Blender VS Mixer
Blending and mixing are two of the most essential processes in pharmaceutical manufacturing and other industries,they are utilized in everything from paint-making to the loaf of the bread you love the most.
Blender VS Mixer have very subtle differences, they do have somewhat very common. Both combine two or more substances, and both give similar results.
Certainly, this is common terminology used in routine life, perhaps you use them interchangeably. But technically they are not.
Are you curious to know the hidden differences- This blog is specially designed to make you learn about ‘Blender VS Mixer’. Keep Reading!
Table of Contents
Ⅰ.Description
Blender
This is used to blend only dry materials. For instance, making pancakes involved the blending of multiple dry components (sugar, milk powders, salts, etc.). Similarly, the blending of free-flowing powders is nothing more than a mixing of different varieties of chemicals altogether. Blender is used to make fine powders in a suitable ratio.
Mixer
The mixer is generally concerned with the combination of various substances to form a new product. The context of pharmaceuticals involves both dry and wet substances.
Dry mixing is a crucial step prior to the granulation. Once both ingredients (intra-granular and extra-granular are dispensed, APIs are mixed through dry mixing, but other ingredients (excipients) are added using blending properties. The operation of the mixer is usually a comprehensive one, you get the result as homogenous as possible.
Ⅱ.When To Use Blender Or Mixer
Chart of Common Blender and Mixer Applications
| Task | Blender | Mixer |
| Granulation | |
|
| Mixing Dry Powder | |
|
| Syrups | |
|
| Creams | |
|
| Eye Drops | |
|
| Crushing | |
|
| Homogenous Solution | |
|
| Suspension | |
|
| Pastes | |
|
| Gentle Mixing | |
|
| Gel | |
When to Use Blender
In the simplest words, a blender transforms solids into liquids, fine powders into granules or powders with uniform surface area. Blenders have powerful running motors that make your excellent formulation where you require crushing, chopping, and mixing of solid particles.
Common Blender Uses:
- Crushing
- Chopping
- Pulverizing
- Dissolving
These machines are suitable for making tablets, capsules, or powder mixing.
When to Use Mixer
When it comes to forming a solution, a mixer is a vital tool. Mixers allow you to create homogenous pastes, knead, manage to suspend agents, and much more. Mixers are a bit gentler than blenders; instead, of pulverizing ingredients they combine the ingredient into a homogenous form.
The Common Mixer Uses are:
- Whipping
- Whisking
- Kneading
- Beating
When You Can Use Either One
Interestingly, for some purposes, you can use either a blender or a mixer. When in doubt; follow the simple rule:
- For breaking down solid particles into fine powder; use a blender.
- For mixing or combination of two states, use a mixer.
Ⅲ.Two Main Process Velocities
Blender: The processing speed of blenders is gentler than a mixer. The aim is to create an even distribution of all components in a blender. The industrial blenders are designed in a way that has lesser contact of ingredients with the blades of the blender.
Mixer: In terms of processing, the mixer allows a vigorous operation to combine materials.
Ⅳ.Phase Uniformity
Blender:allows the mixing of solid-solid material or mixing of bulk solids with a minute quantity of liquid. Most often, this is required to produce indistinguishable granules. As the amount of water content is less than dry content. So, it won’t interrupt the state of the material.
Mixer: allows mixing of content associated with liquid, gas, or viscous materials efficiently. Using a mixer may cause the transformation in the state of material
Ⅴ.The Distinguishable Characteristics
Blender:mixing of coarse and fine particles of powders does not assure a perfect blender since there are more chances of segregation which often does occur. Hence, treating with sifting mandatory step to deal with this problem.
Mixer: Mixing solid-liquid, liquid-gas, and viscous material vigorously have reduced chances of de-mixing as compared to treating bulk powders.
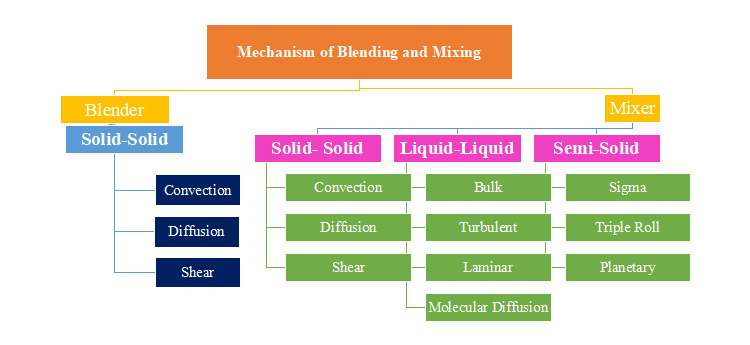
Ⅵ.Primary Mechanism
Blender
There are three primary mechanisms upon which a blender works.
Convection
This is also known as macro-blending where solid particles move from one position to another under gentle tumbling effects.
Diffusion
This is a slow blending process where a gravitational force causes the upper layer of particles to move a newly developed surface ultimately causing a random motion. This is also known as micro-blending.
Shear
Here a shearing force is created within a system of material by the use of stirring arms or bursting air.
Mixer
When it comes to mixing solid-solid; the mechanism would be the same as blending. But here; you’ll deal with some extension for liquid mixing and semi-solids.
A- Liquid Mixing
1.Bulk Transport
It is the transfer of a large portion of an ingredient from one place to another place. This movement is achieved by rotating blades or paddles.
2.Turbulent Mixing
Here a mechanism is based on turbulence; turbulence is a property of velocity gradient between two adjoining layers of a liquid.
3.Laminar /Streamline Mixing
Here two dissimilar liquids are mixed via a laminar flow. The produce shear elongates the interference between them. Due to this various layers and interfacial areas between them are exponentially increasing with time.
4.Molecular diffusion
The process is responsible for mixing at the molecular level. The diffusion is resulting from the production of thermal movement.
B- Semi-Solid Mixing
The three most used semi-solid mixers are:
1.Sigma Blade Mixer
This is used for granulation masses and ointments. This kind of system is composed of two blades operating in a container that has a double trough shape; each blade moves at a different speed.
2.Triple-roller mill
A triple roller mill is used to achieve the complete homogeneity of semi-solid ingredients. The differential speed, as well as narrow clearance between rollers, causes a high shear.
3.Planetary Mixers
It utilizes a rotating mixing arm about its own axis and about a common axis at the center of the mixing wheel. It offers a kneading action while a narrow passage between the blades and wall forms a shear.
Ⅶ.Common Industrial Equipment
Blender
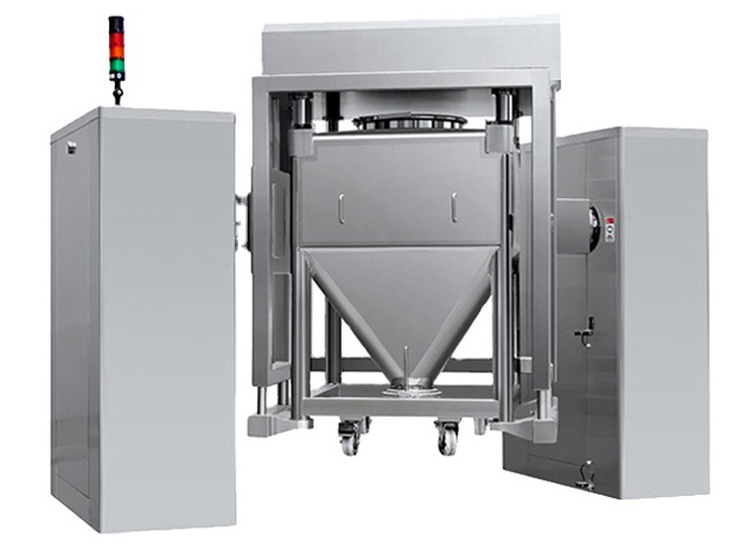
1.Double Cone Blender:A conical-shaped equipment used for dry blending of free-flowing substances.
Aipak double cone blender
2.Twin shell Blender:A V-shaped blending machine used to mix dry particles and designed to break up the formation of clumps.
3.Ribbon Blender:The mixing mechanism is shear that transferred the particles by moving ribbon-shaped blades around the shell.
Mixer
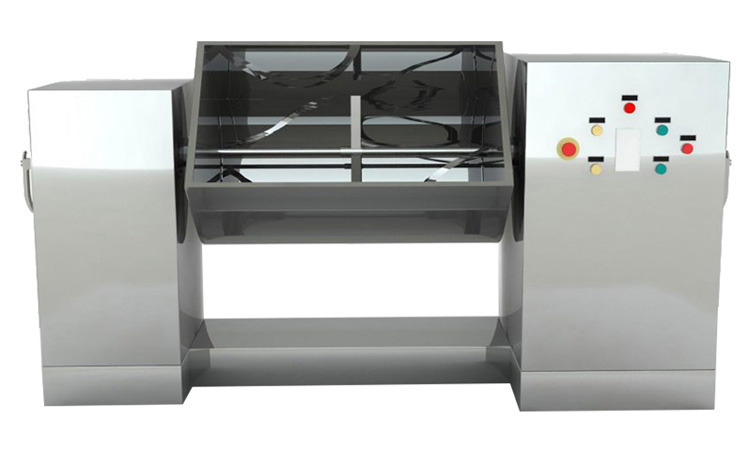
1.Sigma Blade Mixer: It works by creating high shear and kneading action. This is suitable for high-viscosity content.
Aipak sigma blade mixer
2.Planetary Mixer: It is a very simple mixer with two or three-hinged blades that moves the material up and down around the inner cylinder.
3.Propeller: This equipment also works by the principle of high shear force; generally used for liquids.
4.Turbine Mixer: This is used for mixing different types of liquids; mainly works the principle of shearing force.
5.Paddle Mixer: This machine is used for mixing viscous liquids or semi-solid material. It rotates at low frequency and is composed of two long flat blades fixed vertically at a shaft.
Conclusion
Over the past two decades, blending and mixing technologies have greatly improved to address common requirements like blending time, segregation, and large batches. Although selecting the blender or mixer is an art. The article ‘Blender VS Mixer’ is comprehensively written to make you learn minor technical points and understand their differences. For a clearer understanding, we suggest contacting our team of experts. We are always here to help you 24/7/365; give us details and get our services right now.
Don't forget to share this post!
Bin Mixer Related Posts
Bin Mixer Related Products
Bin Mixer Related Videos
CONTACT US
Tell us your raw material and project budget to get quotations within 24 hours.
WhatsApp Us: +86 181 6426 8586
Want the best price & newest pharmaceutical machinery buying guide,tips and trends sent straightly to your box?Sign up for Aipak’s monthly newsletter,we’re free for your consultation and Offer you the most suitable solutions!
The Buyer's Guide
- Capsule Filling Buyer's Guide
- Blister Packaging Buyer's Guide
- Tablet Counting Buyer's Guide
- Tube Filling Buyer's Guide
- Cartoning Buyer's Guide
- Gummy Making Buyer's Guide
- CO2 Extraction Buyer's Guide
- Empty Capsules Buyer's Guide
- Suppository Filling Buyer's Guide
- Tablet Coating Buyer's Guide
- Tablet Press Buyer's Guide
- Softgel Encapsulation Buyer's Guide
Most Popular
- 7 Importance Of Pharmaceutical Packaging In Different Applications You Must Know
- 6 Advantages You Must Know About Tablet Counting Machine
- 8 Advantages of Blister Packaging You Must Know
- 6 Critical Applications of Automatic Capsule Filling Machine
- 6 Stations You must Know to Improve the Filling Quality of Automatic Capsule Filling Machine