Everything You Need To Know About Manufacturing Creams
The cream is a significant formulation of pharmaceutical that is applied topically. Producing a smooth textured cream is somewhat difficult. This is because it has a two-phase system with potential phase variability and materials interaction. So as a result, achieving the desired outcome is very difficult that requires sound knowledge, expertise, and excellent machines. Are you interested in Developing Creams? EVERYTHING YOU NEED TO KNOW ABOUT MANUFACTURING CREAMS will make you learn the important aspects of creams. Keep Reading!
1.WHY CREAM IS IMPORTANT FOR YOUR SKIN?
A topical cream is a science-backed consumer's favorite formulation that helps in replenishing your skin in many ways. An insight of soft and smooth cream has diverse complexities in terms of manufacturing and its potential role.
Just like vital organs, the skin is considered the largest organ in your body, measuring 22 square feet. As it offers a considerable surface area, therefore implementing medication is a wise decision. An emerging science strives hard to bring new advancements and modes of drug delivery via topical applications. Since the very beginning, ancient people have used medicinal plants, leaves, and flowers over their skin to soothe the pain. Today, you can use analgesic creams directly on the affected part, isn’t a blessing? That’s why skin is considered as a significant target to achieve benefits from topical creams.
2.EMULSIFIER- A MAGIC TRICK IN THE FORMULATING OF CREAM
If you’ve ever mixed water and oil in a bottle by vigorous shaking, you might have noticed they don’t mix.
Initially, the oil may break into small droplets, later they make their layer again. When formulating cream, you require to mix the oil and water phase altogether. Here you need to add an emulsifier.
What Is an Emulsifier?You can call it a ‘stabilizer’ that keeps oil and water molecules bind together and prevent them from segregation. Many emulsifiers are available in a wax-like texture in the form of beads or flakes.
You cannot use the same emulsifier for all kinds of creams. For that extensive knowledge about emulsion systems is necessary. The formulation of cream is divided into types of emulsion systems.
The majority of creams are formulated with ‘Oil in Water’or ‘O/W’ This means an emulsion where oil molecules are dispersed in tiny droplets in a large amount of water is termed an ‘oil in water emulsion. For example, vanishing cream.
Similarly, if your cream formulation has a large number of oil molecules as compared to water then you’d need a ‘Water in Oil’or ‘W/O’ emulsifier and this phenomenon is termed water in the oil system. For example, cold cream.
Commercially, oil in water system O/W emulsion is more acceptable and comfortable as they are less greasy and easy to wash. Whereas water in oil or W/O is difficult to handle as compared to O/W. Therefore, it is important for pharmacists to assess the types of emulsion and emulsifying systems before manufacturing the cream.
3.CLASSIFICATION OF CREAMS?
The types of skin care creams are mentioned below:
Cleansing Cream
In ancient times, people were using stones or bones to exfoliate the skin. In 1920, cosmetic cleansing cream was introduced on an industrial scale composed of mineral oils, beeswax, and water. With the advent of modern techniques, cleansing creams are designed with moisturizing and cleansing effects. It is safe and effective for skin care and is popular among post-adolescent girls with sensitive skins.
Cold Cream
A Greece physician Galen was the first who introduced cold cream. This is a soft textured formulation that softens the skin. This is perfect to treat dry and cracky skin, especially elbow, feet, and knees.
Massage Cream
Today, massage creams are popular as it promotes resilience and softness while improving signs of aging.
The great interest of massage creams to restore eternal youth by claiming anti-wrinkles effects. Facial massage creams are significant as it rejuvenates your skin. Side by side it limits psychological distress and stimulates the sympathetic nervous system.
Night Cream
Night creams are formulated that have the capacity to remain on the skin surface for a long time even after a vigorous massage. It is composed of a mixture of oils and cannot disappear with proper rubbing. Night creams are designed with high oily molecules W/O, with extra viscosity.
Moisturizing Cream
Manufacturing companies introduced this term as it offers extremely high moisturization to your skin. These creams are formulated with high lipid components that promote skin hydration and flexibility. It is often regarded as synonymous with night cream. It prevents transepidermal water loss by making a hydrophobic barrier over a topical layer of your skin.
Foundation Creams
Foundation creams can be traced back to 200 B.C. Greek women applied the cream to enhance their beauty and complexion. Roman people were used to applying white powder and tin oxide base to lighten their skin.
Foundation creams have the same properties as vanishing creams. With time, manufacturers offered sun protection by adding sunscreen agents to it. So, foundation creams ensure, skin protection against UV radiation, reduced signs of aging, and lighten your skin tone.
Vanishing Creams
A greaseless cream that is designed for the outer surface of the skin. Its ingredients marvellously protect your skin by keeping it moist. This cream is commonly used to remove your makeup or dirt particles. This is water in oil (W/O)type, it vanishes when applied over the skin.
Hand and Body Creams-All Purpose Creams
Hand and body cream is a purpose cream that nourishes your skin and is excessively applied as a night cream. They are designed with heavy oil and greasy consistency to retain moisture content in your body.
Medicated Creams
Medicated creams are used to treat skin ailments such as burn, infection, allergies, acne, scales, pain, and rough skin. Medicated creams are designed with active pharmaceutical ingredients (APIs). For example, salicylic acid, lidocaine, diclofenac sodium, etc.,
4.MOVING FROM CREATIVITY TO SCIENCE: WHAT ARE THE INGREDIENTS OF CREAMS?
The ingredients of creams vary from brand to brand. It could be very simple or may have a huge list of materials. However, keep in mind that cream is a ‘Two-Phase’ system: an oil and water phase. Formulating cream is mainly based on understanding and control over material blending. So, it won’t be wrong to state that making creams is a complex process.
For your understanding, we are categorizing creams ingredients in three stages:
STAGE 1- OIL PHASE
This phase makes up 11 to 24% of the concentration of a cream. A medicinal cream possibly has a higher proportion of oil phase as compared to water. However, water is always considered a lead player in its formulation.
Some of the major ingredients of the oil phase are:
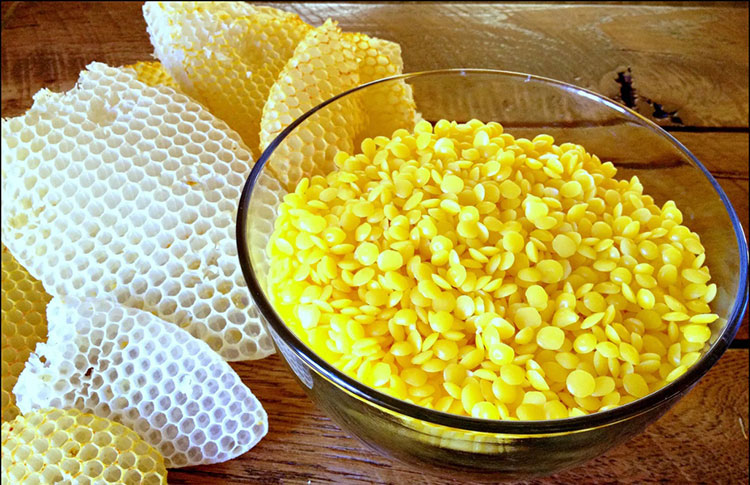
WAXES
It is an important element of cream, ointment, and lotion. It gives solidity to the formulation and ensures the holding of water molecules. Furthermore, the proportion of wax keeps varying depending upon desirable consistency. The commonly used waxes are beeswax, soy wax, olive wax, carnauba, ceresin, spermaceti, etc.,
BUTTERS
Butter has moisturizing, anti-inflammatory, and healing properties. Its addition in creams formulation improves texture and consistency. Commonly used kinds of butter are shea butter, mango butter cocoa butter, etc.,
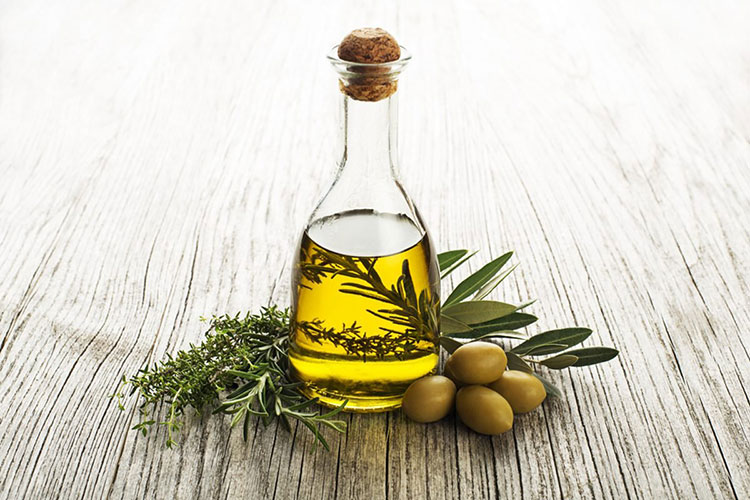
OILS
Oil is a major derivative of a cream. The types of oil used are:
Mineral Oil
Mineral oil (another ingredient of some creams) therapeutically benefits in relieving psoriasis which is a dermatological condition pertaining to red, itchy scales on elbows, knees and scalp.
This is lightweight and inexpensive ingredient widely used in pharmaceutical creams. This is a heavily refined form of hydrocarbon obtained from petroleum oil. It has an affinity of prevent water loss from body and improving moisturization. The commonly used oils are liquid paraffin, liquid petroleum.
Glyceride Oil
They are vegetable oils such as almond, coconut, Arachis, castor, olive oils, etc., These oils sustain skin elasticity and reduce water loss from your skin. The commonly used glyceride oils are Almond oil, Sunflower oil, Avocado oil, etc.,
EMULSIFYING AGENT
Water and oil do not mix their own. You need to add an emulsifying agent to create a stable emulsion of oils and water. It allows two immiscible substances in a mixed form and prevents its separation. The commonly used emulsifying agents are cetyl alcohol, Polyoxymethylene sorbitan, sodium lauryl sulphate (SLS), benzalkonium chloride, etc.,
ANTIOXIDANTS
Antioxidants are used to protect the formulation via scavenging free radicals’ formulation. Moreover, it strengthens your skin by enhancing anti-inflammatory activity, boosts rapid healing, and protects skin against sun damage. The commonly used antioxidants are Co-Enzyme Q-10, Alpha-Lipoic Acid, etc.,
LANOLIN
It is obtained from the wool fat of a sheep. They are available in hydrous(water) and anhydrous forms (without water- odorous). This is mainly used to enhance blending and the product’s stability.
HUMECTANT
It is a multifunctional substance used in every cream formulation. It absorbs and retains moisture on your skin; also considered an exfoliator. Examples of humectants are Sodium PCA and Sodium L-Lactate.
STAGE 2- WATER PHASE
This is the major constituent in most of the creams which are about 61 to 77%. This value may vary; in some creams, the value may be higher or less. The herbal ingredients or active ingredients may be added and solubilized in water except in the oil phase. Many manufacturers use incorporate active ingredients in distilled aromatic water, cold percolate, or decoction to give maximum potency.
HYDROSOLS
This is a water-based solution prepared from the distillation of plants leaves, flowers, fruits, etc., This is a by-product of essential oil with various beneficial properties. Example rose water, cucumber water, etc.,
DISTILLED WATER
A pure form of water that is obtained from water vapors in a condensed form.
GLYCERIN
This is an important ingredient used in the pharmaceutical industry for the manufacturing of ointments, creams, and lotions, etc., Glycerine ensures hydration with rapid healing, anti-aging, and emollient properties.
STAGE 3- MISCELLANEOUS
COLOUR
Before developing modern techniques, turmeric, saffron, etc., were used as a colorant. After the 19thcentury, the colorant is prepared in laboratories with more high pigmentation and safety profile. For example, Mica.
PRESERVATIVE
With time many oils are prone to cause oxidation and rancidification. This reaction is overcome by the addition of preservatives or antioxidants.
This is an essential component to increase the shelf life of the cream. It is used in the lowest concentration but ensures 100% product and consumers' safety. The commonly used preservatives are DMDM hydantoin, imidazolidine urea, glutaraldehyde, parabens
PERFUMES
Perfume is a significant element that enhances the overall property of the cream. Its pleasant smell boosts up your mood and makes you feel fresh. The commonly used natural perfumes are orange blossom, rosy dream, etc.,
5.HOW DO YOU PREPARE CREAMS?
Creams can be prepared by the following method:
Preparation of The O / W Emulsion Cream
To prepare O/W emulsions cream; ingredients of the water phase and oil phase are heated separately in a water bath. The temperature provided may vary from 37 to 60⁰C (It is necessary to maintain the temperature of both phases, otherwise face separation might be occurred).
When both phases are heated, add the water phase gradually into the oil phase with continuously shaking using mixers, homogenizers, or rotor and stator. You need to apply shaking till the cream attains its particular uniformity. At the end of the formulation, preservatives and other miscellaneous ingredients are added.
Preparation of Oil-Free Emulsion Creams
To prepare oil-free emulsion cream, heat the water phase and oil phase separately in a water bath. When all the ingredients are melted triturate them properly.
Add the oil phase slowly into the water phase and mix well using mixers, homogenizers or rotors, and stators till the final consistency is achieved.
6.APPLICATIONS OF CREAMS
Pharmaceutical Creams widely known as topical preparation of dosage forms, in accordance with their purpose of pathophysiological conditions find their applications in:
WOUND HEALING
Imagine you just hurt or scrapped your knees after a bad fall your knees would get a wound and hurt awfully so your doctor prescribes you a cream that would suitably heal your bruise and avoid its infectious spread to prevent worsening of your wound.
EMOLLIENTS AND MOISTURIZERS
That urge to persistently soothe your itchiness where you just had a burn, can go away with over-the-counter topical creams that come under the category of moisturizers and emollients or soothing lotions. Itchiness occurs because the burnt area also destroyed your oil glands which turned your skin dry. Therefore, topical creams leave a cooling effect that soothes the itchy red skin.
ANTI-SEPTIC EFFECT
The anti-septic creams which help to prevent the spread of bacteria to other skin areas or blood and support bactericidal action against gram-positive and gram-negative bacterial infections provide topical treatment for minor cuts and surgeries.
ANALGESIC CREAMS
Analgesic cream vanishes your pain as a topical painkiller. It might contain API (methyl salicylate) which creates a cooling sensation distracting your mind from the pain. Salicylates particularly help in pain near your joints like fingers, knees, and elbow. Moreover, lidocaine numbs away your feeling of pain.
ANTI-ALLERGIC
Conditions like Eczema Atopic Dermatitis and Contact Dermatitis are skin conditions that can best be treated with prevention, over-the-counter creams, and some home remedies which can help to relieve itching and swelling.
7.DIFFERENCE BETWEEN O/W AND W/O EMULSION
| O/W EMULSION | W/O EMULSION |
| Water is a dispersion medium, and oil is a medium to be dispersed. | Oil is a dispersion medium, and water is a medium to be dispersed. |
| They are non-greasy and easily removed. | They are greasy and difficult to be removed. |
| They induce soothing and cooling effects. E.g., vanishing creams | They are inducing extra moisture to protect against the loss of water content from the skin. E.g. cold cream. |
| Drugs with high water solubility are quickly released. | Oil soluble drugs are quickly released. |
8.What are the Challenging Factors you must Consider During Creams Production?
Most topical preparations are formulated by a complicated procedure that needs strict observation and strongly under control considerations. Few critical problems regarding in-process parameters include temperature, rates of heating and cooling, mixing methods, time, speed, and rate of flow.
PRACTICE PROCEDURE CONTROL TOOLS
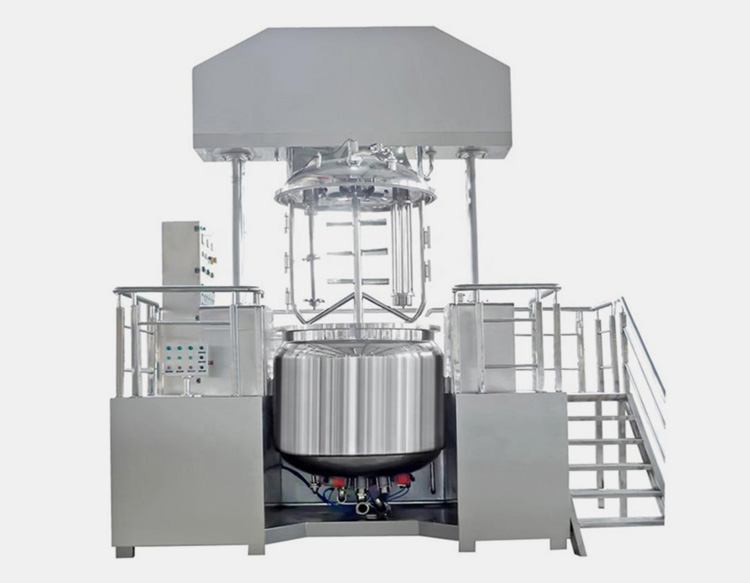
Emulsions can pose a problem for their manufacture as it is thermodynamically unstable, incorporating PLCs (Programmable Logic Controllers) into manufacturing equipment can assist in appropriate control of temperature and mixing rates.
ADD REQUIREMENTS AT A FAVOURABLE STAGE AND ORDER:
If you add ingredients in the correct order, it favors the stability of the formulation. Stabilizers, such as parabens, should be included before emulsification to cut down the time in contact with water-dispersible surfactants at high temperatures. Problems with polymers and gums, such as fisheyes and undissolved solutes, can be overcome by using eductors (tri-blender) or using a less soluble slurry of that polymer.
PROTECT ACTIVE INGREDIENTS FROM DEGRADATION
Few photosensitive components like Retinoic acid are degradable under exposure to UV light, thus they can be protected using amber light containers.
IDENTIFYING MANUFACTURING EQUIPMENT EFFICIENCY
Manufacturers must keep in mind the design and working principles for the operation of machinery. CDMO (Contract Development and Manufacturing Organization) permits synchronization of project manufacturing technology in correspondence with changes in the speed of mixing, temperature control, and order of ingredients.
To scale up a course used for clinical batch manufacturing or allocating commercial processes to a new manufacturing site, the equipment must at least be of the same components also employing a similar type of mixing.
CONCLUSION
The cream is the broadest term that includes emulsifiers, oils, waxes, extracts, and hydrophilic solvents that offer a great skin care solution. Its routine uses to strengthen the pharmaceutical sector with a high market profile. As the pharmaceutical sector progresses, they assure more and more advancement in the coming years. The article ‘Everything You Need to Know About Creams’ has highlighted major aspects and essential parameters during its formulation. Still, if you’ve any queries; just send us a short message. Our High-Tech Consultant Team Will Be Right There to Assist You.
Don't forget to share this post!
Vacuum Emulsifying Mixer Related Posts
Vacuum Emulsifying Mixer Related Products
Vacuum Emulsifying Mixer Related Videos
CONTACT US
Tell us your raw material and project budget to get quotations within 24 hours.
WhatsApp Us: +86 181 6426 8586
Want the best price & newest pharmaceutical machinery buying guide,tips and trends sent straightly to your box?Sign up for Aipak’s monthly newsletter,we’re free for your consultation and Offer you the most suitable solutions!
The Buyer's Guide
- Capsule Filling Buyer's Guide
- Blister Packaging Buyer's Guide
- Tablet Counting Buyer's Guide
- Tube Filling Buyer's Guide
- Cartoning Buyer's Guide
- Gummy Making Buyer's Guide
- CO2 Extraction Buyer's Guide
- Empty Capsules Buyer's Guide
- Suppository Filling Buyer's Guide
- Tablet Coating Buyer's Guide
- Tablet Press Buyer's Guide
- Softgel Encapsulation Buyer's Guide
Most Popular
- 7 Importance Of Pharmaceutical Packaging In Different Applications You Must Know
- 6 Advantages You Must Know About Tablet Counting Machine
- 8 Advantages of Blister Packaging You Must Know
- 6 Critical Applications of Automatic Capsule Filling Machine
- 6 Stations You must Know to Improve the Filling Quality of Automatic Capsule Filling Machine