Type of Solid Dosage Form
To administer any medicine, it requires a proper delivery system to reach its site of action. The solid dosage form is a commonly used drug delivery system since ancient times. This is the most popular mean of drug administration due to its stability, inexpensive, and controlled mode of drug delivery. For instance, sustained release, extended release, etc.
If you examine the Future Market Insights, globally the oral dosage formulation market is expected to be raise from 493.2 billion (2017) USD to 926.3 billion USD till 2027. This global increase in requirement coupled with incredible development of efficient excipients and additional improvement in formulation that exhibits exceptional properties e.g., flowability.
This informative review is comprised of the basic to advanced knowledge relevant to the solid dosage form. If you are a pharmacist, chemist, technician, or research scholar, you must know the pertinent aspects of the solid dosage form to improve your understanding of basic manufacturing elements.
I.A Solid Dosage Form
Medicines are delivered into your body in a variety of ways. Some medicines are solid (tablets, capsules), some of them are liquid (suspensions, syrups, drops). These various mean of delivering a drug into your body is known as dosage forms. More specifically, solid dosage form mainly encompasses two elements: a) active pharmaceutical ingredient, b) excipients.
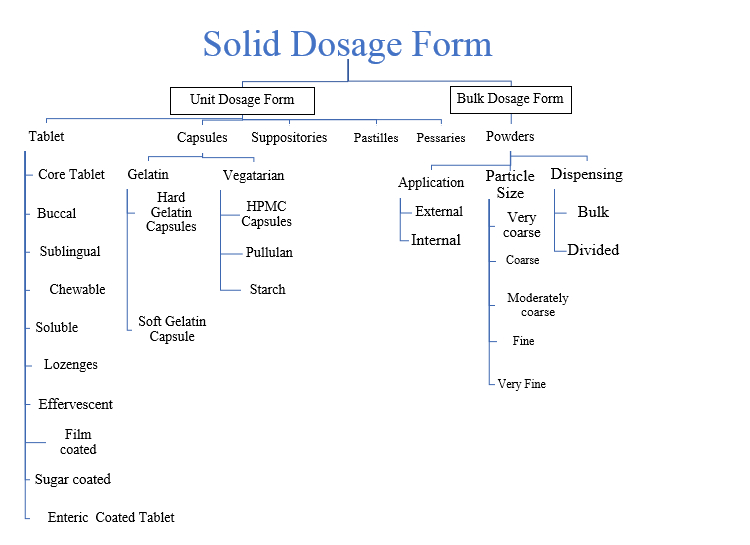
II.Classification of Solid Dosage Form
The solid dosage form can be classified into two main parts depending upon the amount of dose.
Unit Dosage Form
- Tablet
- Capsule
- Suppositories
Bulk Dosage Form
- Pastilles
- Pessaries
- Powders
III.Types of Unit Dose
Dosage form is also known as unit dose. It is a pharmaceutical product that contains with a particular ingredient in a particular configuration into a specific dose. For e.g., 500mg capsule or 100 mg tablet.
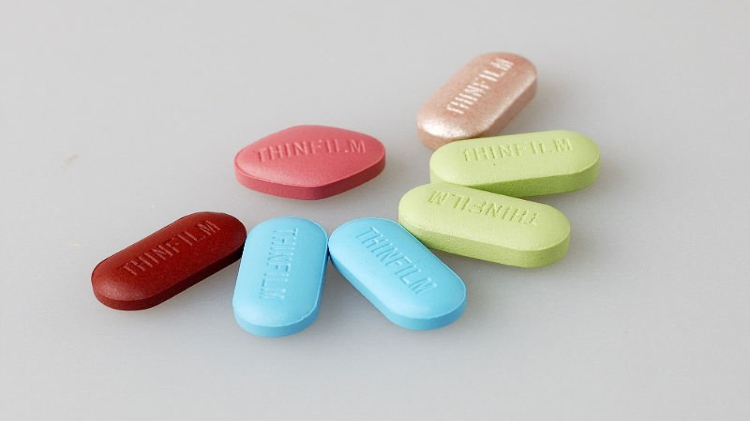
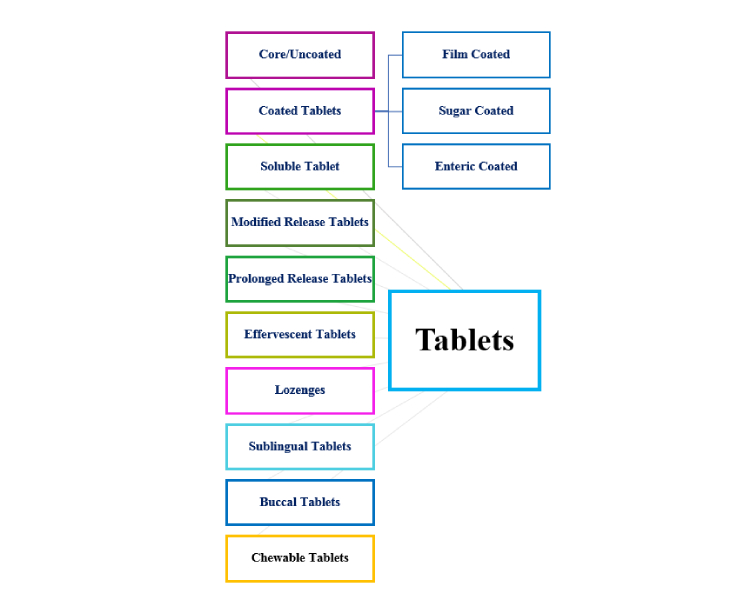
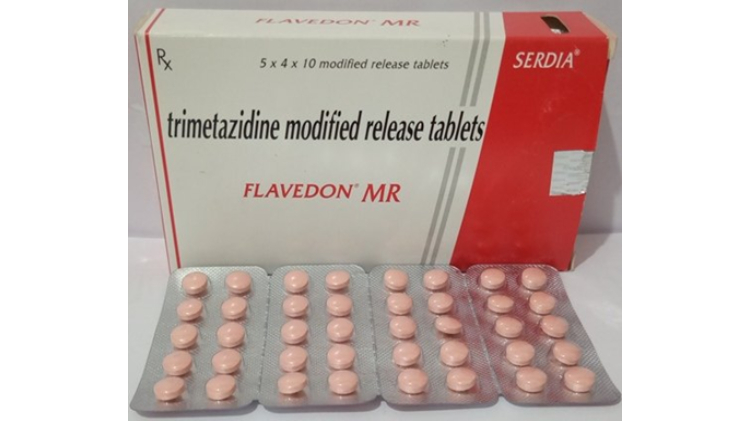
I.Tablets
Tablets are pharmaceutical unit dose that contains an active pharmaceutical ingredient with aid of a suitable excipient. You may find the tablet in various shapes, sizes, thicknesses. Tablets are available in various forms such as:
a.Core/Uncoated Tablets
They are also known as compressed tablets. A high percentage of tablets is included compressed tablets which allow systemic absorption of the medicine. These tablets are devised as such that upon ingestion they readily disintegrate in the gastric fluid and allow quick release of a drug.
High pressure is applied to make compressed tablets from powder or granular material. They can be coated or uncoated, also containing buking agents, binders and other excipients which are not only critical for storing and manufacturing the tablet as well as their usage.
b.Coated Tablets
Tablet coating is special treatment serve to achieve the desired therapeutic properties, Such as:
- Film-Coated Tablets
Film coating is done with a polymer that cover a tablet with a thin layer to enhance durability, aesthetic appearance, give identification, and variety of purposes.
This coating is very well designed and gets disintegrated in the gastric fluid. This is most preferable process due to fast and single step manufacturing.
- Sugar Coated Tablets
Tablets are coated with concentrated sugar which helps in the improvement of the texture, odor, and taste of the product to help better ingestion and release of the curative agent.
As compared to film coating, this is a multistep procedure consumes more time and cost you high.
- Enteric Coated Tablets
These types of tablets are intended to be having delayed disintegration properties. The coating film has a different kind of polymer (e.g., cellulose acetate phthalate, methacrylic acid copolymers) that escapes disintegration by gastric fluid and reaches the intestine where all the releasing process occurs.
They are intended to be dissolved in water prior to being swallowed. Thus, you can take these tablets in a solution form after dissolving them in water.
For instance, aspirin, or painkillers.
d.Modified Release Tablets
The modified release tablets releases the drug with delay after administration followed by a gradual delivery of drugs in an optimum amount required to maintain a therapeutic target for longer period of time such as 8 to 12 hours.
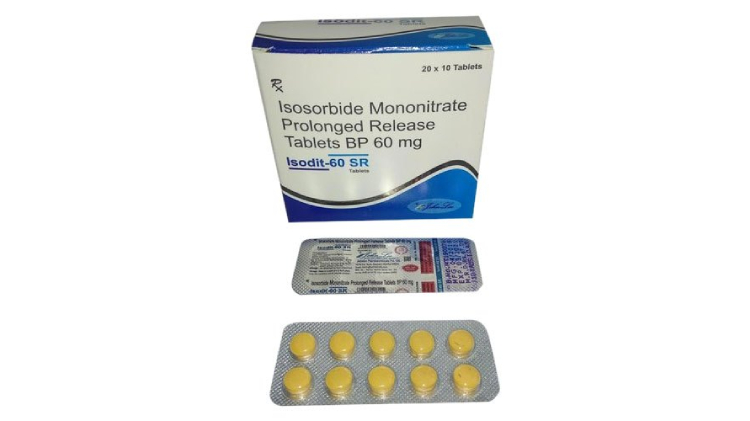
e.Prolonged Release Tablets
These tablets are also known as sustained-release tablets or extended-release tablets. They are designed to deliver the drug in a predetermined pattern for a prolong period to maintain a therapeutic response constantly with minimum side effects.
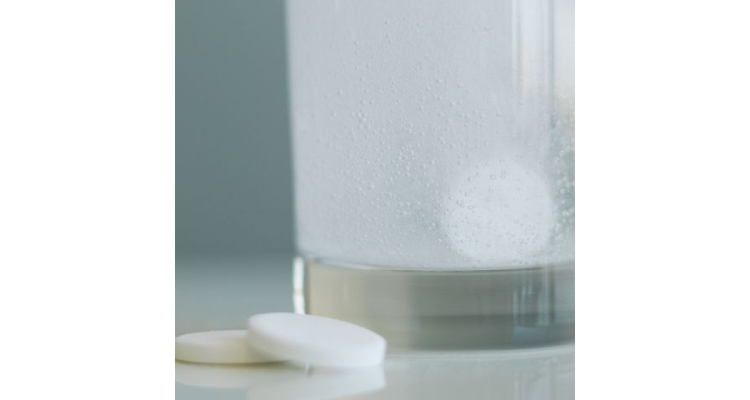
f.Effervescent Tablets
These uncoated tablets comprise of organic acids and salts like sodium bicarbonate along with the excipients. This type of tablet works by reacting rapidly in water where CO2 is produced to release the drug in suspension or aqueous form.
g.Lozenges
Lozenges are solid dosage forms that disintegrate slowly in the mouth. They are prepared with one or more flavoring agents as well as a sweetening agent. Hence, they are pleasant in taste, e.g., strepsils.

Sublingual tablets, as its name shows they are designed to improve the retention of active drug ingredients under the tongue. These are tasteless medicines that dissolved rapidly and produce a desired therapeutic effect available in a small amount.
You must have noticed to reduce blood pressure, individual or patient takes sublingual antihypertensive tablet. That is because this region induces rapid absorption and produces a faster antihypertensive response. For instance nitroglycerine. Other examples of sublingual tablets are loratadine, mirtazapine, etc.
i.Buccal Tablets
Buccal tablets dissolve between cheek and gum (a buccal pouch), which enables a direct absorption of therapeutic active ingredients via the oral mucosa. This route of medication is employed when you require a quick absorption of medicine or when the child is not conscious. For e.g., antihypertensive, antidepressants, etc.
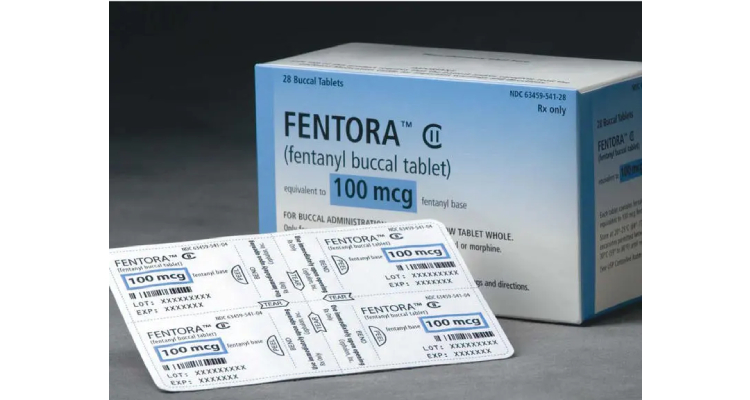
They are big-sized chewy tablets and chewed in the buccal cavity, having difficulty in swallowing due to their bigger size. These tablets can only be used where the drug is acceptable taste-wise.
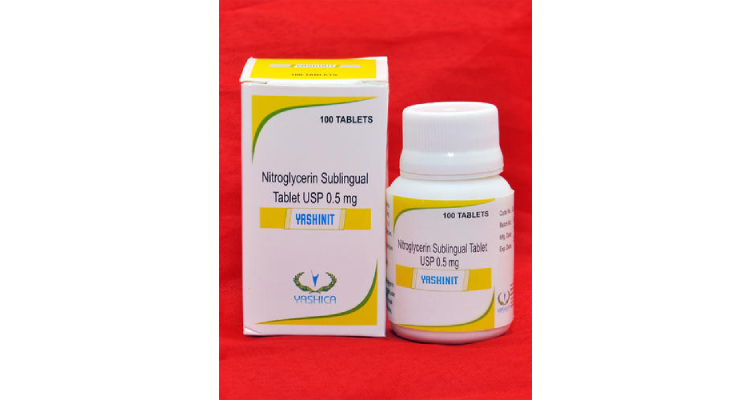
Capsules are solid unit dosage form that encloses medication in a hard shell or softshell. This shell is commonly prepared from gelatin that disintegrates in the digestive tract. These are mainly used for life-saving drugs, minerals, nutritional supplements. Indeed, this form of solid dosage form carries greater consumer compliance.
According to raw material capsules are divided into two basic types:
a.Gelatin Capsule
A global preference- gelatin capsules are an elegant form of solid dosage form composed of gelling agent, gelatin. Gelatin means ‘stiff’ which is a colorless powder used for centuries in the health and food sector.
Gelatin is a pure protein extracted from animal collagen (bovine, porcine sources).
Gelatin capsules are of two types:
- Hard Gelatin Capsule: made up of two parts, a body and cap. These two parts fit together to enclose and protect filled/encapsulated drugs.
- Soft Gelatin Capsule: This is also known as a one-piece capsule. This is composed of single- or one-piece capsule, hermetically sealed that encapsulate liquid, semi-solid substances.
b)Vegetarian Capsule
Many health-conscious people prefer vegetarian capsules over gelatin capsules. This is for a variety of reasons such as religious or personal reasons, nontoxic, obtained purely from a natural source.
There are two main types of vegetarian capsules.
- HPMC Capsules: prepared from cellulose, suitable for vegetarians.
- Pullulan Capsules: extracted from Tapioca roots, tasteless and without any unpleasant smell.
- Starch Capsules: commonly extracted from potato starch.
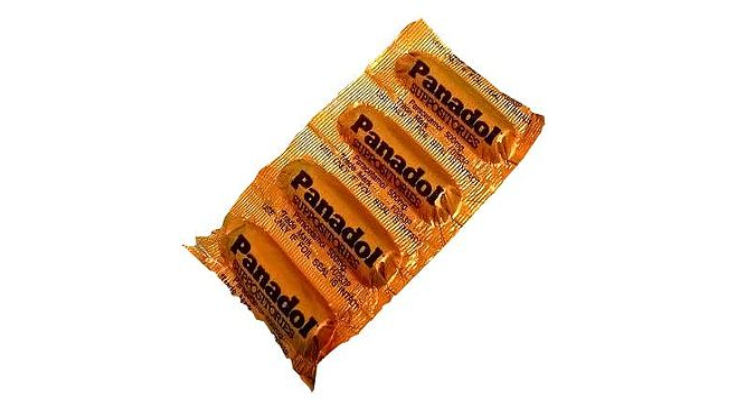
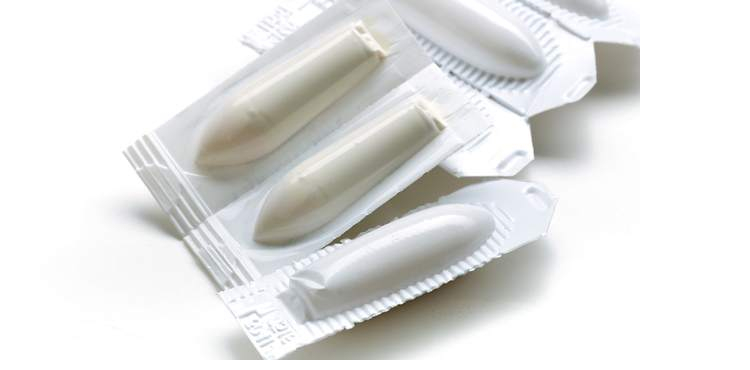
III.Suppositories
A suppository is a solid dosage form intended to deliver therapeutic effect by insertion of it via body orifice where it dissolves to generate local or systemic effects.
If you see their composition, they have a base of cocoa butter, polyethylene glycol, hydrogels as well as glycerinated gelatin.
There are three types of suppositories
Rectal Suppositories
Rectal suppositories are solid dosage forms intended to be inert in the rectum to produce their therapeutic effects. They are available in many shapes and sizes but generally narrower at each end. Rectal suppositories are meant to deliver various kinds of medication such as glycerine, etc.,
b)Vaginal Suppositories
They are designed for vaginal application with a special applicator. This suppository works very fast than the oral route of administration.
- Urethral Suppositories
Urethral suppositories are intended for urethral lining, can be applied using the applicator.
IV.Pastilles
Pastilles are solid dosage forms intended for oral use like lozenges. Pastilles dissolve in the mouth slowly and release their effects. Although pastilles are softer as compared to lozenges. They are prepared by glycerol and gelatin as well as containing a medicament solution or suspension. You can add acacia and sugar when desired to get a hard pastille. e.g., Eucalyptus, or squill pastilles.
V.Pessaries
a.Molded pessaries: are cone-shaped that are manufactured in a way as molded suppositories.
b.Compressed pessaries: are prepared in a variety of shapes and manufactured in a way as compressed oral tablets.
c.Vaginal capsules: are similar to soft gelatin capsules, they are available in different shapes and sizes.
IV.Types of Bulk Dose
Bulk doses mean substances are in bulk form. For instance, powders.
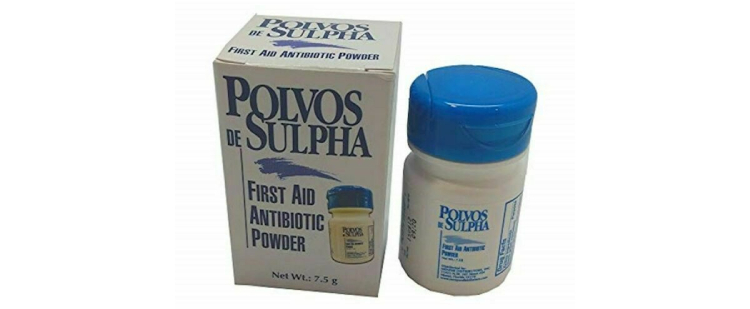
Powders are a form of remedy which includes a fine mixture of drugs and excipients. It is the oldest form of therapy.
Powders are classified into various types depending upon them
I.APPLICATION
Powders are divided into two types based on their use which are
a.External Use
These types of powders have a variety of fineness and include solid, dry, and free-flowing substances which are used for dermal application.
These are formed by active ingredients and excipients and sometimes coloring agents.
Sorbent powders should not be put on wounds as hard scabs may develop.
b.Internal Use
These powders are orally taken like oral antibiotics or are dispensed via nose such as snuff. These powders are also used as insufflations.
II.PARTICLE SIZE
Powders are classified according to their particle size after their preparation. These powder classifications are as follows:
a.Very Coarse Powders
The particles of these powders can go through the number 8 sieve having a size of 2.38 mm.
b.Coarse Powders
The particles of these powders can easily go through no. 20 sieve. This sieve has a hole size of 0.84 mm. About 40% of these particles go across a No. 60 sieve.
c.Moderately Coarse Powders
The particles of these powders can pass no. 40 sieve. This sieve has a hole size of 0.42 mm. About 40% of these particles go across a No. 80 sieve.
d.Fine Powders
All of the particles of these powders go across the No. 60 sieve (0.25 mm).
e.Very fine Powder
These powders are extremely fine, and these particles go through No. 80 sieve (0.18 mm).
III.WAY OF DISPENSING
Based on the way of dispensing powders are categorized into two types. These are:
a)Bulk Powders
These are the mixture of drugs that are generally non-potent and are packaged into containers or bottles (glass or plastic). These powders can be used for an external purpose or internal purposes.
Some examples of bulk powders are antiacid, laxatives, douches, oral antibiotics, etc.
b)Divided Powders
These are also called cartilage and contain a single dose of drug mixtures which are packaged into paper, plastic, or aluminum wrapper or packages. For instance, insufflations.
V.Pros of Solid Dosage Form
Solid dosage forms have many benefits over the other forms of dosage. Some of the advantages are discussed below:
- Precision
These medications have high accuracy of dosing and are highly advantageous for the patients as they have maximum therapeutic relief.
- Stability
These are a highly stable form of dosage in their chemical and physical characteristics also preservatives are used in this medication which does not allow microbes to grow. These medications do not allow active ingredients to deteriorate on exposure to harsh conditions like high humidity, extreme temperature, and light. These medications also have a longer shelf life.
- Production as per Requirement
These medications can be produced in a variety of colors, sizes, and flavors by keeping in mind the need of consumers.
- Transport and Storage
These therapeutic agents have ease of packaging, handling, and transportation. These medicines do not have requirements for storage.
VI.Cons of Solid Dosage Form
The solid dosage form is a widely used form of the therapeutic agent. But there are a few disadvantages as well, such as:
- Swallowability
These dosage forms are difficult to ingest especially for children and elderly patients. Also, these medications cannot be administered to patients who are vomiting and unconscious.
- Active ingredients
Active ingredients that are used to prepare solid dosage forms have decreased water solubility and have a small rate of suspension. These ingredients are high absorption in the digestive tract and are decrease density.
- Cost of Manufacturing
These medications have increased the cost of production due to the coating and encapsulation of drugs inside the capsules.
- Patient’s Discomfort
Some patients are not able to take solid dosage form (tablets and capsules) as these medications have a harsh taste and pungent smell.
- Irritation
These medications especially tablets cause discomfort and irritation inside the gastrointestinal tract.
- Hygroscopic Drugs
These therapeutic agents are not appropriate for packing hygroscopic drugs.
VII. What is Common Used Solid Dosage Form?
The oral usage of the pharmaceutical solid dosage form is commonly prescribed medication worldwide. They are complex systems as you can see diversified structures such as powders, compressed tablets, soluble tablets, and capsules, etc.
Importantly, solid dosage form was the first dosage form that was recognized by the International Conference on Harmonization (ICH).
According to a research review, the most common solid forms consume worldwide are single or multiunit-tablets or capsules. They are highly prescribed medication among various categories of solid dosage form due to:
- High patient compliance.
- Cost economical
- Safety profile
- Product stability and easy to administer
- Both forms comprise an active pharmaceutical ingredient (drug).
- Higher drug absorption
- Protective for sensitive ingredients.
- Easy to carry & easy to dispense.
Conclusion
Solid dosage forms are the most prescribed and commonly used pharmaceuticals. As compared to other forms of medication, these are easy and cost-effective modes of manufacturing to pharmaceutical production units. That’s why the market growth of solid dosage form is kept increasing significantly, hence contributing to a high production market and good healthcare dominance.
Don't forget to share this post!
Tablet Coating Machine Related Posts
Tablet Coating Machine Related Products
Tablet Coating Machine Related Videos
CONTACT US
Tell us your raw material and project budget to get quotations within 24 hours.
WhatsApp Us: +86 181 6426 8586
Want the best price & newest pharmaceutical machinery buying guide,tips and trends sent straightly to your box?Sign up for AIPAK’s monthly newsletter,we’re free for your consultation and Offer you the most suitable solutions!
The Buyer's Guide
- Capsule Filling Buyer's Guide
- Blister Packaging Buyer's Guide
- Tablet Counting Buyer's Guide
- Tube Filling Buyer's Guide
- Cartoning Buyer's Guide
- Gummy Making Buyer's Guide
- CO2 Extraction Buyer's Guide
- Empty Capsules Buyer's Guide
- Suppository Filling Buyer's Guide
- Tablet Coating Buyer's Guide
- Tablet Press Buyer's Guide
- Softgel Encapsulation Buyer's Guide
Most Popular
- 7 Importance Of Pharmaceutical Packaging In Different Applications You Must Know
- 6 Advantages You Must Know About Tablet Counting Machine
- 8 Advantages of Blister Packaging You Must Know
- 6 Critical Applications of Automatic Capsule Filling Machine
- 6 Stations You must Know to Improve the Filling Quality of Automatic Capsule Filling Machine
Tell us your material or budget,we'll reply you ASAP within 24 hours