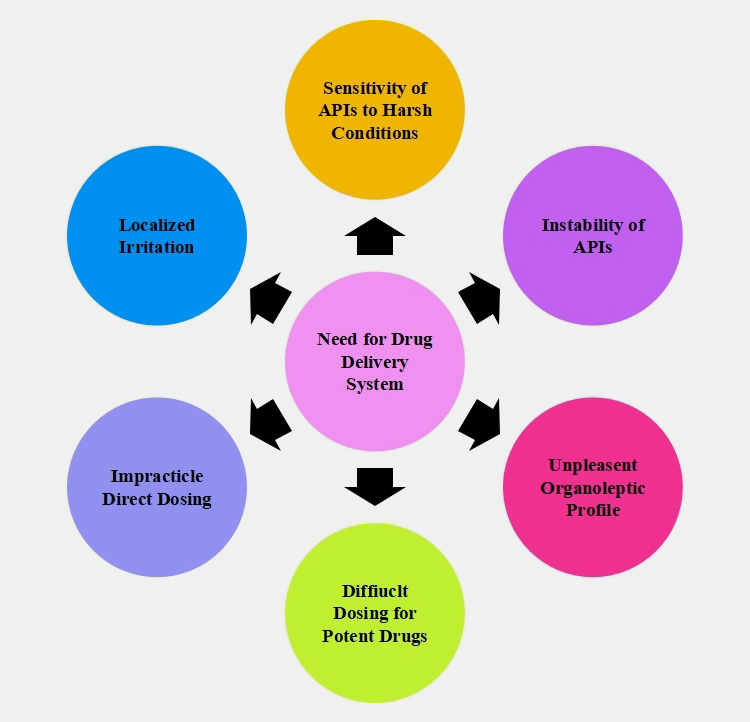
1.Need for Drug Delivery System
The system is employed for ease of dispensing drugs. There are various reasons why the drug delivery system (DDS) is routinely utilized. For instance:
- Active pharmaceutical ingredients (APIs) are rarely directly given for clinical use. It is quite difficult to process and accurately dose APIs for smaller doses and potent drugs.
- Direct APIs dispensing to body cavities such as the rectum and lungs are unfeasible.
- Instability of drugs in severe environmental conditions such as low pH, high temperature, and high humid conditions.
- Localized irritation at the target site if a drug is directly administered.
- APIs have an unlikable organoleptic profile (flavor, odor, and color) that decreases medication compliance in patients.
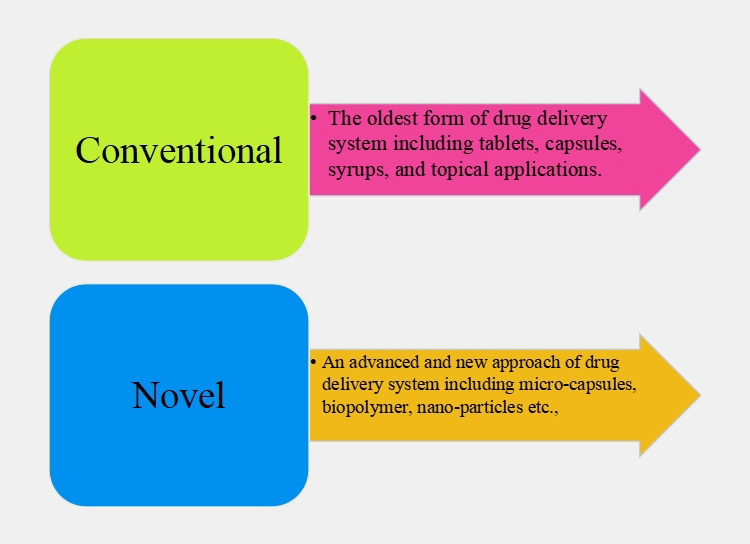
2.Classification of Drug Delivery System
DDS is categorized into two types based on drug evolution:
CONVENTIONAL DRUG DELIVERY SYSTEM
It is the traditional DDS and has been in use since the old times. This DDS is commercially developed in 1950s. First and second generations of drugs delivery systems are included in these DDS.
There are many conventional drug delivery dosage forms such as pills, capsules, injections, mixtures, suspension, aerosols, creams, gel, etc.
There is problem of drug level fluctuation in blood plasma when conventional drug delivery systems are used. Usually multiple doses are required for producing steady therapeutic impact.
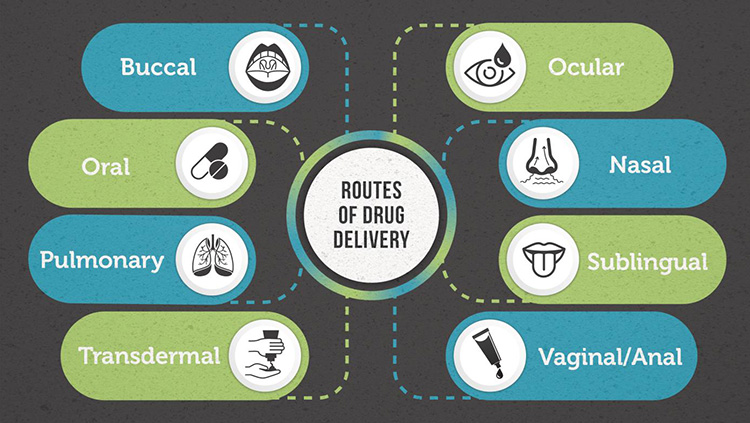
Conventional drug delivery systems are further sub-categorized into several types. These kinds are penned below for penned below for your understanding.
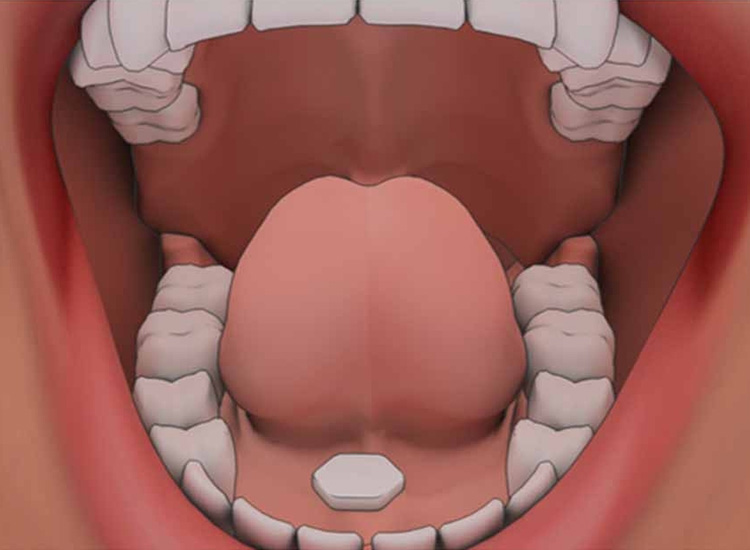
Buccal
A buccal pill or liquid dose is placed inside the buccal pouch, a region between gums and inner surface of cheeks. This drug system is usually given when immediate effect is required or person is unconscious and cannot take medicine orally.
Symptoms are resolved within 5 to 10 minutes because drugs quickly go in the bloodstream through buccal tissues.
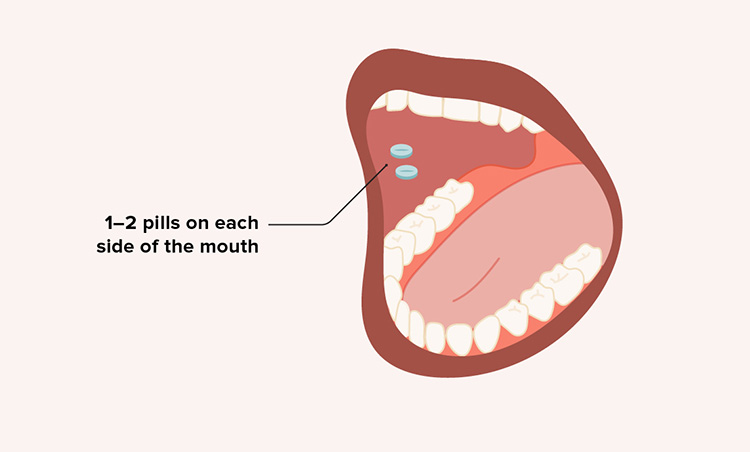
Sub-lingual
Sub-lingual medications are generally put underneath the tongue. These drugs come in the form of films, tablets, and sprays. The tiny blood vessels under the tongue aid in fast absorption of sub-lingual medicines. It takes only few minutes for sub-lingual drug to take effect.
These medicines do not pass through gastric tract so they are not chemically altered in liver. Sub-lingual route of drug administration is particularly suitable for angina relieving medicines.
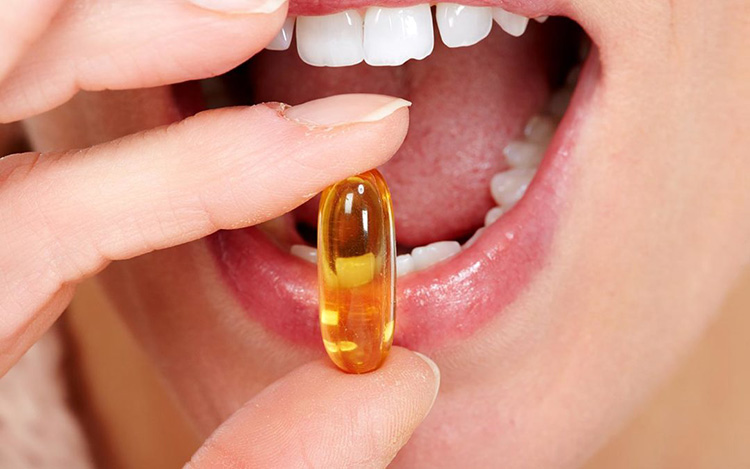
Enteral
Several dosage forms for instance liquids, solids, powders, are administered via enteral route because it is inexpensive, safe, and convenient. These drug are usually taken by mouth and go across entire digestive tract ultimately reaching small intestine from where they are absorb into blood circulation.
They reach liver where these drugs are chemically modified consequently the amount of drug is lowered when reaching target site.
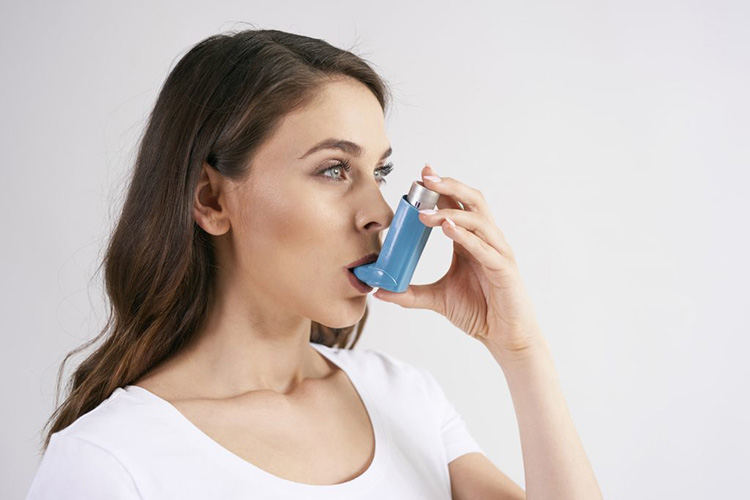
Inhalable
This drug delivery system is given via mouth to lungs and then carried into blood stream. Inhalable drugs are aerosols and are administered by means of specialized devices called inhaler for producing atomized smaller droplets of medication for easy passage through windpipe.
Generally asthmatic drugs and anesthesia gases are supplied by this delivery system.
Nasal
The nasal drugs are applied in the form of small atomized droplets to outer nostrils and then inhaled via air. This drug delivery system is used for treating allergies, sinusitis, congestion, and headaches.
This DDS carries active drugs directly to brain and does not involve the use of needles. The drug easily bypasses brain barrier and provides systemic effect.
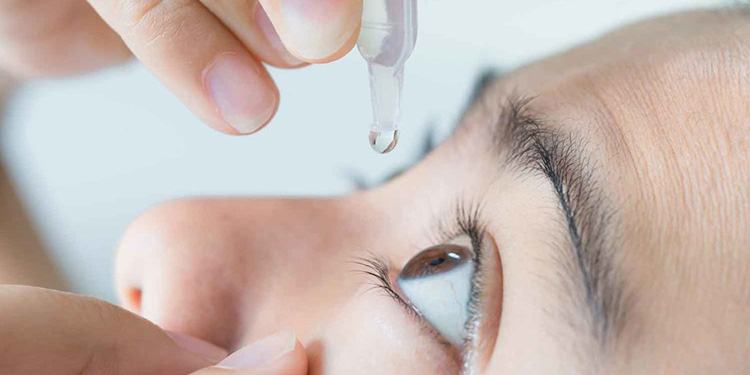
Ophthalmic
This type of conventional DDS is employed for treating various ophthalmic disorders such as glaucoma, conjunctivitis. The ocular drugs are mixed with inactive compounds or excipients for forming ointments, drops, or gels.
Liquid eyes drops are most commonly used because they are easily applied to eyes. But these have limitation of flowing flow away from eyes instantly even before they are absorbed. Gel and creams have longer contact with eyes but they can blur vision.
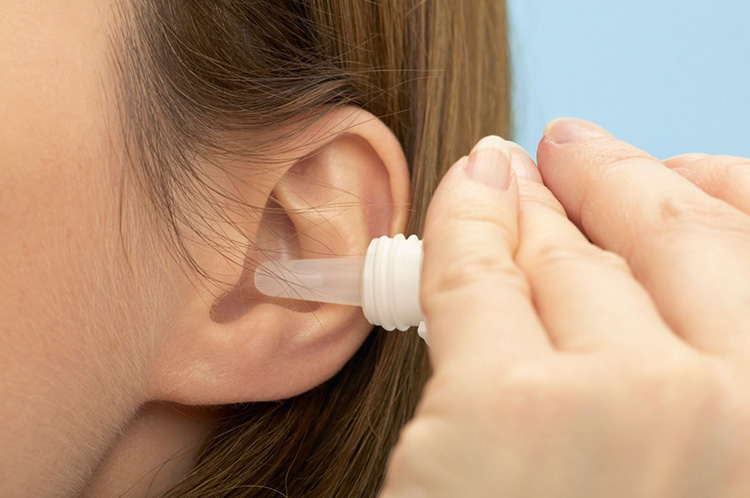
Otic
In otic drug delivery, the solution or suspensions containing medication is directly put in outer ear for curing ear infections or for numbing ears. Little to no drug administered via otic route enters the blood circulation hence there are no side effects associated with otic drugs.
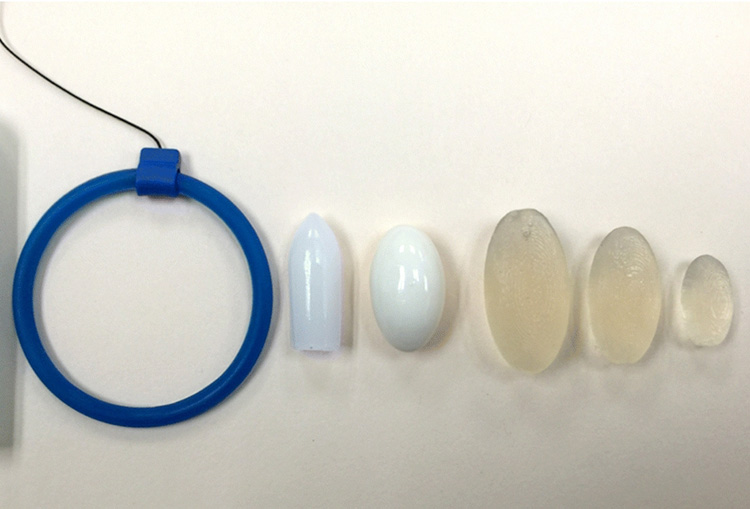
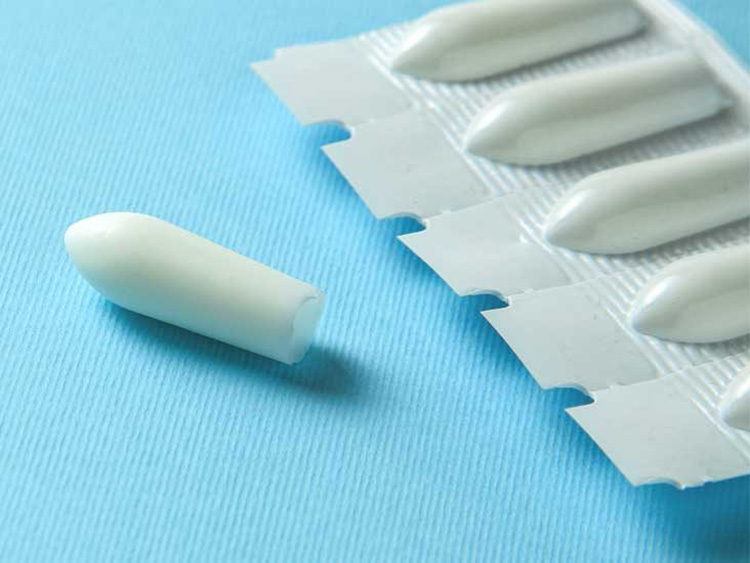
Rectal
Various enteral drugs are dispensed rectally to patients who have nausea, vomiting, or eating restrictions. Rectal drugs are typically suppository capsules formed by combination of drug and waxy liquid. This liquid aids in dissolution of drug in rectum. From rectum drug is immediately absorb because former lining is thinner and has rich supply of blood.
Vaginal
These drugs are delivered to vaginal area in the form of solution, gel, suppository capsule to treat microbial infection. Sometimes a ring is also placed for releasing contraceptive hormones for pregnancy prevention.
This system is also employed for administrating estrogen hormones for relieving symptoms of menopause.
Topical
In this DDS, medications are applied externally to any part of the body. These systems are used for treating various infection, allergies, burns, and other ailments. They are in form of medicated lotions, formulated creams, pastes, gels, tinctures, sponges, ointments, and powders.
Tropical DDS is easily administered by simple rubbing on body part. These are generally epi-cutaneous and are applied to upper layer of skin. They have fewer side effects but can cause localized irritation or rashes.
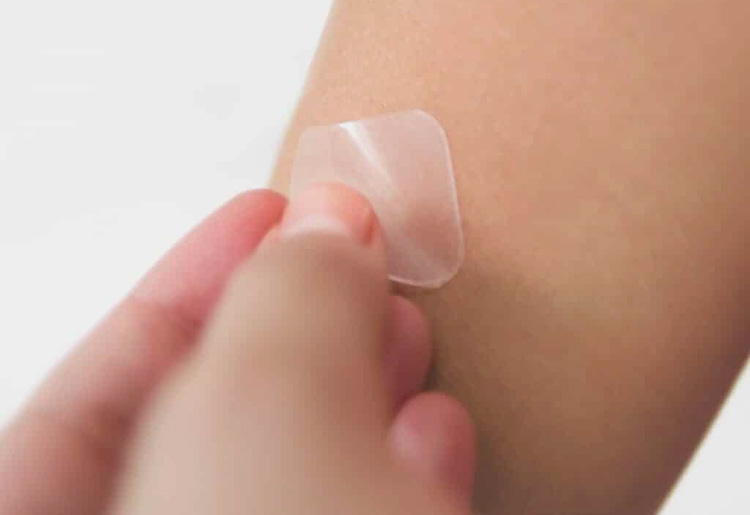
Transdermal
Skin or transdermal patches are used for supplying small doses of medication to all body parts in order to treat symptoms of motion sickness, chest pain, and high blood pressure.
These drugs are combined with chemicals such as alcohols for boosting the drug infiltration in blood stream through skin.
Active ingredients are released gradually by patch for several hours or even days. Only small doses of drugs are delivered by means of transdermal patches.
Infused
Catheter or needles are used for meting out infused drugs. These drugs are difficult to dispense orally because they lose their effect upon exposure to stomach acidity. These systems have benefit of distributing drugs at controlled rate.
Infused drugs are usually antibiotics, biologics, anti-cancerous drugs, growth hormones and nutritional supplements.
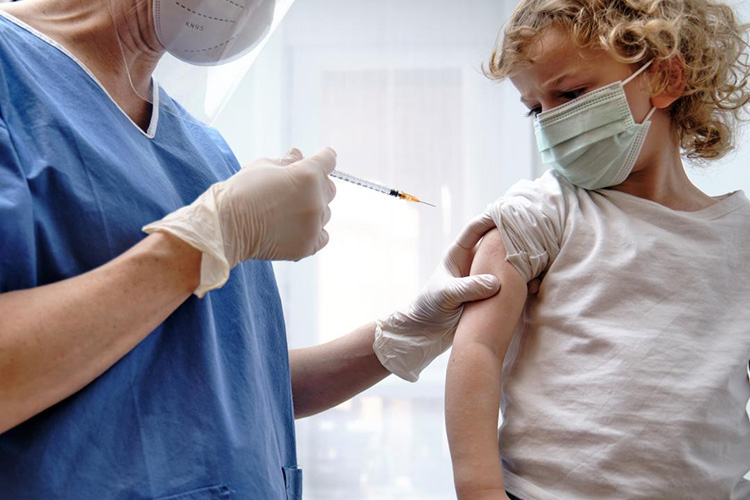
Intramuscular
This route is favored to subcutaneous one when delivery of larger drug volume is required. A longer needle is utilized for administrating these drugs since muscular tissues are located below skin and fatty tissues. Intramuscular medicines are usually injected in upper arm, upper leg or backside.
Absorption of these drugs is depended upon the blood supply to injected area. If blood circulation is lower to target region then medicine is absorbed slowly.
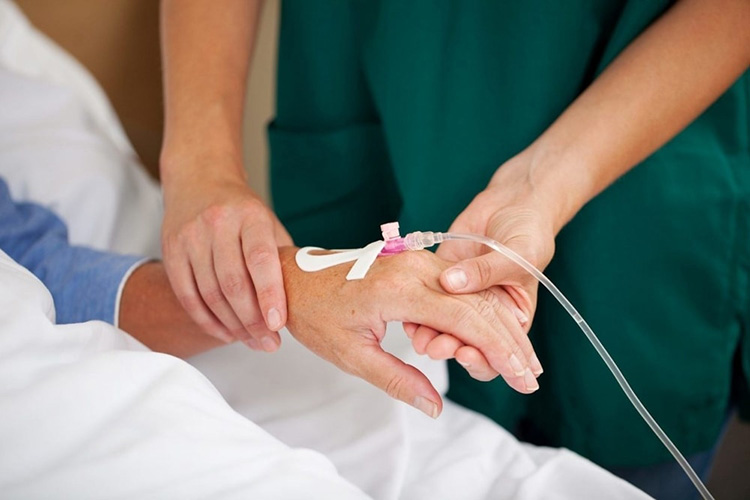
Intravenous
For this DDS, a needle is injected in the vein of forearm. This system is used for dispensing both single dose and continuous infusion. It is the ideal mean for fast and precise drug administration. Intravenous DDS is right for distribution irritating therapeutics which would cause pain and tissue injury if given intramuscularly or subcutaneously.
These drugs provide instant relief and have maximum bioavailability since they are directly dispensed in blood.
Subcutaneous
In this drug delivery system, an injection needle is inserted in the fatty tissues present just below the skin layer. This drug then goes inside blood capillaries and is ultimately carried to blood circulation. Alternatively these medications may also enter lymphatic vessels after being injected.
Subcutaneous delivery system is suited for administrating large protein such as insulin or contraceptive hormones to body.
Novel Drug Delivery System
This drug delivery system has gained quite traction over the recent years. They are the combination of new approaches and advanced formulation for better drug dispensing and therapeutic effect. They are significantly superior to traditional or conventional DDS.
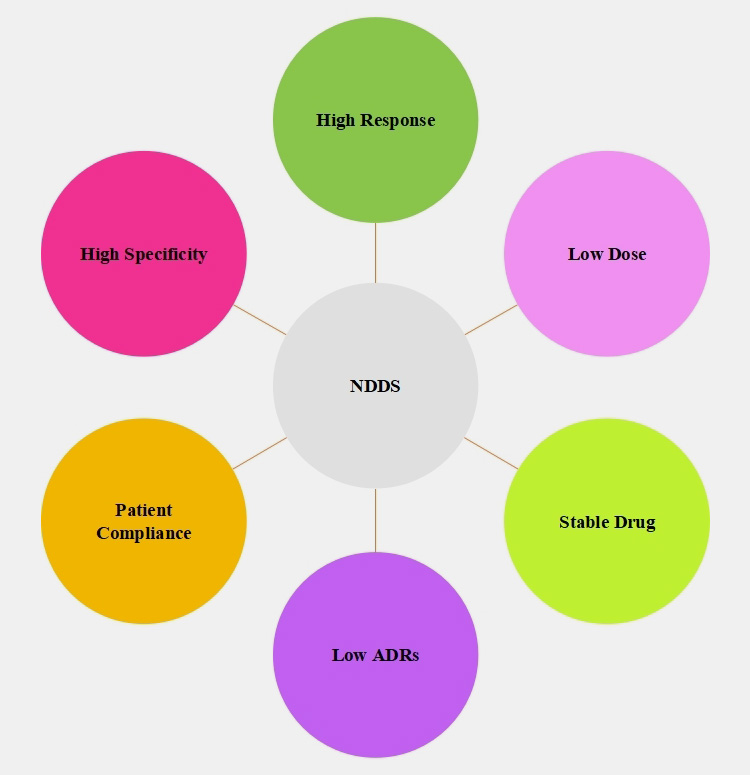
NDDS are invented for boosting controlled, sustained, and targeted effect of drugs. Various biopolymers, nanoparticles, micro-capsules, etc. are used for dispensing novel drugs.
NDDS have many advantages over conventional drugs systems such as stability of APIs, higher response rate, low toxicity and side effects, and better patient acceptance.
These are further classified into three sub-categories which are detailed below:
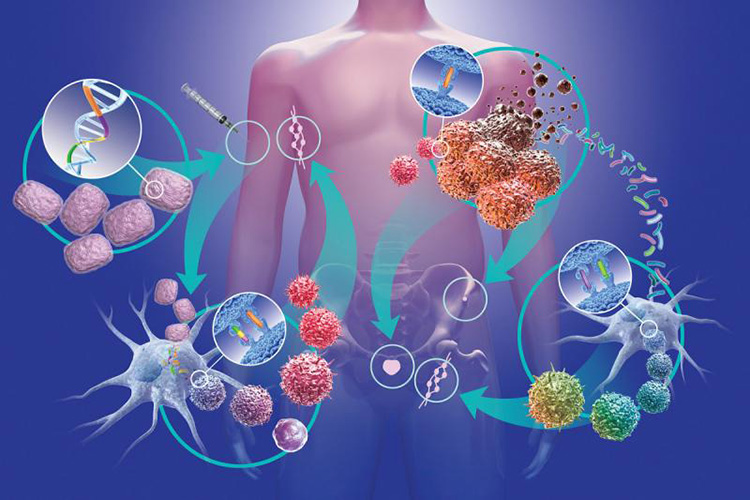
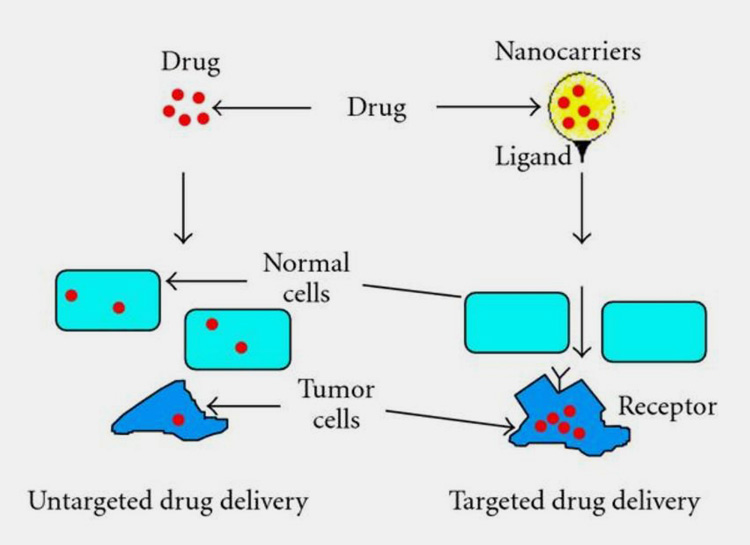
Targeted Drug Delivery
This is also known as smart drug delivery. Targeted Drug Delivery (TDDS) is generally given to patient at a particular region unlike conventional drugs which are delivered or entire body or a specific organ. TDDS is the fourth generation of drug delivery systems.
This drug delivery combines the knowledge of various disciplines such as chemistry, pharmacology, immunology and molecular biology. The ultimate goal of TDDS is to increase treatment response while lowering side effects.
It is also referenced to as magic bullet and is typically improving cancer treatment. In TDDS, the active substances are usually delivered via small molecules (nanoparticles) to cancerous tissues.
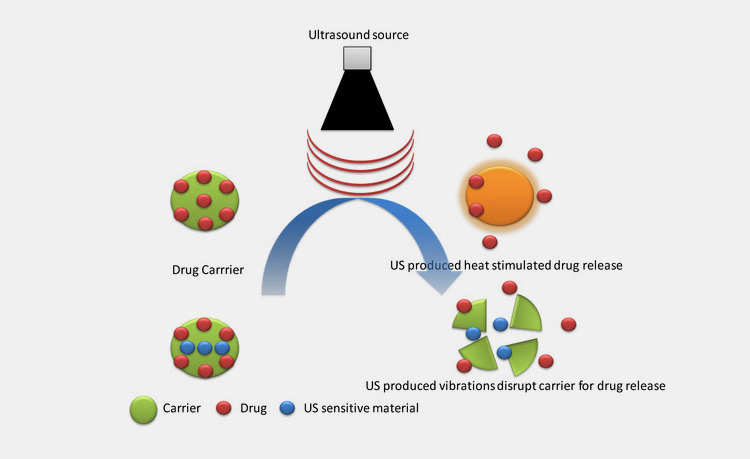
Modulated Drug Delivery
This belongs to fourth generation of drug delivery system. The release of drug is modulated according chemical and physical environmental stimuli in modulated drug delivery system (MDDS). By this, the drug is administered to area of interest as per requirement.
The medication is released in reaction to certain condition in patient or to pre-determined stimuli. MDDS can be internally or externally modulated. Various stimuli such as ultrasonic rays, magnetic pulse, thermal radiations or mechanical stimulation are included in external modulation.
Internal or self-regulated MDDS deliver drugs in particular organ or tissue upon sensing specific pH or enzymatic condition. Drug modulation is done for bypassing adverse characteristics of drugs.
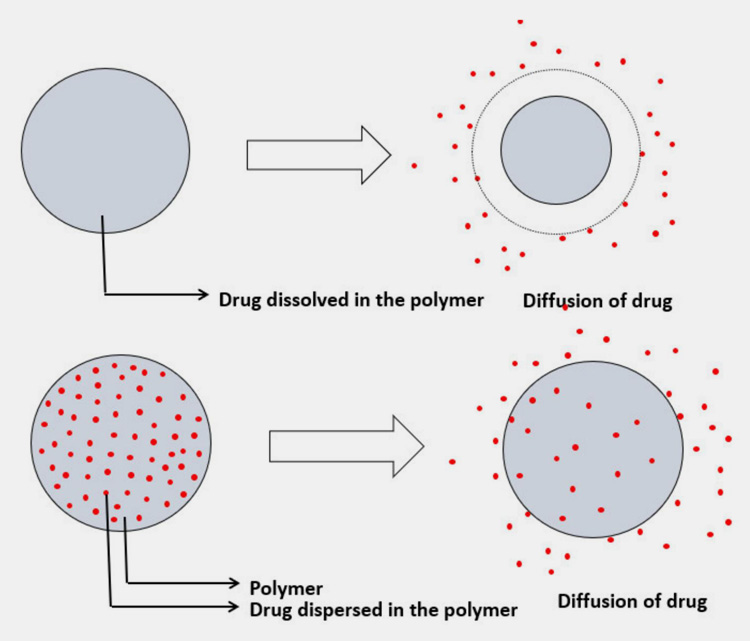
Controlled Drug Delivery
This is the third generation of drug delivery system and involves diffusion, osmosis, and dissolution for drug absorption.
In this delivery system, the constant level of medication is maintained in blood stream or organ tissue.
Fixed amount drug is released gradually from single dose at specific times for pre-determined duration for achieving steady levels of drugs in control drug delivery system (CDDS). This has the benefit of lowering frequency of dosing and has a better patient compliance.
Since the biological drug exposure is low in CDDS so the toxicity associated with medication is considerably decreased.
CDDS is utilized for delivering molecules that have low stability under harsh conditions. These molecules include antibody, proteins, peptides, DNA, etc.
Conclusion
Drug delivery systems are needed for dispensing small doses of bitter tasting medication inside the body. Conventional systems are the oldest form of drug administration involving oral, buccal, sub-lingual, tropical, and intravenous mode of drug distribution. Recent advances in delivery systems have led to discovery of novel drug delivery systems that include targeted, modulated and control drug delivery systems that provide sustained and localized therapeutic effect. How To Design a Drug? What Is the Useful Equipment for Drug Manufacturing? If any question knocks your mind: Do not hesitate to contact us now! We’re available to answer you 24/7/365.
Don't forget to share this post!
Vacuum Emulsifying Mixer Related Posts
Vacuum Emulsifying Mixer Related Products
Vacuum Emulsifying Mixer Related Videos
CONTACT US
Tell us your raw material and project budget to get quotations within 24 hours.
WhatsApp Us: +86 181 6426 8586
Want the best price & newest pharmaceutical machinery buying guide,tips and trends sent straightly to your box?Sign up for Aipak’s monthly newsletter,we’re free for your consultation and Offer you the most suitable solutions!
The Buyer's Guide
- Capsule Filling Buyer's Guide
- Blister Packaging Buyer's Guide
- Tablet Counting Buyer's Guide
- Tube Filling Buyer's Guide
- Cartoning Buyer's Guide
- Gummy Making Buyer's Guide
- CO2 Extraction Buyer's Guide
- Empty Capsules Buyer's Guide
- Suppository Filling Buyer's Guide
- Tablet Coating Buyer's Guide
- Tablet Press Buyer's Guide
- Softgel Encapsulation Buyer's Guide
Most Popular
- 7 Importance Of Pharmaceutical Packaging In Different Applications You Must Know
- 6 Advantages You Must Know About Tablet Counting Machine
- 8 Advantages of Blister Packaging You Must Know
- 6 Critical Applications of Automatic Capsule Filling Machine
- 6 Stations You must Know to Improve the Filling Quality of Automatic Capsule Filling Machine