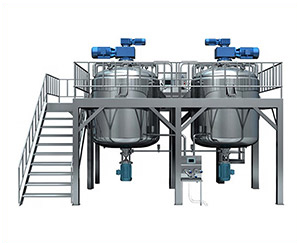
Types Of Semisolid Dosage Form
Do you know semisolid dosage form is a preferable means for treating localized infections? Are you aware that their application goes beyond the pharmaceutical sector?
The utility of semisolid dosage forms, like gels, ointments, and creams for healing dates back to ancient times. Nowadays, it represents a distinct class of pharmaceutical dosage form due to its unique texture that's neither fully solid nor fully liquid. It is well-accepted by patients who do not like to take pills or have a fear of injections. It's because of their ease of administration and non-invasive application.
Are you associated with pharmaceutical manufacturing? Studying pharmacology? Or simply interested in learning about types of semisolid forms? This guide will take you through every facet of semisolid dosage forms. So, let’s buckle up!
1.How do you define a semisolid dosage form?
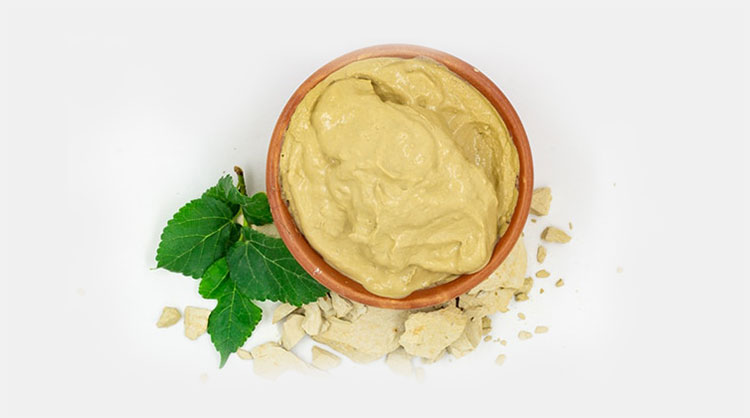
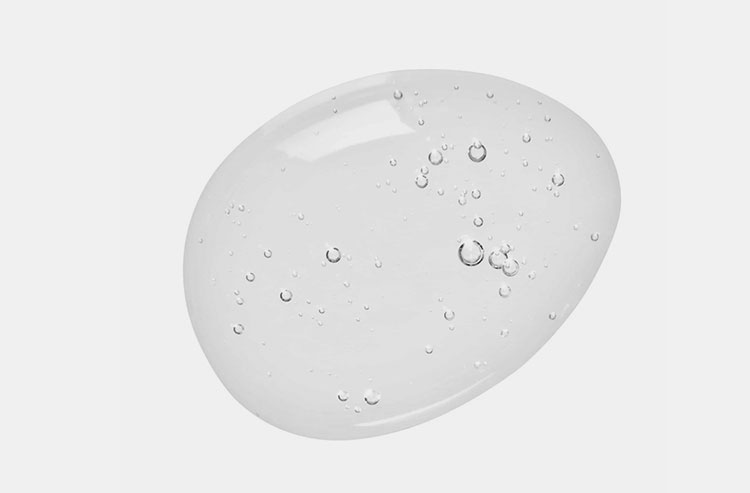
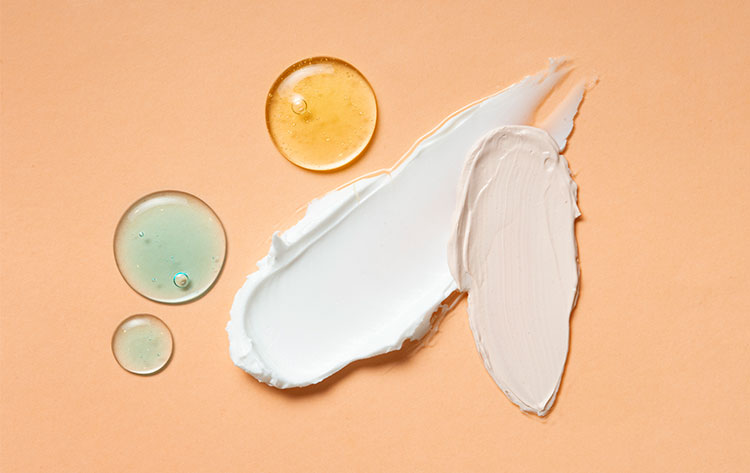
Semisolid Dosage Form- Picture Courtesy: Sleepy Bee
Semi-solid by definition means a material that has both solid and liquid traits. Thus, the semisolid dosage form is in between the solid dosage form and the liquid dosage form in terms of its consistency. It is usually intended for topical administration but also applied to the mucosal membrane, such as the eye surface, buccal cavity, nasal passageway, ear, urethral, rectal, and vaginal tissues.
They are not quite solid, not quite liquid, and have solid particles dissolved or suspended in a liquid base or vehicle. They feature soft or gooey thickness due to which they are easily spread on skin or mucosal linings.
Semi-solid dosage form has a smooth texture and does not have any grittiness or greasiness. These dosage forms are biphasic systems, consisting of aqueous (water) or oleaginous (oily) phases: water and oil. The solubility or dispersion of active pharmaceutical ingredients in one or both phases is dependent upon their physiochemical characteristics.
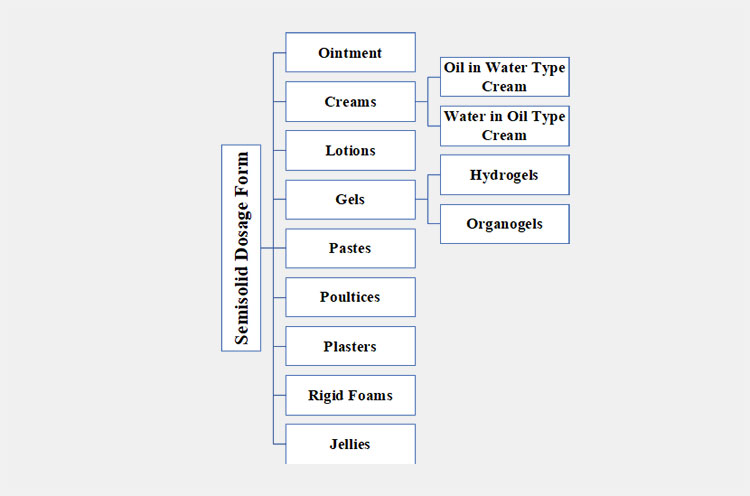
2.What are the types of semisolid dosage form?
You've probably seen creams, gels, lotions, and jellies for sale, right? They are types of semisolid dosage form. These dosage forms come in a variety of classes, depending upon their physical form, composition, and intended application. The primary kinds of semisolid dosage forms are:
Ointment
Ointment- Picture Courtesy: Healthline
Have you ever used ointments for burns? It is the form of semisolid dosage form with thick and greasy properties and has a higher ratio of oil to water. It is also termed unguent or salve. It acts as occlusive meaning it creates a barrier on skin to retain moisture content. It is usually formed from medicinal components and treats superficial skin conditions, such as burns, cracked heels, eczema, and psoriasis. It is designed to stay on the skin for an extended time; subsequently, has the highest product absorption.
Creams
Creams- Picture Courtesy: Lifestyle Asia
You would’ve used cream in the morning or before bed. They are semisolid formulations and are typically oil-in-water or water-in-oil emulsions. They have more water content than ointments and, therefore, have a more smooth and fluffy consistency than ointments, hold their shape well, and are easily spread on the skin. They are excellent for hydrating dry skin, rashes, skin wounds, etc. due to their higher water content and also protect against water loss.
| Oil in Water Type Cream | It is a type of emulsion in which tiny droplets of oils are dispersed in the continuous aqueous phase and surfactants are added to this emulsion to stabilize it. In this type of cream, water is present in more quantity than oil. It is lightweight and used as a moisturizer or sunscreen. |
| Water in Oil Type Cream | It is a semisolid emulsion in which water molecules are scattered throughout a continuous oily medium. It has a thicker and heavier texture than oil in water cream and has a more occlusive role. It locks hydration; thus, is preferred for a deep moisturizing and soothing effect on chafed or inflamed skin. |
Lotions
Lotions- Picture Courtesy: VerywellHealth
Consumers frequently confuse lotion or cream with each other but they are vastly diverse types of semisolid dosage forms. They are formulated with higher water volume than creams, making them the lightest and thinner of all semisolid dosage forms. Some types of lotions also have alcoholic components in them. Lotions have a fast absorption rate, due to their runny consistency.
Gels
Gels- Picture Courtesy: Cosmetics & Toiletries
They are a colloidal dispersion in an aqueous medium, where a liquid phase is trapped inside a 3D web of large organic molecules. Gels are meant for both topical or transdermal use and are commonly employed as drug delivery aids and lubricants. They have characteristic clarity or translucency with a smooth texture, facilitating their uniform spread on extensive skin areas.
| Hydrogels | This type of gel is composed of water as a suspension media. They are hydrophilic and absorb huge quantities of water without losing their composition. They are soft and pliable, usually imitating characteristics of tissues. |
| Organogels | This gel class contains organic solvent as a liquid phase. Typically, ethanol, acetone, or oils are employed as a liquid medium in organogels. They are hydrophobic and stable in non-aqueous conditions. They are used in transdermal drug delivery. |
Pastes
Pastes- Picture Courtesy: BeBeautiful
They are more viscous than gels and are prepared by mixing powders in a liquid vehicle. Powders are scattered in liquids, offering pastes stiff, thick, and porous consistency. Hence, they are more difficult to rub on the skin. They are excellent for external and localized disorders, such as athlete's foot, as they absorb water and distribute antifungal components right to the infected region.
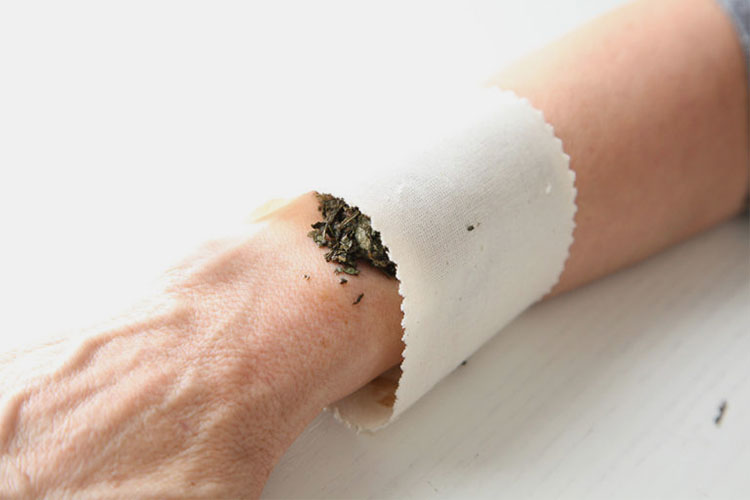
Poultices
Poultices- Picture Courtesy: The HerbalAcademy
Did you know this is one of the oldest ways people have used medicine? It is also called cataplasm. It is a soft, wet mass of herbs and seeds and is devised for topical use. This formulation is initially put on a clean cloth or dressing, then the dressing is placed on to affected area for treatment. It treats skin disorders, for instance, boils or sunburns. They are frequently used for reducing soreness and inflammation.
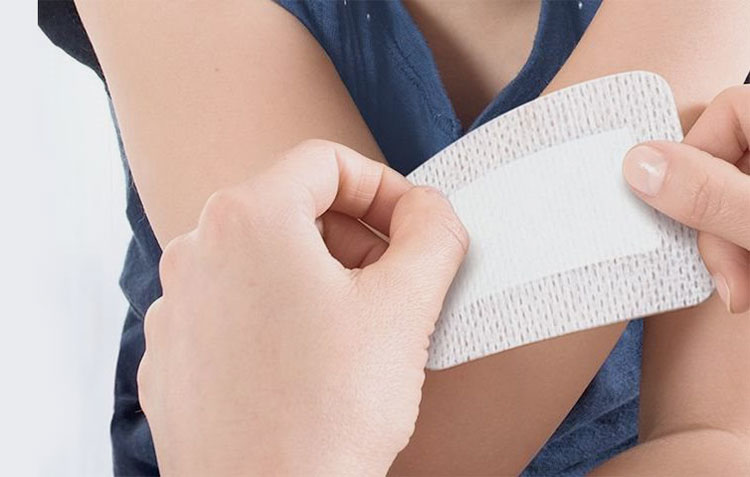
Plasters
Plasters- Picture Courtesy: Elastoplast
This semisolid dosage form is formulated with mixing plaster, water, and active ingredients. It is designed for external use because its texture makes it easy to apply it on skin or dressing. It hardens on application to the skin and gradually releases medicated substances over time, providing sustained relief.
Rigid Foams
Rigid Foams
Have you heard of rigid foams for skin healing? They are also called medicated forms and are distinct types of drug delivery methods. These pharmaceutical foams are comprised of a gaseous medium dispersed in the liquid phase, which has soluble active pharmaceutical excipients for efficacy. They are like bubbly liquids with medications, for instance, corticosteroids, antimicrobials, and chemical sunscreens.
Jellies
Jellies- Picture Courtesy: Vaseline
This class of semisolid dosage form is transparent or translucent in appearance with a non-greasy and soft texture. They are mainly developed for mucosal tissue treatments, such as antifungal jellies and antibacterial jellies. Jellies are often utilized for lubricating surgical gloves and rectal thermometers. Moreover, they also have a contraceptive role.
3.Why types of semisolid dosage form are popular in the healthcare sector?
Semisolid dosage forms are favored in the healthcare and medicinal sector owing to their wide range of handy benefits, for example, direct drug delivery to the target site, ease of utility, and so much more. So, without further ado, let’s discover the reasons for the popularity of types of semisolid dosage forms:
External Application
External Application- Picture Courtesy: The New York Times
One of the biggest benefits of this type of semisolid dosage form is its external application and non-invasive nature. It is mostly used for treating external wounds, burns, scaling, or oral ulcers. It provides soothing relief and a cooling sensation; therefore, offering immediate treatment relief. Moreover, it is also designed to heal delicate and fragile tissues, such as the eyes, oral cavity, or rectal areas.
Reduce Side Effects
Reduce Side Effects
One of the major pros due to which this dosage form gained traction among patients and medical practitioners is its minimal number of side effects. It exerts its therapeutic response at the site of administration or surrounding areas; thus, does not generate adverse drug reactions with systematic effects, like anaphylaxis, liver damage, nausea, vomiting, or stomach irritation.
Ease of Application
Ease of Application- Picture Courtesy: MetroDerm
The type of semisolid dosage form, for example, pastes, gels, or creams has a thicker yet soft texture, so it offers convenience in drug administration. They are easily applied, rubbed, or spread on the desired area without the need for specialized instruments, like spoons or droppers. Due to this, it is well-accepted by patients.
No First Pass Effect
No First Pass Effect- Picture Courtesy: Health Channel
Are you aware that first-pass metabolism is typically the cause of lower drug availability in blood circulation? Consequently, reducing the effectiveness of medication. However, types of semisolid dosage forms, intended for dermatological, topical, or mucosal routes, go straight into vascular systems, thereby, circumventing first-pass metabolism in the liver and potentially enhancing therapeutic efficacy to target sites.
Diverse Composition
Diverse Composition of Semisolid Dosage Form
Pharmaceutical manufacturers can choose either between hydrophilic or lipophilic bases, so types of semisolid dosage forms are prepared with water-soluble and fat-soluble ingredients. This makes them suitable for treating diverse types of skin conditions- from antimicrobial infections to hydrating skin, and more.
4.In what sectors the types of semisolid dosage form are utilized?
You will find it hard to believe but applications of types of semisolid dosage forms are not limited to the healthcare sector but it is also employed as a treatment aid in cosmetic or nutraceutical industries as well. Let’s have a close look at the multitude of uses of types of semisolid dosage forms:
Healthcare and Pharmaceutical Sector
Pharmaceutical Gels and Creams
Types of semisolid dosage form are primarily utilized in the pharmaceutical sector, where they have vital dermatological applications. Certainly! They treat a diverse range of skin infections, such as acne, eczema, psoriasis, and inflammation. You can also apply gels, jellies, pastes, and, creams for minimizing pain in joints or muscles and curing wounds.
Cosmetic Field
Cosmetic Creams- Picture Courtesy: BBC Distributors
Nowadays, types of semisolid dosage forms are heavily formulated and distributed for cosmetic and personal care use. Diverse types of semisolid preparations serve as whitening creams, anti-aging gels, hydrating masks, wrinkle-vanishing lotions, and hair-styling jellies in the cosmetic industry. They are also prepared as makeup products, like foundations, primers, and serums.
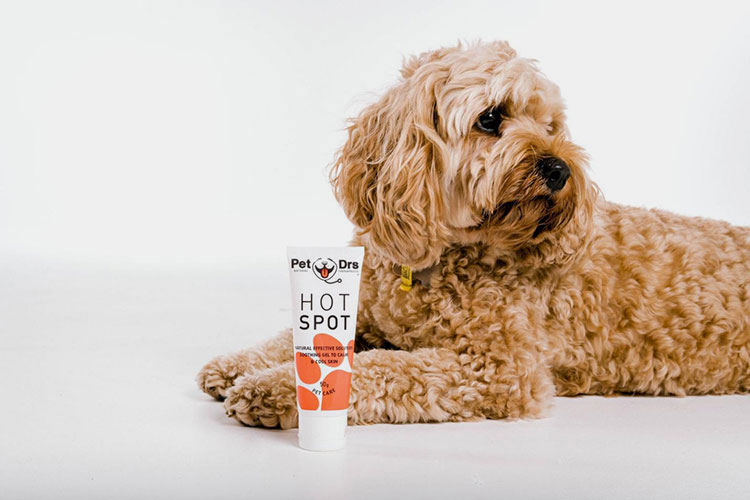
Veterinary Sector
Pet Creams- Picture Courtesy: Swaggle
Are your pets suffering from skin infections? You can also utilize types of semisolid dosage forms for curing topical and systematic disorders. Pets and wild animals often get cuts, bruises, or scrapes, so vets use antiseptic ointments for injuries to heal them. Also, gel formulations are ideal for treating ectoparasitic infestations, such as fleas, ticks, and mites.
Nutraceutical Sector
Nutraceutical Creams- Picture Courtesy: Stoelzle Glass Group
Types of semisolid dosage form are an instant hit in the nutraceutical industry because of simple administration, pliability, and faster drug delivery. Different nutrients and herbal extracts are formulated as cream, gel, or paste preparations, which not only mask undesirable tastes but also make them easier to consume. It increases the absorption rate of nutrients and allows their prolonged release. They can be applied to local topical areas or mucosal lining to deliver supplements for localized uses.
Biomedical Research
Biomedical Gels- Picture Courtesy: Cosmederma Remedies
Types of semisolid dosage forms have found their use in research and diagnostics because of their bio-adhesive characteristics and flexibility of preparation. Researchers are making strides in developing bio-adhesive gels for target drug administration and scaffolds for cell growth.
5.What are the basic components of types of semisolid dosage form?
Have you ever wondered about the composition of your daily-use creams or moisturizers? There are a variety of ingredients incorporated into them to offer them the desired texture and therapeutic effect. Let’s read about various components in the types of semisolid dosage forms:
Active Ingredients
Active Ingredients- Picture Courtesy: Boots
They are the main pharmaceutical constituent of the types of semisolid dosage forms and are responsible for the desired treatment response. They have different physiochemical profiles and can be hydrophilic, lipophilic, and both (amphiphilic). Active ingredients are either solubilized or dispersed in the base. They can be antifungal, antiseptic, or, anesthetic.
Base or Vehicle
Base or Vehicle- Picture Courtesy: Allure
It is one of the core components involved in the preparation of semisolid dosage forms. What functions does base have in semisolid dosage form? It has two integral jobs: acting as a carrier of active ingredients and regulating the rate of medication absorption. It has a diverse set of properties, for instance, inertness, emollient, non-greasy texture, non-allergenic nature, and easy wash-off ability. It has different categories including:
| Oleaginous Bases | They are also known as hydrocarbon bases or oleaginous ointment bases. They are composed of water-insoluble compounds like oils and fats. They do not absorb water and are considered anhydrous. Their penetration through the skin takes time. However, they are excellent occlusive and emollient. Their examples are hard paraffin, white petroleum, carnauba wax, beeswax, etc. |
| Absorption Bases | They are also anhydrous bases; although they have the capacity to absorb large quantities of water, yet they maintain an ointment-like texture. They are categorized into two types: non-emulsified bases (lipophilic bases that do not have water at their initial stages but can soak up water and generate water in oil emulsion) and water in oil emulsion bases (water is included in their preparation and in suspended in the oily phase). Their examples are wool oil, lanolin, cold cream, and more. |
| Emulsifying Bases | These bases are also termed water-miscible or water-removal bases. They are water-loving in nature and can absorb water easily. It is quite easy to remove them from the skin due to their water-washable nature. They include cetrimide cream base and cetostearyl alcohol. |
| Water soluble Bases | They are grease-less because they do not have even a tiny quantity of oil. They are completely soluble in water. Water-soluble bases are often composed of polyethylene glycol. |
Buffers
Buffers- Picture Courtesy: Connect Chemicals
Are you curious as to why buffers are added to types of semisolid dosage forms? There are different purposes of buffers, for instance, they increase drug compatibility with skin and enhance drug stability and solubility.
Humectants
Humectants- Picture Courtesy: Clariant
It is composed of numerous hydrophilic groups and hence, it is hygroscopic. It is included in the formulation because it improves the solubility of active ingredients, facilitates transdermal permeation, and boosts skin hydration. It prevents dryness and crustiness of semisolid dosage form containers.
Preservative
Preservative- Picture Courtesy: Cosmetics & Toiletries
Some types of semisolid dosage forms easily resist microbial invasion. Why? Because they have preservatives with microbial-inhibiting characteristics that do not allow the growth of microorganisms. Some examples are benzoic acid, propylparaben, phenol, and others.
Antioxidants
Antioxidants- Picture Courtesy: SELF
They are fundamental compounds that safeguard skin or mucosal cells from potential damage due to free radicals- generated by oxygen. They prevent the oxidation of biomolecules in cells.
Emulsifier
Emulsifier- Picture Courtesy: COSSMA
It assists in keeping oil and water mixed together in the types of semisolid dosage forms. It produces a barrier between oil and aqueous phase by minimizing the forces that attract oil droplets and aggregate together.
Gelling Agent
Gelling Agent- Picture Courtesy: Garnier
As the name indicates, these agents, when mixed in a liquid medium, create a colloidal system with weakly bonded mesh. This contains a liquid phase, leading to the formation of the gel. They are usually gelatin, pectin, cellulose derivatives, etc.
Permeation Enhancer
Permeation Enhancer- Picture Courtesy: Minimalist
They are like helpers that boost the rate of drug permeation through the skin barrier. Generally, oleic acid, limeone, and methanol are employed as permeation enhancers.
Surfactant
Surfactant- Picture Courtesy: Formula Botanica
Surfactants are like detergents with both polar and nonpolar components. The addition of surfactants in semisolid preparation has a role in the assembly of micelles. These micellar structures trap and solubilize lipophilic or water-insoluble components by incorporating them into their hydrophobic interior.
6.How do you prepare the semisolid dosage form?
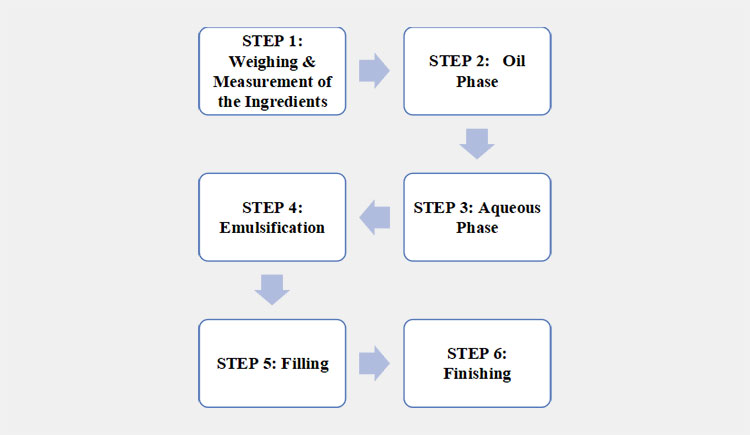
The semisolid dosage form is processed by the following steps described below:
Preparatory steps of types of semisolid dosage form
STEP 1: Weighing & Measurement of the Ingredients
Preparation of semisolid dosage- Picture Courtesy: Gattefosse
The semisolid dosage form ingredients are composed of oil based and water-based ingredients. These are mostly available either in powdered form as well as in flakes, granules, and pellets form.
Moreover, there are number of emulsifying agents available, and they need to mix in the ingredients to make a stable semisolid dosage form.
You must first measure the required ingredients and then subject them to uniform blending. For that you will require constant mixing and heating.
Name of Ingredients
| Oil Based | The oil-based substances are hydrophobic hydrocarbons which are included; hard, soft liquid paraffin, animal extracted fats, various synthetic glycerides, etc. |
| Water Based | The water base or aqueous substances are glycerin, water. |
| Emulsifying Agents | The emulsifying agents are fatty acids, alcohol, wool fats, waxes, tweens, and fatty esters. |
STEP 2: Oil Phase
Oil phase- Picture Courtesy: Purenatural NZ
All ingredients related to oil phase are positioned inside the double jacketed steaming kettle or storage tank which is ensuring you the constant mixing and temperature enabling the uniform melting of the entire substances. The temperature is usually kept between 60 to 70 °C and in some cases, you may maintain them at 100 °C.
STEP 3: Aqueous Phase
Aqueous Phase- Picture Courtesy: Numis
Similarly, at the same temperature but in the separate pot, add the ingredients of water-based substances. For example, water or distilling water, glycerin, or related substances such as propylene glycol are heated. You must be careful not to fluctuate the temperature and maintain the temperature at the temperature of oil phase.
STEP 4: Emulsification
Emulsification- Picture courtesy: gattefosse
First understand the word ‘emulsification’. This is the process where you alter the state of two immiscible liquids. Homogenization is an important property that approaches the two states and mixes them with a uniform composition.
Here, with the help of homogenizer, you slowly incorporate the aqueous phase into oil phase under impact of constant homogenization to achieve stable emulsion. When you are preparing semisolid dosage form ‘oil and water’ you add water based into the oily phase and vice versa (in case of water in oil emulsion with gradually cooling the process.
In this state, you can add APIs, preservative, fragrance, any additive such as thickening agents etc.
Hence, if you ignore the property of maintaining temperature or the continuous stirring, then face separation chances would be high. Therefore, vigorous shaking is essential when it comes to emulsification phase.
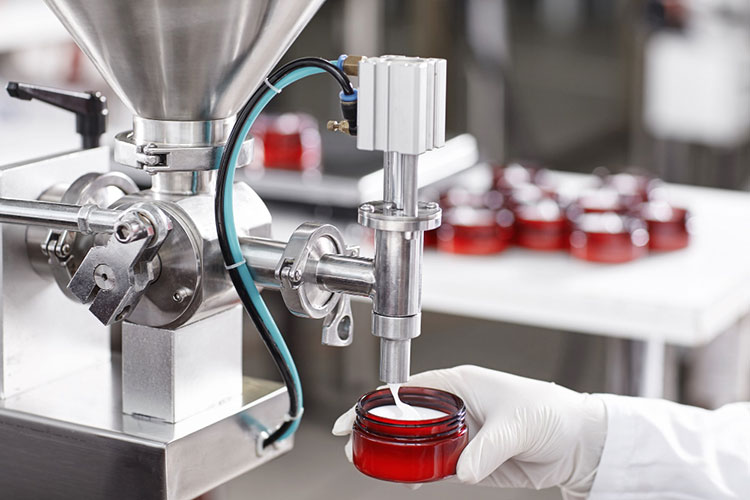
STEP 5: Filling
Filling- Picture Courtesy: EZ life Pharmaceutics
It is time to fill the semisolid dosage form either in tubes, jars, containers, or pouches. This can be achieved by transporting the preparation toward the filling machine where the filling nozzles ensure the accurate and precise dispensing of the solution into your desirable packaging materials.
STEP 6: Finishing
Finishing
The finished products are now in the packaging materials that have to be treated with capping, induction sealing machine and labeling machine. That’s it! Your semisolid dosage form is now ready for final approval and market.
7.What mixing force is used for types of semisolid dosage form?
There are the various types of mixing pattern involved in the manufacturing of types of semisolid dosage form. We have described the main categories just right below:
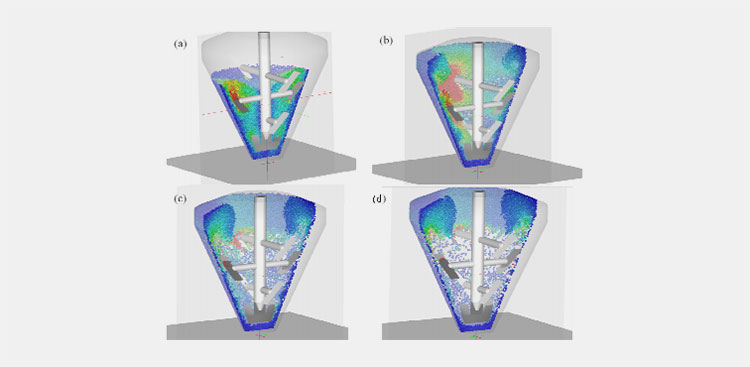
Centrifugal force
Centrifugal force- Picture Courtesy: Polymer innovation
The basic working principle of machines are based on the centrifugal force. This machine the force which is produced just by the central axis and keeps rotating to induce the hydrostatic pressure and give rise to a huge buoyancy that makes through mixing of the particles.
High-speed or Supersonic force
High-speed or Supersonic force
This is the mixing machine that is mainly based on the action of rotary paddle at a high speed along side with heat to induce the melting of the ingredients with high mixing. In this machine, you can add ingredients that are best known for thermal stability with constant stirring to up to required time.
Radial Force
Radial flow mixer- Picture Courtesy: MXD process
This type of mixer is ensuring the mixing of the ingredients toward the outer edges of the container. So, the particles hit the walls and move downwards and keep hitting the wall to form an intense radial pattern to break down the ingredients and induce a high blending.
Shear Force
High shear force-Picture Courtesy: ResearchGate
This is a high rate mixing than a conventional mixing where a tip rotor speed is as high as it can reaches 10 to 50 m/s. The rate of shear is observed from 20,000 to 100,000 s-1 (how fast the fluid layers move).
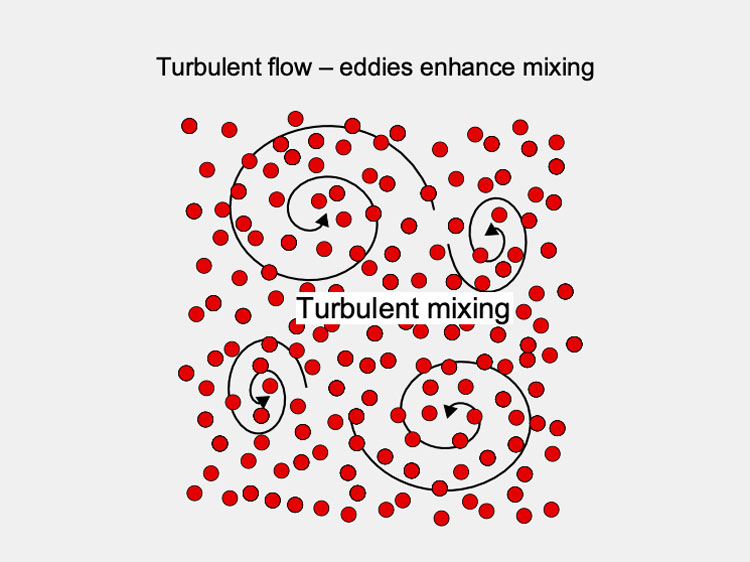
Turbulent Force
Turbulent force- picture courtesy: Eagle pub
A turbulent mixing utilizes a strong force to induce greater mixing velocity in order to fragment, dilute and form a strong and stable mix. This type of mixing follows an irregular and chaotic pattern to blend the materials.
8.What are machines used in types of semisolid dosage form preparation?
The various machines used in semisolid dosage form are described below:
High Shear Mixer
This is a high frequency-controlled machine where a stirring blade and cutter. It ensures a better control over reducing the particle size and allowing through mixing without risk of involvement of any external factors such as air. A compact sealed mixing tank provide high thermostatic operation with an improved results due to high shear mixing properties.
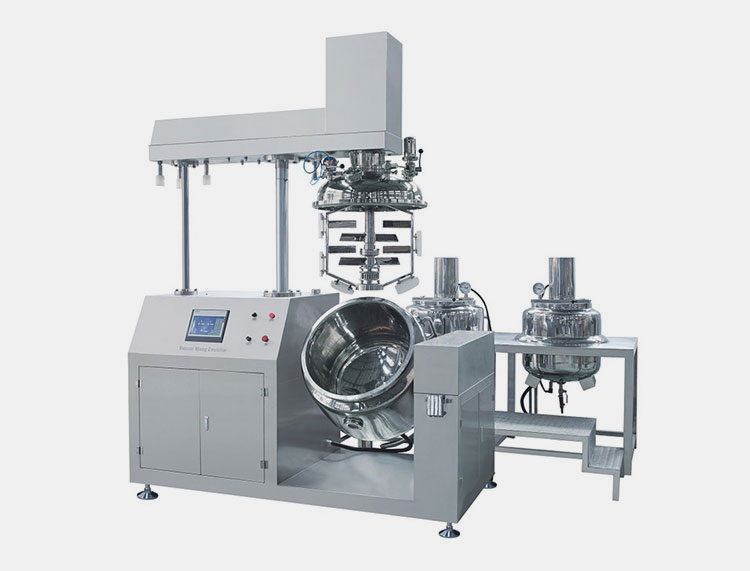
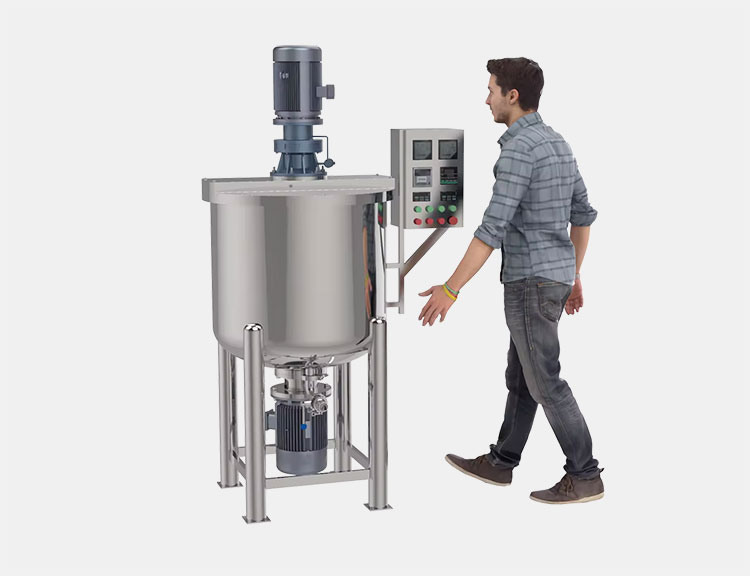
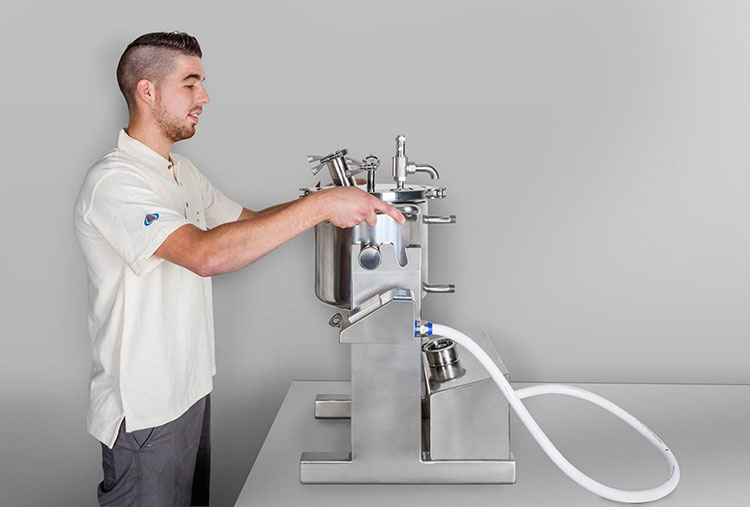
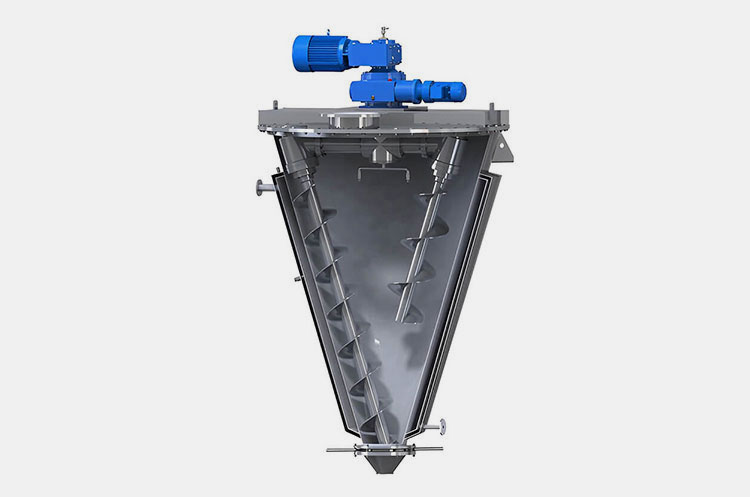
Vacuum Emulsifying Mixer
AIPAK vacuum emulsifying mixer
This is suitable for sensitive APIs and pharmaceutical emulsification of various products. The process of mixing is taken place under vacuum and high velocity of rotating impellers present inside the tank of the machine. It helps in the creation of emulsion related to high matric viscosity of ingredients easily such as toothpaste, gels, ointments etc.
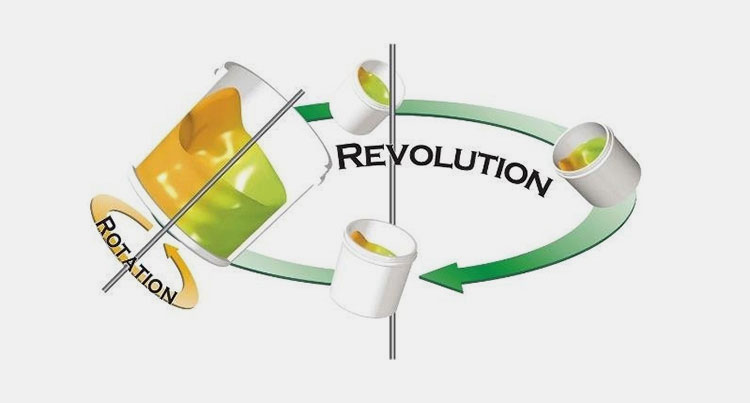
Planetary Mixer
Planetary mixer
In the planetary mixer, the number mixing pattern is taken place just like various planets move around the orbit system of the sun. With the help of number of mixing blades, thick or highly viscous ingredients can be emulsified in a flexible way to produce a uniform and a consistent blend.
Jet Mixer
Jet mixer- Picture Courtesy: Jongia
This is a suitable mixer for sustainable production line and capable of generating gel shaped polymeric formulation with nano sizes particles. In this machine the momentum coefficient is considered as the most essential factor to offer you a high speed mixing to prepare semisolid preparations.
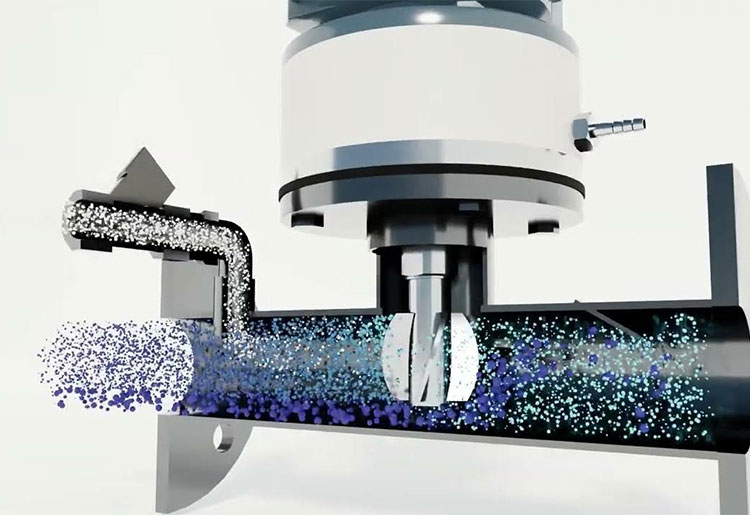
Inline Mixer
Inline mixer
This type of mixer homogenously mixes the semisolid dosage preparatory materials and is useful in various formation of pastes and gel. However, this type of mixer can be used for macro as well as micro-scale operations. Due to static element in its structure, the mixing shaft inside the mixing chamber of the machine induce the emulsification of formulation to form a uniform blend.
Micro Fluidizing Mixer
Micro mixer- Picture Courtesy: KRIEGER AG
This type of mixer is used to mimic the manufacturing of semisolid dosage form preparation ranges from small sizes such as from 100 ml to 10 liter confined to a small tank. This is an ideal device to deal shear sensitive materials by mixing under vacuum.
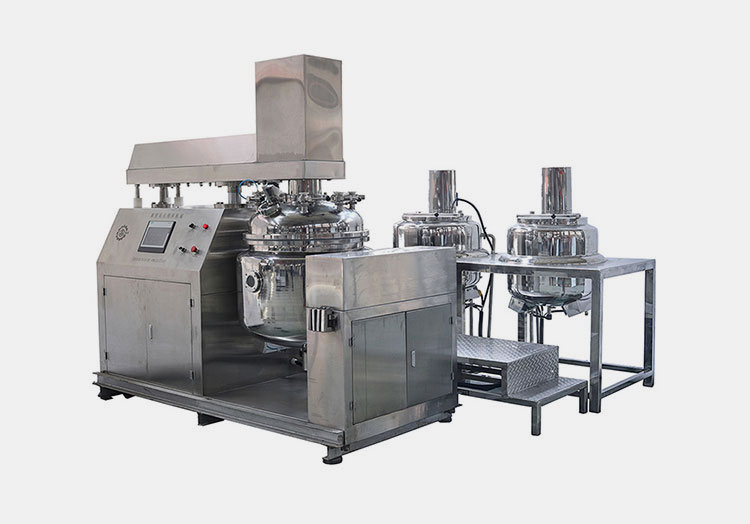
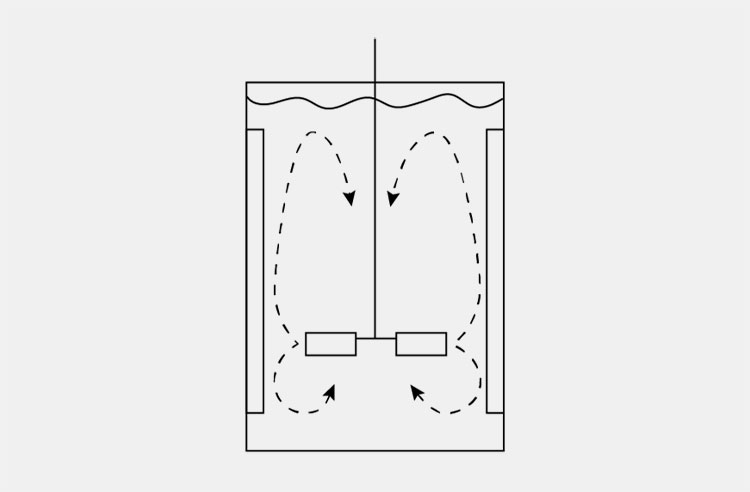
Homogenizers
AIPAK Bottom Homogenizer Vacuum Emulsifying Mixer
This is mainly used for industrial production of semisolid dosage form where greater production capacity has to fulfilled. The machine is facilitated with separate oil and water pots where you can dissolve the respective materials that are sucked by the pipes system into the homogenizing tank for further mixing of the substances under vacuum and following temperature required by the protocol till you get an emulsified blend.
9.What are the kinds of blades used for types of semisolid dosage preparation?
To mix or blend semisolid dosage formulation, there are the following mixing blades that have to use for the procedure.
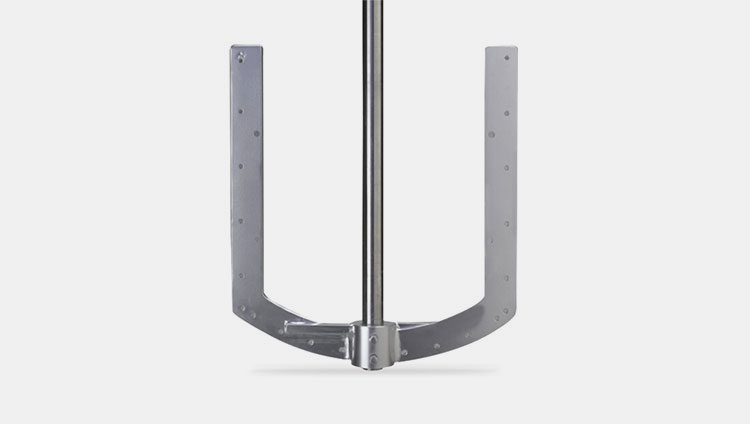
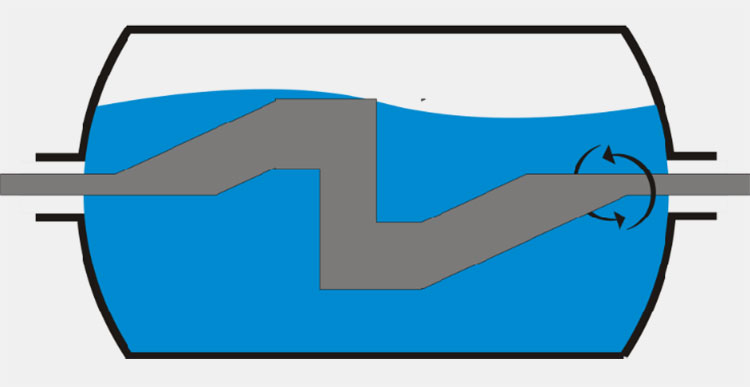
Anchor Blade
Anchor blades- Picture Courtesy: Premix technology
These types of blades are mainly used in hemispherical kettles with a bowl shaped tank to ensure smooth impeller forces at a reduced speed.
Sigma Z Blade
Sigma Z blades- Picture Courtesy: ResearchGate
The sigma Z blades are mainly applied in planetary mixers where they induce the whip ad kneading mixing to form a through and uniform blending of the materials.
Paddle Blade
Paddle Blades
These types of blades are composed by two pairs of the rotary and flat blades that are fixed around the fixed shaft to induce low as well as high rotational force.
Screw Blade
Screw blades- Picture Courtesy: Excellence in particle
These types of blades are segmented in design and mounted at the shaft to create a torque to produce high speed and mainly used in the formation in semisolid dosage for mixing of creams, gels, pastes.
Turbine Blade
Turbine blades- Picture Courtesy: Agetic
The turbine blades are composed of impellers with four or more than four and mounted vertically around the fixed shaft to give high rotational force per minute. These blades give radial and axial flow forces for the mixing of the semi solid dosage formulation.
Helical Ribbon Impeller
Helical ribbon blades- Picture Courtesy: Galan
As the name shows, the helical ribbon impellers are capable of giving high force and ideal for treating the high viscosity substances.
10.Can types of semisolid dosage forms be used for systemic drug delivery?
Semisolid Dosage Forms for Systemic Use- Picture Courtesy: Epicuren Discovery
Indeed, some types of semisolid dosage forms are employed as drug delivery methods for systematic effect. Even though, typically various types of semisolid dosage forms are exclusively devised for localized skin or mucosal administration. There are some kinds of semisolid medications that deliver drugs to the bloodstream by absorption via skin or mucosal tissues.
Transdermal gels and creams are major types of semisolid dosage forms that distribute hormones, analgesics, or nicotine to blood circulation. They have permeation enhancers to expedite drug permeation.
Nowadays, you have buccal, sublingual, rectal, or vaginal gels that are smeared on mucosal tissues in the mouth, rectum, or vagina, respectively to rapidly supply nitroglycerin gels or progesterone gel. This is because of the rich vascular supply in these regions.
11.What are the challenges in manufacturing types of semisolid dosage form?
Yes, it is not always simple to devise types of semisolid dosage forms and pharmaceutical manufacturers often run into problems with formulation materials, interaction between ingredients, and meeting regulatory standards. Some unique challenges in the development of types of semisolid dosage form and their mitigation solutions are discussed below:
Creating a Homogenous Blend
Creating a Homogenous Blend
It is a serious problem and it is difficult to achieve smooth and consistent distribution of active drug components and other excipient substances because oily bases have high viscosity, hindering the mixing outcome. Moreover, generally, fat-soluble ingredients are incorporated in the formulation that may remain insoluble in water or segregate due to variations in particle size.
Solution
Although, it is quite a tricky problem; however, you can easily rectify it by utilizing advanced types of industrial mixers, for example, planetary mixers or homogenizers. You can also narrow down size distribution through sifters or millers.
Changes in Formulation Stability
Changes in Formulation Stability
Types of semisolid dosage forms are formed using diverse types of ingredient profiles, so it can be challenging to maintain the stability of ingredients. As they could degrade through reaction with oxygen and on encounter with light or temperature. Phase separation commonly happens in emulsion, affecting stability. Some types of semisolid preparations have a high proportion of water that leads to microbial colonization.
Solution
It’s a tough problem but with some simple techniques, you can easily solve this problem. You can mix antioxidants, stabilizers, and preservatives to increase formulation stability. You can also pack them in appropriate packaging made with air-proof and light-resistant materials. You should perform stability testing for ingredients in the semisolid dosage form.
Vaporization of Moisture Content
Vaporization of Moisture Content
Sometimes, you’ll observe complete drying of preparations, such as gels or creams. Why is that? It is because of the evaporation of watery material inside them, causing a texture alteration or decreased potency. They may form a hard crust, causing difficulty in their application and skin penetration.
Solution
You can optimize temperature and humidity during product development and manufacturing to prevent moisture vaporization. You can also add emulsifying agents to boost medium stability. It is also advised to employ high-barrier packaging materials to prevent vaporization.
Upholding Product Aesthetics
Upholding Product Aesthetics
Since types of semisolid dosage forms are put on the skin; therefore, they must look and feel smooth and soft. The attainment of desired rheological characteristics, appearance, color, and fragrance poses a significant challenge. Because now and then, coloring agents, perfumes, or active ingredients are incompatible with the base. Moreover, errors in manufacturing can lead to a final product with an irregular or gritty texture.
Solution
You can easily overcome this issue with some simple approaches by utilizing high-quality materials and modifying processing techniques. Also, you should first carry out a sensory assessment for aesthetics during product manufacturing.
Incompatibility in Packaging
Incompatibility in Packaging
It is vital to choose suitable packaging materials that are fully compatible with the physiochemical characteristics of products. Sometimes, product leaks or spills occur due to improper design of packaging.
Solution
You can overcome incompatibility issues by designing collapsible aluminum tubes for ointments. It helps in reducing air contact of oily formulations. Airless pumps are also essential in reducing air contact with sensitive preparations.
Conclusion
In short, the types of semisolid dosage form are the benchmark in the dermatology and cosmetology fields. Due to its softness, ease of spreading, and targeted drug delivery, it is the first choice of numerous patients. Whether it’s a relieving cream, transfusing gel, or a protective ointment, they successfully address the multitude of therapeutic needs. They stand out among other dosage forms due to their minimal internal side effects. The increased demand for types of semisolid dosage forms translates into promising avenues of financial returns for manufacturers. If you’re seeking information on the latest instrument for the production of types of semisolid dosage forms or have more queries related to their preparation, then the AIPAK expert customer care team is ready to assist you anytime and anywhere.
Don't forget to share this post!
Vacuum Emulsifying Mixer Related Posts
Vacuum Emulsifying Mixer Related Products
Vacuum Emulsifying Mixer Related Videos
CONTACT US
Tell us your raw material and project budget to get quotations within 24 hours.
WhatsApp Us: +86 156 0710 8630
Want the best price & newest pharmaceutical machinery buying guide,tips and trends sent straightly to your box?Sign up for AIPAK’s monthly newsletter,we’re free for your consultation and Offer you the most suitable solutions!
The Buyer's Guide
- Capsule Filling Buyer's Guide
- Blister Packaging Buyer's Guide
- Tablet Counting Buyer's Guide
- Tube Filling Buyer's Guide
- Cartoning Buyer's Guide
- Gummy Making Buyer's Guide
- CO2 Extraction Buyer's Guide
- Empty Capsules Buyer's Guide
- Suppository Filling Buyer's Guide
- Tablet Coating Buyer's Guide
- Tablet Press Buyer's Guide
- Softgel Encapsulation Buyer's Guide
Most Popular
- 7 Importance Of Pharmaceutical Packaging In Different Applications You Must Know
- 6 Advantages You Must Know About Tablet Counting Machine
- 8 Advantages of Blister Packaging You Must Know
- 6 Critical Applications of Automatic Capsule Filling Machine
- 6 Stations You must Know to Improve the Filling Quality of Automatic Capsule Filling Machine